Abstract
Background
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether or not angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker irbesartan (ARB) with a partial agonist of PPAR-γ could protect against chronic nocturnal intermittent hypoxia (CIH)–induced cardiac Fas/FasL-mediated to mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.
Methods
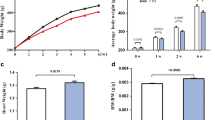
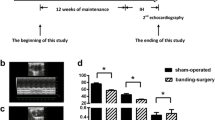
Sprague–Dawley rats were in a normoxic control group (CON-G), or rats were in a chronic nocturnal intermittent hypoxia group (HP-G, from 3 to 7% oxygen versus 21% oxygen per forty seconds cycle, nocturnally 8 h per day for 1 month), or rats were in a chronic nocturnal intermittent hypoxia group pretreated with ARB (50 mg/kg/day, S.C.) (ARB-HP-G). Echocardiography, H&E staining, TUNEL staining, and Western blotting were measured in the left ventricle.
Results
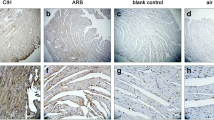
Hypoxia-induced SIRT1 degradation, Fas receptors, FADD, active caspase-8 and caspase-3 (Fas/FasL apoptotic pathway) and Bax, tBid, active caspase-9 and -3 (mitochondrial apoptotic pathway) and TUNEL-positive apoptosis were reduced in ARB-HP-G when compared with HP-G. IGF-I, IGF1 receptor, p-PI3k, p-Akt, Bcl2, and Bcl-XL (IGF1/PI3K/AKT pro-survival pathway) were increased in ARB-HP-G compared to HP-G.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that the ARB may prevent cardiac Fas/FasL to mitochondrial apoptotic pathways and enhance cardiac IGF1/PI3K/AKT pro-survival pathway in the sleep apnea model associated with JNK de-activation and SIRT1 upregulation. ARB prevents chronic sleep apnea–enhanced cardiac apoptosis via enhancing survival pathways.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caples SM, Garcia-Touchard A, Somers VK (2007) Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular risk. Sleep 30:291–303
Pack AI (2006) Advances in sleep-disordered breathing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200509-1478OE
Kapa S, SertKuniyoshi FH, Somers VK (2008) Sleep apnea and hypertension: interactions and implications for management. Hypertension 51:605–608. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.106.076190
Lopez-Jimenez F, SertKuniyoshi FH, Gami A, Somers VK (2008) Obstructive sleep apnea: implications for cardiac and vascular disease. Chest 133:793–804. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.07-0800
Aguilar M, Gonzalez-Candia A, Rodriguez J, Carrasco-Pozo C, Canas D, Garcia-Herrera C, Herrera EA, Castillo RL (2018) Mechanisms of cardiovascular protection associated with intermittent hypobaric hypoxia exposure in a rat model: role of oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020366
Baguet JP, Barone-Rochette G, Tamisier R, Levy P, Pepin JL (2012) Mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea. Nat Rev Cardiol 9:679–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2012.141
Borovac JA, Dogas Z, Supe-Domic D, Galic T, Bozic J (2019) Catestatin serum levels are increased in male patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 23:473–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-018-1703-x
Fletcher EC, Bao G, Li R (1999) Renin activity and blood pressure in response to chronic episodic hypoxia. Hypertension 34:309–314
Yuan ZM, Chen BY, Wang PX, Li SY, Chen YL, Dong LX (2004) Changes of angiotensin II and its receptor during the development of chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced hypertension in rats. Zhonghua jie he he hu xi za zhi = Zhonghua jiehe he huxi zazhi = Chinese journal of tuberculosis and respiratory diseases 27:577–580
Silvestre JS, Tamarat R, Senbonmatsu T, Icchiki T, Ebrahimian T, Iglarz M, Besnard S, Duriez M, Inagami T, Levy BI (2002) Antiangiogenic effect of angiotensin II type 2 receptor in ischemia-induced angiogenesis in mice hindlimb. Circ Res 90:1072–1079
Walther T, Menrad A, Orzechowski HD, Siemeister G, Paul M, Schirner M (2003) Differential regulation of in vivo angiogenesis by angiotensin II receptors. FASEB J Off Publ Feder Am Soc Exp Biol 17:2061–2067. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-0129com
Rakusan K, Chvojkova Z, Oliviero P, Ostadalova I, Kolar F, Chassagne C, Samuel JL, Ostadal B (2007) ANG II type 1 receptor antagonist irbesartan inhibits coronary angiogenesis stimulated by chronic intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats. American journal of physiology. Heart Circ Physiol 292:H1237-1244. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00965.2006
Watanabe R, Suzuki J, Wakayama K, Kumagai H, Ikeda Y, Akazawa H, Komuro I, Isobe M (2016) Angiotensin II receptor blocker irbesartan attenuates cardiac dysfunction induced by myocardial infarction in the presence of renal failure. Hypertens Res Off J Jpn Soc Hypertens 39:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2015.141
Lai CH, Pandey S, Day CH, Ho TJ, Chen RJ, Chang RL, Pai PY, Padma VV, Kuo WW, Huang CY (2019) beta-catenin/LEF1/IGF-IIR signaling axis galvanizes the angiotensin-II- induced cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Mol Sci 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174288
Lin YM, Huang SK, Wang HF, Chen LM, Tsai FJ, Hsu HH, Kuo CH, Wang PS, Huang CY, Lee SD (2008) Short-term versus long-term intermittent hypobaric hypoxia on cardiac fibrosis and Fas death receptor dependent apoptotic pathway in rat hearts. Chin J Physiol 51:308–316
Dong Y, Chen H, Gao J, Liu Y, Li J, Wang J (2019) Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 136:27–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.09.001
Brunner HR (1997) The new angiotensin II receptor antagonist, irbesartan: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations. Am J Hypertens 10:311S-317S. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0895-7061(97)00391-9
Fujino M, Miura S, Kiya Y, Tominaga Y, Matsuo Y, Karnik SS, Saku K (2010) A small difference in the molecular structure of angiotensin II receptor blockers induces AT(1) receptor-dependent and -independent beneficial effects. Hypertens Res Off J Jpn Soc Hypertens 33:1044–1052. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2010.135
Kusunoki H, Taniyama Y, Rakugi H, Morishita R (2013) Cardiac and renal protective effects of irbesartan via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorgamma-hepatocyte growth factor pathway independent of angiotensin II Type 1a receptor blockade in mouse model of salt-sensitive hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc 2:e000103. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.113.000103
Wang W, Song A, Zeng Y, Chen X, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Lin Y, Luo W (2018) Telmisartan protects chronic intermittent hypoxic mice via modulating cardiac renin-angiotensin system activity. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 18:133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-018-0875-4
Ren Y, Sun C, Sun Y, Tan H, Wu Y, Cui B, Wu Z (2009) PPAR gamma protects cardiomyocytes against oxidative stress and apoptosis via Bcl-2 upregulation. Vascul Pharmacol 51:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2009.06.004
Suleiman MS, Singh RJ, Stewart CE (2007) Apoptosis and the cardiac action of insulin-like growth factor I. Pharmacol Ther 114:278–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.03.001
Fuenzalida K, Quintanilla R, Ramos P, Piderit D, Fuentealba RA, Martinez G, Inestrosa NC, Bronfman M (2007) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma up-regulates the Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic protein in neurons and induces mitochondrial stabilization and protection against oxidative stress and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 282:37006–37015. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M700447200
Ren GD, Cui YY, Li WL, Li FF, Han XY (2019) Research on cardioprotective effect of irbesartan in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through MAPK-ERK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:5487–5494. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201906_18218
Lin KH, Kuo WW, Jiang AZ, Pai P, Lin JY, Chen WK, Day CH, Shen CY, Padma VV, Huang CY (2015) Tetramethylpyrazine ameliorated hypoxia-induced myocardial cell apoptosis via HIF-1alpha/JNK/p38 and IGFBP3/BNIP3 inhibition to upregulate PI3K/Akt survival signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:334–344. https://doi.org/10.1159/000374076
Huang CY, Kuo WW, Yeh YL, Ho TJ, Lin JY, Lin DY, Chu CH, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Huang CY (2014) ANG II promotes IGF-IIR expression and cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting HSF1 via JNK activation and SIRT1 degradation. Cell Death Differ 21:1262–1274. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2014.46
Wang JM, Wang Y, Zhu ZS, Zhang MC, Zou Y, Li JJ, Li MJ, Jiang XJ, Li XY (2004) Diverse effects of long-term treatment with imidapril and irbesartan on cell growth signal, apoptosis and collagen type I expression in the left ventricle of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Life Sci 75:407–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2003.10.040
Wu T, Wu D, Wu Q, Zou B, Huang X, Cheng X, Wu Y, Hong K, Li P (2016) Effect and mechanism of irbesartan on occurrence of ventricular arrhythmias in rats with myocardial ischemia through connexin43 (cx43). Asian Pac J Trop Med 9:1007–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.07.022
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Michael Burton for proofreading the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially supported by Asia University and China Medical University (Asia-106-CMUH-05) as well as Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 107–2314-B-468–002-MY3). This study was partially supported by National Taipei University of Nursing and Health Science, Taiwan; Weifang Medical University, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Y.H and S.D.L were responsible for conceptualization; P.Y.P.,Y.Y.L., and Y.F.L. were responsible for data curation and methodology; S.H.Y., C. Y. L., X.B.W., K.S.H., and J.KS.W were responsible for funding acquisition; P.Y.P.,Y.Y.L., C.Y.H., and S.D.L. were responsible for visualization; P.Y.P., Y.Y.L., S.H.Y., C. Y. L., K.S.H., X.B.W., J.KS.W., C.Y.H., and S.D.L were responsible for final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experiments were performed in accordance with National Institutes of Health guidelines. The protocols were approved by the Standing Committee on Ethics and Animal Experimentation at China Medical University. The animal experiments were performed after approval from the Standing Committee on Ethics and Animal Experimentation at China Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pai, PY., Lin, YY., Yu, SH. et al. Angiotensin II receptor blocker irbesartan attenuates sleep apnea–induced cardiac apoptosis and enhances cardiac survival and Sirtuin 1 upregulation. Sleep Breath 26, 1161–1172 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-021-02499-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-021-02499-6