Abstract
Background
The Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) is a largely wide used scale for sleepiness assessment. Measurement properties are studied in a sample of Portuguese adults, using different statistical procedures.
Methods
The sample consisted of 222 Portuguese adults (97 men and 125 women) with a mean age of 42 years old (SD = 12.5), 46 of which had obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) confirmed by polysomnography. The participants were assessed with the ESS, which was tested through a quantitative analysis based on the classical measurement theory (CMT) or the Rasch model (RM) conventions.
Results
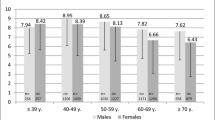
A principal component factor analysis was performed according to the CMT, revealing a single factor explaining 39.92 % of the total variance of the scale. Internal consistency measured by Cronbach’s α coefficient was of .77. The mean of inter-item correlation was of .31 (.05 < r > .47), whereas the item-total correlations were considered good (.46 < r > .73). The ESS total score for OSA patients was significantly higher than healthy participants (p < .05). Overall data from the RM analysis was consistent with the guidelines of Linacre and essential unidimensionality was empirically corroborated (61 % the percentage of variance explained by the Rasch analysis). Model fit is adequate and the reliability coefficients for both items (.99) and subjects (.78) were considered good. The Cronbach’s α coefficient was also satisfactory (.78).
Conclusions
The ESS showed an adequate structural, internal, and criterion validity, both in the CMT and the RM, suggesting this as a useful and effective measure for assessing sleepiness in Portuguese adults.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johns M (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Johns M (1994) Sleepiness in different situations measured by the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 17:703–710
Johns M (1998) Rethinking the assessment of sleepiness. Sleep Med Rev 2:3–15
Johns M (2000) Sensitivity and specificity of the multiple sleep latency test (MSLT), the maintenance of wakefulness test and the Epworth Sleepiness Scale: failure of the MSLT as a gold standard. J Sleep Res 9:5–11
Johns M (1993) Daytime sleepiness, snoring, and obstructive sleep apnea. The Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Chest 103:30–36
Furuta I, Kaneda R, Kosaka K et al (1999) Epworth Sleepiness Scale and sleep studies in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 51:301–302
Silva GE, Vana KD, Goodwin JL, Sherill DL, Quan SF (2011) Identification of patients with sleep disordered breathing: comparing the four-variable screening tool, STOP, STOP-bang, and Epworth Sleepiness Scales. J Clin Sleep Med 7:467–472
Aloé F, Pedro A, Tavares SM (1997) Epworth Sleepiness Scale outcome in 616 Brazilian medical students. [Article in Portuguese]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 55:220–226
Bertolazi AN, Fagondes SCH, Hoff LS et al (2009) Portuguese-language version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale: validation for use in Brazil. [Article in Portuguese]. J Bras Pneumol 35:877–833
Chung KF (2000) Use of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in Chinese patients with obstructive sleep apnea and normal hospital employees. J Psychosom Res 49:367–372
Chen N-H, Johns MD, Li H-W et al (2002) Validation of a Chinese version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Qual Life Res 11:817–821
Kaminska M, Jobin V, Mayer P et al (2010) The Epworth Sleepiness Scale: self -administration versus administration by the physician, and validation of a French version. Can Respir J 17:e23–e34
Bloch KE, Schoch OD, Zhang JN, Russi EW (1999) German version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Respiration 66:440–447
Sauter C, Popp R, Danher-Hopfe H et al (2007) Normative values of German Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Somnolgie 11:272–278
Tsara V, Serasli E, Amfilochiou A, Constantinidis T, Christaki P (2004) Greek version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breathing 8:91–95
Vignatelli L, Plazzi G, Barbato A et al (2003) Italian version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale: external validity. Neurol Sci 23:295–300
Takegami M, Suzukamo Y, Wakita T et al (2009) Development of a Japanese version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (JESS) based on item response theory. Sleep Med 5:556–565
Cho YW, Lee JH, Son HK et al (2011) The reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breathing 15:377–384
Gander PHH, Marshall NS, Harris R, Reid P (2005) The Epworth Sleepiness Scale: influence of age, ethnicity, and socioeconomic deprivation. Epworth Sleepiness Scores of adults in New Zealand. Sleep 28:249–253
Beiske KK, Kjelsberg FN, Ruud EA, Stavem K (2009) Reliability and validity of a Norwegian version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breathing 13:65–72
Sanford SD, Lichstein KL, Durrence HH et al (2006) The influence of age, gender, ethnicity, and insomnia on Epworth Sleepiness Scores: a normative US population. Sleep Med 7:319–326
Rosales-Mayor E, Castro JR, Huaynay L, Zagaceta K (2012) Validation and modification of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in Peruvian population. Sleep Breathing 16:59–69
Kopitovic I, Trajanovic N, Prodic S et al (2011) The Serbian version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breathing 15:775–780
Chiner E, Arriero JM, Signes-Costa J, Marco J, Fuentes I (1999) Validation of the Spanish version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in patients with a sleep apnea syndrome [article in Spanish]. Arch Bronconeumol 35:422–427
Banhiran W, Assanasen P, Nopmaneejumruslers C, Metheetrairut C (2011) Epworth Sleepiness Scale in obstructive sleep disordered breathing: the reliability and validity of the Thai version. Sleep Breathing 15:571–577
Izci B, Ardic S, Firat H et al (2008) Reliability and validity studies of the Turkish version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breathing 12:161–168
Jiménez-Correa U, Haro R, Poblano A et al (2009) Mexican version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Open Sleep J 2:6–10
Johns M (1992) Reliability and factor analysis of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 15:376–381
Knutson KL, Rathouz PJ, Yan LL, Liu K, Lauderdale D (2006) Stability of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index and the Epworth sleepiness questionnaires over 1 year in early middle-aged adults: the CARDIA study. Sleep 11:1503–1506
Miletin MS, Hanly PJ (2003) Measurement properties of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Med 4:195–201
Smith SS, Oei TP, Douglas JA et al (2008) Confirmatory factor analysis of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 9:739–744
Martinez D, Breitenbach TC, Lumertz MS et al (2011) Repeating administration of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in clinical useful. Sleep Breathing 15:763–773
Ulander M, Arested K, Svanborg E, Johansson B, Broström A (2012) The fairness of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale: two approaches to differential item functioning. Sleep Breathing 17:157–165
Mokkink LB, Terwee CB, Knol DL et al (2010) The COSMIN checklist for evaluating the methodological quality of studies on measurement properties: a clarification of its content. BMC Med Res Methodol 10:22
Mokkink LB, Terwee CB, Patrick LD et al (2010) The COSMIN checklist for assessing the methodological quality of studies on measurement properties of health status measurement instruments: an international Delphi study. Qual Life Res 19:539–549
Andrich D (1988) Rasch models for measurement. Sage, London
Wright BD, Mok M (2004) An overview of the family of Rasch measurement models. In: Smith EV, Smith RM (eds) Introduction to Rasch measurement. JAM Press, Maple Grove
Prieto G, Delgado AR, Perea MV, Ladera V (2010) Scoring neuropsychological tests using the Rasch model: an illustrative example with the Rey-Osterrieth complex figure. Clin Neuropsychol 24:45–56
Wilson M (2005) Constructing measures. LEA, Mahwah
Bond TG, Fox CM (2007) Applying the Rasch model, 2ªth edn. LEA, Mahwah
Linacre JM (2002) Optimizing rating scale category effectiveness. J Appl Meas 3:85–106
Linacre JM (2013) A user’s guide to Winsteps Ministep—Rasch-model computer programs. Winsteps.com, Chicago
Sanford SD, Lichstein KL, Durrence HH et al (2011) The influence of age, gender, ethnicity, and insomnia on Epworth Sleepiness Scores: a normative US population. Sleep Med 7:319–326
Morrell MJ, Finn L, McMillan A, Peppard P (2012) The impact of ageing and sex on the association between sleepiness and sleep disordered breathing. Eur Respir J 40:386–393
Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH (1994) Psychometric theory, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, USA
Conflict of interest
None, for all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sargento, P., Perea, V., Ladera, V. et al. The Epworth Sleepiness Scale in Portuguese adults: from classical measurement theory to Rasch model analysis. Sleep Breath 19, 693–701 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1078-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1078-6