Abstract
Study objectives
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a major concern in modern medicine; however, it is difficult to diagnose. Screening questionnaires such as the Berlin questionnaire, Rome questionnaire, and BASH'IM score are used to identify patients with OSA. However, the sensitivity and specificity of these tools are not satisfactory. We aim to introduce an artificial intelligence method to screen moderate to severe OSA patients (apnea–hypopnea index ≧15).
Patients and methods
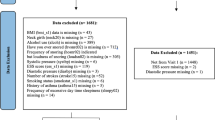
One hundred twenty patients were asked to complete a newly developed questionnaire before undergoing an overnight polysomnography (PSG) study. One hundred ten validated questionnaires were enrolled in this study. Genetic algorithm (GA) was used to build the five best models based on these questionnaires. The same data were analyzed with logistic regression (LR) for comparison.
Results
The sensitivity of the GA models varied from 81.8% to 88.0%, with a specificity of 95% to 97%. On the other hand, the sensitivity and specificity of the LR model were 55.6% and 57.9%, respectively.
Conclusions
GA provides a good solution to build models for screening moderate to severe OSA patients, who require PSG evaluation and medical intervention. The questionnaire did not require any special biochemistry data and was easily self-administered. The sensitivity and specificity of the GA models are satisfactory and may improve when more patients are recruited.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Netzer NC, Stoohs RA, Netzer CM, Clark K, Strohl KP (1999) Using the Berlin questionnaire to identify patients at risk for the sleep apnea syndrome. Ann Intern Med 131:485–491
Casale M, Rinaldi V, Bressi F, Di-PecoV BP, Sadun B, Urrestarazu E, Trivelli M, Salvinelli F (2008) A suitable test for identifying high risk adult patients of moderate–severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 12:275–280
Dixon JB, Schachter LM, O’Brien PE (2003) Predicting sleep apnea and excessive day sleepiness in the severely obese. Chest 123:1134–1141
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Boston
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J (2000) Longitudinal study of moderate weight change and sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA 284:3015–3021
Strohl KP, Redline S (1996) Recognition of obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154:279–289
Bixler EO, Vgontzas AN, Ten Have T, Tyson k, Kales A (1998) Effects of age on sleep apnea in men. I. Prevalence and severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:144–148
Kim JK, In HK, Kim JH, You SH, Kang KH, Shim JJ, Lee SY, Lee JB, Lee SG, Par C, Shin C (2004) Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in middle-aged Korean men and women. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1108–1113
Weinreich G, Plein K, Teschler T, Resler J, Teschler H (2006) Is the Berlin questionnaire an appropriate diagnostic tool for sleep medicine in pneumological rehabilitation? Pneumologie 60:737–742
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Rosenthal LD, Dolan DC (2008) The Epworth sleepiness scale in the identification of obstructive sleep apnea. J Nerv Ment Dis 196:249–431
Jones G, Willett P, Glen RC, Leach AR, Taylor R (1997) Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J Mol Biol 267:727–748
Zhang C, Wong KC (1997) A genetic algorithm for multiple molecular sequence alignment. Bioinformatics 13:565–581
Arslanian-Engoren C, Engoren M (2007) Using a genetic algorithm to predict evaluation of acute coronary syndromes. Nurs Res 56:82–88
Ahmad R, Bath PA (2005) Identification of risk factors for 15-year mortality among community-dwelling older people using Cox regression and a genetic algorithm. J Gerontol A-Biol 60:1052–1058
Kentala E, Laurikkala J, Pyykko l, Juhola M (1999) Discovering diagnostic rules from a neurotologic database with genetic algorithms. Ann Oto Rhinol Laryn 108:948–954
Jefferson MF, Pendleton N, Lucas SB, Horan MA (1997) Comparison of a genetic algorithm neural network with logistic regression for predicting outcome after surgery for patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 79:1338–1342
Acknowledgments
This work was performed at the Taipei Medical University Hospital and Sleep Center of Far Eastern Medical Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan. No external funding was obtained.
Disclosure
No financial support; no off-label or investigational use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L.M., Chiu, HW., Chuang, C.Y. et al. A prediction model based on an artificial intelligence system for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 15, 317–323 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-010-0384-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-010-0384-x