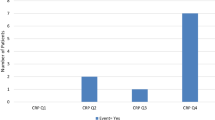
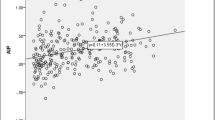
Abstract
Background
It is unclear whether obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is independently associated with increased levels of the acute-phase reactant C-reactive protein (CRP). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between OSA and high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) levels according to the presence or absence of metabolic syndrome (MetS).
Methods
This study recruited 245 male bus drivers from one transportation company in Taiwan. Each participant was evaluated by a polysomnography (PSG) test, blood lipids examination, and hs-CRP. Severity of OSA was categorized according to the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI).
Results
Subjects were categorized into severe OSA group (n = 44; 17.9 %), moderate and mild OSA group (n = 117; 47.8 %), and non-OSA group (n = 84; 34.3 %). AHI had a significant association with hs-CRP (β = 0.125, p = 0.009) adjusting for age, smoking, drinking, and MetS status. Hs-CRP was elevated with severe OSA (β = 0.533, p = 0.005) even adjusting for BMI and MetS. Moreover, there was an independent effect for adjusted odds ratios (AORs) between the stratification of the severity for OSA and MetS.
Conclusion
Elevated hs-CRP level is associated with severe OSA, independent of known confounders. The effect of OSA in CRP is independent of MetS was identified.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Punjabi NM (2008) The epidemiology of adult obstructive sleep apnea. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:136–143
Lindberg E, Gislason T (2000) Epidemiology of sleep-related obstructive breathing. Sleep Med Rev 4:411–433
Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ (2002) Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:1217–1239
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J (2000) Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med 342:1378–1384
Nieto FJ, Young TB, Lind BK et al (2000) Association of sleep-disordered breathing, sleep apnea, and hypertension in a large community-based study. Sleep heart health study. JAMA 283:1829–1836
Ip MS, Lam B, Ng MM, Lam WK et al (2002) Obstructive sleep apnea is independently associated with insulin resistance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:670–676
Punjabi NM, Sorkin JD, Katzel LI, Goldberg AP, Schwartz AR, Smith PL (2002) Sleep-disordered breathing and insulin resistance in middle-aged and overweight men. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:677–682
Kiely JL, McNicholas WT (2000) Cardiovascular risk factors in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J 16:128–133
Schafer H, Pauleit D, Sudhop T, Gouni-Berthold I, Ewig S, Berthold HK (2002) Body fat distribution, serum leptin, and cardiovascular risk factors in men with obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 122:829–839
Kohler M, Stradling JR (2010) Mechanisms of vascular damage in obstructive sleep apnea. Nat Rev Cardiol 7:677–685
Garvey JF, Taylor CT, McNicholas WT (2009) Cardiovascular disease in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome: the role of intermittent hypoxia and inflammation. Eur Respir J 33:1195–1205
Ohga E, Tomita T, Wada H, Yamamoto H, Nagase T, Ouchi Y (2003) Effects of obstructive sleep apnea on circulating ICAM-1, IL-8, and MCP-1. J Appl Physiol 94:179–184
Yokoe T, Minoguchi K, Matsuo H et al (2003) Elevated levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome are decreased by nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Circulation 107:1129–1134
Shamsuzzaman AS, Winnicki M, Lanfranchi P et al (2002) Elevated C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 105:2462–2464
Taheri S, Austin D, Lin L, Nieto FJ, Young T, Mignot E (2007) Correlates of serum C-reactive protein (CRP)–no association with sleep duration or sleep disordered breathing. Sleep 30:991–996
Tasali E, Ip MS (2008) Obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic syndrome: alterations in glucose metabolism and inflammation. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5:207–217
AASM (2001) The international classification of sleep disorders : diagnostic and coding manual. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester
Ruehland WR, Rochford PD, O’Donoghue FJ, Pierce RJ, Singh P, Thornton AT (2009) The new AASM criteria for scoring hypopneas: impact on the apnea hypopnea index. Sleep 32:150–157
Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare. The Definition of the Metabolic Syndrome in Adults, 2007. Available online: http://www.hpa.gov.tw/BHPNet/Web/HealthTopic/TopicArticle.aspx?No=200712250123&parentid=200712250023 Accessed 01 May 2007
Lin YC, Yen LL, Chen SY et al (2003) Prevalence of overweight and obesity and its associated factors: findings from national nutrition and health survey in Taiwan, 1993–1996. Prev Med 37:233–241
Pan WH, Flegal KM, Chang HY, Yeh WT, Yeh CJ, Lee WC (2004) Body mass index and obesity-related metabolic disorders in Taiwanese and US whites and blacks: implications for definitions of overweight and obesity for Asians. Am J Clin Nutr 79:31–39
Ridker PM, Paynter NP, Rifai N, Gaziano JM, Cook NR (2008) C-reactive protein and parental history improve global cardiovascular risk prediction: the Reynolds risk score for men. Circulation 118:2243–2251
Harris TB, Ferrucci L, Tracy RP et al (1999) Associations of elevated interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in the elderly. Am J Med 106:506–512
Kanagy NL, Walker BR, Nelin LD (2001) Role of endothelin in intermittent hypoxia-induced hypertension. Hypertension 37:511–515
Lesske J, Fletcher EC, Bao G, Unger T (1997) Hypertension caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia–influence of chemoreceptors and sympathetic nervous system. J Hypertens 15:1593–1603
Drager LF, Bortolotto LA, Figueiredo AC, Krieger EM, Lorenzi GF (2007) Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on early signs of atherosclerosis in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:706–712
Kohler M, Ayers L, Pepperell JC et al (2009) Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on systemic inflammation in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnoea: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax 64:67–73
West SD, Nicoll DJ, Wallace TM, Matthews DR, Stradling JR (2007) Effect of CPAP on insulin resistance and HbA1c in men with obstructive sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes. Thorax 62:969–974
Minoguchi K, Yokoe T, Tazaki T et al (2005) Increased carotid intima-media thickness and serum inflammatory markers in obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:625–630
Lui MM, Lam JC, Mak HK et al (2009) C-reactive protein is associated with obstructive sleep apnea independent of visceral obesity. Chest 135:950–956
Ryan S, Nolan GM, Hannigan E, Cunningham S, Taylor C, McNicholas WT (2007) Cardiovascular risk markers in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and correlation with obesity. Thorax 62:509–514
IOTF (2000) Asia–Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. International Obesity Task Force, Western Pacific Region, Sydney
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the administrators and drivers from the bus company for their participation and cooperation. This study was partly supported by the National Health Research Institutes of Taiwan (98-EO-PP01, 99-EO-PP01, and 100-EO-PP01) and the Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (IOSH96-M102 and IOSH97-M102), Taiwan. The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors have any potential, perceived, or real conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 84 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, WT., Tsai, SS., Shih, TS. et al. The impact of obstructive sleep apnea on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in subjects with or without metabolic syndrome. Sleep Breath 19, 1449–1457 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-015-1166-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-015-1166-2