Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to determine whether functional gastrointestinal disorders are more common among adolescents with self-reported poor sleep.
Methods
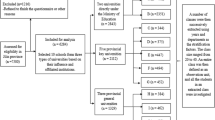
Junior middle school and senior high school students (n = 1,362) were recruited from schools in Shanghai. Students completed two questionnaires: the questionnaire for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in adolescents and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index.
Results
The prevalence of poor sleep was 34.29% [95% confidence interval (CI) = 31.77–36.81] and there was no significant difference between genders (P = 0.991). The tendency towards poor sleep increased with age, with age group yielding a significant effect (P = 0.001). In junior middle school and senior high school students, the propensity towards poor sleep was 30.10% (95% CI = 27.08–33.12%) and 42.11% (95% CI = 37.67–46.55%), respectively. Among students with poor sleep, the prevalence of IBS was 19.70% (95% CI = 16.09–23.31). After adjusting for age, sex, night pain, and psychological factors, IBS was significantly more common in students with poor sleep (odds ratio = 1.92; 95% CI = 1.07–2.58).
Conclusion
We conclude that IBS is prevalent in students with poor sleep. Poor sleep was independently associated with IBS among adolescents in Shanghai China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu X, Zhao Z, Jia C, Buysse (2008) Sleep patterns and problems among Chinese adolescents. Pediatrics 121:1165–1173
Liu X (2004) Sleep and adolescent suicidal behavior. Sleep 27:1351–1358
Heaton KW, O'Donnell LJ, Braddon FE, Mountford RA, Hughes AO, Cripps PJ (1992) Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in a British urban community: consulters and nonconsulters. Gastroenterology 102:1962–1967
Jones R, Lydeard S (1992) Irritable bowel syndrome in the general population. BMJ 304:87–90
Talley NJ, Zinsmeister AR, Van Dyke C, Melton LJ 3rd (1991) Epidemiology of colonic symptoms and the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 101:927–934
Drossman DA, Li Z, Andruzzi E, Temple RD, Talley NJ, Thompson WG, Whitehead WE, Janssens J, Funch-Jensen P, Corazziari E (1993) U.S. householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact. Dig Dis Sci 38:1569–1580
Fass R, Fullerton S, Tung S, Mayer EA (2000) Sleep disturbances in clinic patients with functional bowel disorders. Am J Gastroenterol 95:1195–1200
Jarret M, Heitkemper M, Cain KC, Burr RL, Hertig V (2000) Sleep disturbance influences gastrointestinal symptoms in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 45:952–959
Dong L, Dingguo L, Xiaoxing X, Hanming L (2005) An epidemiologic study of irritable bowel syndrome in adolescents and children in China: a school-based study. Pediatrics 116:e393–e396
Chitkara DK, Di Lorenzo C (2006) Pharmacotherapy for functional gastrointestinal disorders in children. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:536–540
Zhao ZT (2000) Methods and application in epidemiologic research. Science Press, Beijing
Drossman DA (2006) Rome III: the functional gastrointestinal disorders, 3rd edn. Degnon, McLean
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ (1989) The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res 28:193–213
Tsai PS, Wang SY, Wang MY, Su CT, Yang TT, Huang CJ, Fang SC (2005) Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (CPSQI) in primary insomnia and control subjects. Qual Life Res 14:1943–1952
Galland BC, Tripp EG, Gray A, Taylor BJ (2011) Apnea–hypopnea indices and snoring in children diagnosed with ADHD: a matched case–control study. Sleep Breath 15:455–462
Ting H, Wong RH, Yang HJ, Lee SP, Lee SD, Wang L (2011) Sleep-disordered breathing, behavior, and academic performance in Taiwan schoolchildren. Sleep Breath 15:91–98
Ghanizadeh A (2008) ADHD, bruxism and psychiatric disorders: does bruxism increase the chance of a comorbid psychiatric disorder in children with ADHD and their parents? Sleep Breath 12:375–380
Daskalopoulou EG, Liavvas C, Nakas CT, Vlachogiannis EG, Bouros D, Dombros NV (2011) Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome promotes reversal albuminuria during sleep. Sleep Breath 15:589–597
Falavigna A, de Souza Bezerra ML, Teles AR, Kleber FD, Velho MC, Steiner B, Beckenkamp NL, Lazzaretti L, Barazzetti D, Abruzzi F, Baseggio N, de Braga GL, Ferrari P, de Souza MV (2011) Sleep disorders among undergraduate students in Southern Brazil. Sleep Breath 15:519–524
National Sleep Foundation (2003) Sleep in America Poll. Washington, DC: National Sleep Foundation. Available at: www.sleepfoundation.org/2003poll.cfm. Accessibility verified October 21, 2004
Roehrs T, Hyde M, Blaisdell B, Greewald M, Roth T (2006) Sleep loss and REM sleep loss are hyperalgesic. Sleep 29:145–151
Locke GR III (1996) The epidemiology of functional gastrointestinal disorders in North America. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 25:1–19
Vege SS, Locke GR 3rd, Weaver AL, Farmer SA, Melton LJ 3rd, Talley NJ (2004) Functional gastrointestinal disorders among people with sleep disturbances: a population based study. Mayo Clin Proc 79:1501–1506
Roehrs T, Hyde M, Blaisdell B, Greenwald M, Roth T (2006) Sleep loss and REM sleep loss are hyperalgesic. Sleep 29:145–151
Heitkemper M, Jarrett M, Burr R, Cain KC, Landis C, Lentz M, Poppe A (2005) Subjective and objective sleep indices in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 17:523–530
Cremonini F, Camilleri M, Zinsmeister AR, Herrick LM, Beebe T, Talley NJ (2009) Sleep disturbances are linked to both upper and lower gastrointestinal symptoms in the general population. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:128–135
Ono S, Komada Y, Kamiya T, Shirakawa S (2008) A pilot study of the relationship between bowel habits and sleep health by actigraphy measurement and fecal flora analysis. J Physiological Anthropol 27:145–151
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a conflict of interest involved in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, HQ., Yao, M., Chen, GY. et al. Functional gastrointestinal disorders among adolescents with poor sleep: a school-based study in Shanghai, China. Sleep Breath 16, 1211–1218 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-011-0635-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-011-0635-5