Abstract
Purpose
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common clinical problem that is associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes attributed to the oxidative stress due to sympathetic overstimulation. Treatment approaches targeting oxidative stress have been tried by multiple investigators. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety of such approaches.
Methods
Pubmed and Embase databases were searched for human studies evaluating the utility of antioxidant therapies in patients with OSA.
Results
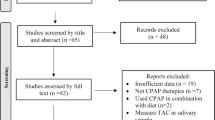
A total of six studies (five randomized trials and one case–control study) were included, including 160 patients with OSA using N-acetyl cysteine, vitamin C, carbocysteine, superoxide dismutase, vitamin E, allopurinol, and their combinations. There was a significant improvement in flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) following antioxidants, with the pooled effect being 2.16 % (95% CI 1.65–2.67) using the random-effects model (I2 = 0% and p<0.001). It was also associated with a significant reduction in malondialdehyde levels and an increase in reduced glutathione (GSH) levels. There was also a significant improvement in the Epworth sleepiness scale, oxygen desaturation index, and minimum oxygen saturation during sleep without any significant adverse effects.
Conclusion
Antioxidant therapy in patients with OSA is associated with improved endothelial function, reduced oxidative stress, and improved sleep parameters. These results call for future multicentre studies with longer follow-ups to assess the utility of antioxidant therapy in patients with OSA.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AHI:
-
Apnea-hypopnea index
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CPAP:
-
Continuous positive airway pressure
- ESS:
-
Epworth sleepiness scale
- FMD:
-
Flow-mediated dilatation
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- IMT:
-
Intima-media thickness
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NAC:
-
N-acetyl cysteine
- ODI:
-
Oxygen-desaturation index
- OSA:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
- OSAS:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- PA:
-
Progressive augmentation
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- RCT:
-
Randomized controlled trial
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TNF- α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- vLTF:
-
Ventilatory long-term facilitation
References
(1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 22(5):667–89
Lavie L (2003) Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome–an oxidative stress disorder. Sleep Med Rev 7(1):35–51
Celec P, Jurkovičová I, Buchta R, Bartík I, Gardlík R, Pálffy R et al (2013) Antioxidant vitamins prevent oxidative and carbonyl stress in an animal model of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 17(2):867–871
Cofta S, Wysocka E, Piorunek T, Rzymkowska M, Batura-Gabryel H, Torlinski L (2008) Oxidative stress markers in the blood of persons with different stages of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Physiol Pharmacol 59(Suppl 6):183–190
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J (2000) Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med 342(19):1378–1384
de Sousa Rodrigues CF, Lira AB (2015) Correlation between the severity of apnea and hypopnea sleep, hypertension and serum lipid and glycemic: a case control study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(6):1509–1515
Sadasivam K, Patial K, Vijayan VK, Ravi K (2011) Anti-oxidant treatment in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 53(3):153–162
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D et al. The Newcastle- Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 21 Sep 2023
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50(4):1088–1101
Serra A, Maiolino L, Cocuzza S, Di Luca M, Campione G, Licciardello L et al (2016) Assessment of oxidative stress markers and hearing thresholds in patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnoea treated with cysteine and superoxide dismutase therapy. Acta Biomed 87(3):253–258
El Solh AA, Saliba R, Bosinski T, Grant BJB, Berbary E, Miller N (2006) Allopurinol improves endothelial function in sleep apnoea: a randomised controlled study. Eur Respir J 27(5):997–1002
Wu K, Su X, Li G, Zhang N (2016) Antioxidant Carbocysteine Treatment in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 11(2):e0148519
Lee DS, Badr MS, Mateika JH (2009) Progressive augmentation and ventilatory long-term facilitation are enhanced in sleep apnoea patients and are mitigated by antioxidant administration. J Physiol 587(Pt 22):5451–5467
Grebe M, Eisele HJ, Weissmann N, Schaefer C, Tillmanns H, Seeger W et al (2006) Antioxidant vitamin C improves endothelial function in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173(8):897–901
Orrù G, Storari M, Scano A, Piras V, Taibi R, Viscuso D (2020) Obstructive Sleep Apnea, oxidative stress, inflammation and endothelial dysfunction-An overview of predictive laboratory biomarkers. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(12):6939–6948
Veasey SC, Davis CW, Fenik P, Zhan G, Hsu YJ, Pratico D et al (2004) Long-term intermittent hypoxia in mice: protracted hypersomnolence with oxidative injury to sleep-wake brain regions. Sleep 27(2):194–201
Nogawa H, Ishibashi Y, Ogawa A, Masuda K, Tsubuki T, Kameda T et al (2009) Carbocisteine can scavenge reactive oxygen species in vitro. Respirology 14(1):53–59
Berman RS, Martin W (1993) Arterial endothelial barrier dysfunction: actions of homocysteine and the hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase free radical generating system. Br J Pharmacol 108(4):920–926
Butler R, Morris AD, Belch JJ, Hill A, Struthers AD (2000) Allopurinol normalizes endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetics with mild hypertension. Hypertension 35(3):746–751
Farquharson CAJ, Butler R, Hill A, Belch JJF, Struthers AD (2002) Allopurinol improves endothelial dysfunction in chronic heart failure. Circulation 106(2):221–226
McEvoy RD, Antic NA, Heeley E, Luo Y, Ou Q, Zhang X et al (2016) CPAP for Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. N Engl J Med 375(10):919–931
Ye L, Li W, Willis DG (2022) Facilitators and barriers to getting obstructive sleep apnea diagnosed: perspectives from patients and their partners. J Clin Sleep Med 18(3):835–841
Lonn E, Bosch J, Yusuf S, Sheridan P, Pogue J, Arnold JMO et al (2005) Effects of long-term vitamin E supplementation on cardiovascular events and cancer: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 293(11):1338–1347
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
PROSPERO ID: CRD42023450687
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11325_2024_3050_MOESM1_ESM.png
Supplementary file1 The risk of bias summary for the 5 RCTs. The green dot with the + sign indicates low bias while the red dot with the – sign indicates high risk of bias. An empty box denotes an unclear risk of bias. (PNG 89 KB)
11325_2024_3050_MOESM2_ESM.png
Supplementary file2 The funnel plot of the studies reporting the change in Flow-mediated dilatation as an outcome; SE: standard error, MD: mean difference. (PNG 3 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Boppana, T.K., Mittal, S., Madan, K. et al. Antioxidant therapies for obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-024-03050-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-024-03050-z