Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to assess the reliability and validity of a Norwegian version of the self-administered Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS).
Materials and methods
Two samples responded to the ESS: (1) 226 patients previously evaluated for obstructive sleep apnea, of whom 51 also responded to a retest 2 weeks later, and (2) 37 ambulant patients complaining of excessive daytime sleepiness, who were referred to multiple sleep latency testing (MSLT). We assessed internal consistency reliability with Cronbach’s alpha and test–retest reliability with weighted kappa (Kw) or an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The validity of the Norwegian ESS was assessed by correlating ESS item and total scores with the number of times a patient fell asleep and the mean latency found on the MSLT.
Results
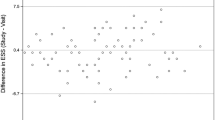
Internal consistency reliability, as assessed with Cronbach’s alpha, was 0.84 (n = 154). Test–retest reliability for the eight ESS items ranged from Kw of 0.61 to 0.80 (n = 50) and for the total score. ICC was 0.81.There was only fair to moderate correlation of ESS item and total scores with MSLT variables, mainly in a subset of patients with total ESS score >10.
Conclusions
The Norwegian version of the ESS had acceptable internal consistency and test–retest reliability. The association of the ESS items and total score with the MSLT was only fair to moderate, in line with previous studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Vignatelli L, Plazzi G, Barbato A et al (2003) Italian version of the Epworth sleepiness scale: external validity. Neurological Sciences 23:295–300
Chung KF (2000) Use of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in Chinese patients with obstructive sleep apnea and normal hospital employees. J Psychosom Res 49:367–372
Chervin RD, Aldrich MS, Pickett R, Guilleminault C (1997) Comparison of the results of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale and the Multiple Sleep Latency Test. J Psychosom Res 42:145–155
Olson LG, Cole MF, Ambrogetti A (1998) Correlations among Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores, multiple sleep latency tests and psychological symptoms. J Sleep Res 7:248–253
Fong SY, Ho CK, Wing YK (2005) Comparing MSLT and ESS in the measurement of excessive daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. J Psychosom Res 58:55–60
Johns MW (1994) Sleepiness in different situations measured by the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 17:703–710
Chervin RD, Aldrich MS (1999) The Epworth Sleepiness Scale may not reflect objective measures of sleepiness or sleep apnea. Neurology 52:125–131
Furuta H, Kaneda R, Kosaka K, Arai H, Sano J, Koshino Y (1999) Epworth Sleepiness Scale and sleep studies in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Psychiatr Clin Neurosci 53:301–302
Benbadis SR, Mascha E, Perry MC, Wolgamuth BR, Smolley LA, Dinner DS (1999) Association between the Epworth sleepiness scale and the multiple sleep latency test in a clinical population. Ann Intern Med 130:289–292
Chen NH, Johns MW, Li HY et al (2002) Validation of a Chinese version of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Qual Life Res 11:817–821
Izci B, Ardic S, Firat H, Sahin A, Altinors M, Karacan I (2007) Reliability and validity studies of the Turkish version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath 12:161–168
Stavem K, Kjelsberg FN, Ruud EA (2004) Reliability and validity of the Norwegian version of the Functional Outcomes of Sleep Questionnaire. Quality of Life Research 13:541–549
Johns MW (2000) Sensitivity and specificity of the multiple sleep latency test (MSLT), the maintenance of wakefulness test and the epworth sleepiness scale: failure of the MSLT as a gold standard. J Sleep Res 9:5–11
AASM Task Force (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 22:667–689
Thorpy MJ (1992) The clinical use of the Multiple Sleep Latency Test. The Standards of Practice Committee of the American Sleep Disorders Association. Sleep 15:268–276
Littner MR, Kushida C, Wise M et al (2005) Practice parameters for clinical use of the multiple sleep latency test and the maintenance of wakefulness test. Sleep 28:113–121
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. NIH Publication No. 204. Washington, DC
Kundel HL, Polansky M (2003) Measurement of observer agreement. Radiology 228:303–308
Altman DG (1991) Practical Statistics for Medical Research. Chapman and Hall, London
Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH (1994) Psychometric theory. McGraw-Hill, New York
Bloch KE, Schoch OD, Zhang JN, Russi EW (1999) German version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Respiration 66:440–447
Tsara V, Serasli E, Amfilochiou A, Constantinidis T, Christaki P (2004) Greek version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath 8:91–95
Nguyen AT, Baltzan MA, Small D, Wolkove N, Guillon S, Palayew M (2006) Clinical reproducibility of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. J Clin Sleep Med 2:170–174
Johns MW (2002) Sleep propensity varies with behaviour and the situation in which it is measured: the concept of somnificity. J Sleep Res 11:61–67
Carskadon MA, Dement WC, Mitler MM, Roth T, Westbrook PR, Keenan S (1986) Guidelines for the multiple sleep latency test (MSLT): a standard measure of sleepiness. Sleep 9:519–524
Pallesen S, Nordhus IH, Omvik S, Sivertsen B, Tell GS, Bjorvatn B (2007) Prevalence and risk factors of subjective sleepiness in the general adult population. Sleep 30:619–624
Kim H, Young T (2005) Subjective daytime sleepiness: dimensions and correlates in the general population. Sleep 28:625–634
Johns MW (1992) Reliability and factor analysis of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 15:376–381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beiske, K.K., Kjelsberg, F.N., Ruud, E.A. et al. Reliability and validity of a Norwegian version of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep Breath 13, 65–72 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-008-0202-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-008-0202-x