Abstract
Purpose
Obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) is associated with neurocognitive impairment. We examined the role of the systemic inflammatory response, measured by high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) assay, and the effect of CPAP treatment on hsCRP and cognitive impairment in patients with OSAHS.
Methods
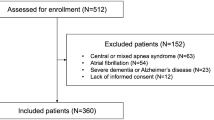
Eligible subjects (n = 178) were categorized into two groups: absent or mild OSAHS, and moderate to severe OSAHS. First, the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and serum hsCRP concentration were measured. Then, the moderate to severe OSAHS group was further divided into a conservative treatment subgroup (n = 68) and a CPAP subgroup (n = 68). After 6 months of treatment, MoCA scores and hsCRP concentrations were re-measured in the moderate to severe group.
Results
Compared with the absent or mild OSAHS group, hsCRP concentration was higher (1.00 ± 1.28 mg/L versus 2.71 ± 1.8, p < 0.001) and MoCA scores were significantly lower (27.4 ± 1.4 versus 26.3 ± 2.0, p < 0.001) in the moderate to severe group. After adjustment for age, education, body mass index, and neck circumference, hsCRP and MoCA scores correlated with parameters of overnight hypoxia. hsCRP and the proportion of time spent with blood oxygen saturation < 90 % (T90) predicted MoCA score. hsCRP and MoCA score improved, and the subdomains of the MoCA were partially improved, in the CPAP treatment subgroup. In conservatively managed patients, hsCRP concentration increased, and there was no improvement in neurocognitive dysfunction, with the memory subdomain significantly worse.
Conclusions
hsCRP may play a role in neurocognitive dysfunction in OSAHS. Long-term CPAP treatment could normalize the serum hsCRP concentration and partially reverse cognitive dysfunction in OSAHS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Douglas NJ, Polo O (1994) Pathogenesis of obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome. Lancet 344:653–655
Sharma SK, Agrawal S, Damodaran D, Sreenivas V, Kadhiravan T, Lakshmy R, Jagia PKumar A (2011) CPAP for the metabolic syndrome in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med 365:2277–2286. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1103944
Shah NA, Yaggi HK, Concato JMohsenin V (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for coronary events or cardiovascular death. Sleep Breath 14:131–136. doi:10.1007/s11325-009-0298-7
Lal C, Strange CBachman D (2012) Neurocognitive impairment in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 141:1601–1610. doi:10.1378/chest.11-2214
Sahlin C, Sandberg O, Gustafson Y, Bucht G, Carlberg B, Stenlund HFranklin KA (2008) Obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for death in patients with stroke: a 10 years follow-up. Arch Intern Med 168:297–301. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2007.70
Vaessen TJ, Overeem SSitskoorn MM (2015) Cognitive complaints in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med Rev 19:51–58. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2014.03.008
Olaithe MBucks RS (2013) Executive dysfunction in OSA before and after treatment: a meta-analysis. Sleep 36:1297–1305. doi:10.5665/sleep.2950
Bédard MA, Montplaisir J, Richer F et al (1991) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: pathogenesis of neuropsychological deficits. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 13:950–64
Chen R, Xiong KP, Huang JY, Lian YX, Jin F, Li ZH, Zhao MY, Liu CF (2011) Neurocognitive impairment in Chinese patients with obstructive sleep apnoea hypopnoea syndrome. Respirology 16:842–848. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.01979.x
Ridker PM, Koenig WFuster V (2004) C-reactive protein and coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 351:295–298, author reply 295–298
Lui MM, Lam JC, Mak HK, Xu A, Ooi C, Lam DC, Mak JC, Khong PL, Ip MS (2009) C-reactive protein is associated with obstructive sleep apnea independent of visceral obesity. Chest 135:950–956. doi:10.1378/chest.08-1798
Gozal D, Crabtree VM, Sans Capdevila O, Witcher LA, Kheirandish-Gozal L (2007) C-reactive protein, obstructive sleep apnea, and cognitive dysfunction in school-aged children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:188–193. doi:10.1164/rccm.200610-1519OC
Roberts RO, Geda YE, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Christianson TJ, Pankratz VS, Kullo IJ, Tangalos EG, Ivnik RJ, Petersen RC (2009) Association of C-reactive protein with mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement 5:398–405. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2009.01.025
Guo Y, Pan L, Ren DXie X (2013) Impact of continuous positive airway pressure on C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 17:495–503. doi:10.1007/s11325-012-0722-2
Katzman R, Zhang M, Qu OY et al (1988) A Chinese version of the mini-mental state examination; impact of illiteracy in a hanghai dementia survey. J Clin Epidemiol 41:971–978
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–5
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson AL, Quan SF (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester, IL
Kylstra WA, Aaronson JA, Hofman WF, Schmand BA (2013) Neuropsychological functioning after CPAP treatment in obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev 17:341–347. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2012.09.002
Caselli RJ (2008) Obstructive sleep apnea, apolipoprotein E e4, and mild cognitive impairment. Sleep Med 9:816–817. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2007.11.015
Kim SJ, Lee JH, Lee DY, Jhoo JH, Woo JI (2011) Neurocognitive dysfunction associated with sleep quality and sleep apnea in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Am J Geriatr Psychiatr 19:374–381. doi:10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181e9b976
De Mello MT, Narciso FV, Tufik S, Paiva T, Spence DW, Bahammam AS, Verster JC, Pandi-Perumal SR (2013) Sleep disorders as a cause of motor vehicle collisions. Int J Prev Med 4:246–257
Pendlebury ST, Mariz J, Bull L, Mehta ZRothwell PM (2012) MoCA, ACE-R, and MMSE versus the national institute of neurological disorders and stroke-Canadian stroke network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards neuropsychological battery after TIA and stroke. Stroke 43:464–469. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.633586
Daurat A, Foret J, Bret-Dibat JL, Fureix CTiberge M (2008) Spatial and temporal memories are affected by sleep fragmentation in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 30:91–101. doi:10.1080/13803390701236116
Shpirer I, Elizur A, Shorer R, Peretz RB, Rabey JM, Khaigrekht M (2012) Hypoxemia correlates with attentional dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 16:821–827. doi:10.1007/s11325-011-0582-1
Aoki K, Matsuo M, Takahashi M, Murakami J, Aoki Y, Aoki N, Mizumoto H, Namikawa A, Hara H, Miyagawa M, Kadotani HYamada N (2014) Association of sleep-disordered breathing with decreased cognitive function among patients with dementia. J Sleep Res 23:517–523. doi:10.1111/jsr.12167
Guven SF, Turkkani MH, Ciftci B, Ciftci TU, Erdogan Y (2012) The relationship between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels and the severity of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 16:217–221. doi:10.1007/s11325-011-0492-2
Wersching H, Duning T, Lohmann H et al (2010) Serum C-reactive protein is linked to cerebral microstructural integrity and cognitive function. Neurology 74:1022–1029
Kohler M, Ayers L, Pepperell JC, Packwood KL, Ferry B, Crosthwaite N, Craig S, Siccoli MM, Davies RJ, Stradling JR (2009) Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on systemic inflammation in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnoea: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax 64:67–73. doi:10.1136/thx.2008.097931
Schiza SE, Mermigkis C, Panagiotis P, Bouloukaki I, Kallergis E, Tzanakis N, Tzortzaki E, Vlachaki ESiafakas NM (2010) C-reactive protein evolution in obstructive sleep apnoea patients under CPAP therapy. Eur J Clin Investig 40:968–975. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02348.x
Kushida CA, Nichols DA, Holmes TH, Quan SF, Walsh JK, Gottlieb DJ, Simon RD Jr, Guilleminault C, White DP, Goodwin JL, Schweitzer PK, Leary EB, Hyde PR, Hirshkowitz M, Green S, Mcevoy LK, Chan C, Gevins A, Kay GG, Bloch DA, Crabtree TDement WC (2012) Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on neurocognitive function in obstructive sleep apnea patients: the apnea positive pressure long-term efficacy study (APPLES). Sleep 35:1593–1602. doi:10.5665/sleep.2226
O’donoghue FJ, Wellard RM, Rochford PD, Dawson A, Barnes M, Ruehland WR, Jackson ML, Howard ME, Pierce RJ, Jackson GD (2012) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and neurocognitive dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea before and after CPAP treatment. Sleep 35:41–48. doi:10.5665/sleep.1582
Ferini-Strambi L, Baietto C, Di Gioia MR, Castaldi P, Castronovo C, Zucconi MCappa SF (2003) Cognitive dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): partial reversibility after continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Brain Res Bull 61:87–92. doi:10.1016/s0361-9230(03)00068-6
Harper RM, Kumar R, Ogren JA, Macey PM (2013) Sleep-disordered breathing: effects on brain structure and function. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 188:383–391. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2013.04.021
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 81270147, 81302016 and 8117070), the Ministry of Health Research Fund Project of China (grant 2012w4) and the Fund of Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital (yzucms201504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committees of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University and Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, and was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
All patients provided written informed consent.
Additional information
Shu Qing Wu and Qing Chi Liao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S.Q., Liao, Q.C., Xu, X.X. et al. Effect of CPAP therapy on C-reactive protein and cognitive impairment in patients with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 20, 1185–1192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1331-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1331-2