Abstract
Objectives
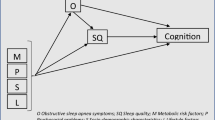
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can have adverse effects on cognitive functioning, mood, and cardiovascular functioning. OSA brings with it disturbances in sleep architecture, oxygenation, sympathetic nervous system function, and inflammatory processes. It is not clear which of these mechanisms is linked to the decrease in cognitive functioning. This study examined the effect of inflammatory parameters on cognitive dysfunction.
Materials and methods
Thirty-nine patients with untreated sleep apnea were evaluated by polysomnography and completed a battery of neuropsychological tests. After the first night of evaluation in the sleep laboratory, blood samples were taken for analysis of interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and soluble TNF receptor 1 (sTNF-R1).
Results
sTNF-R1 significantly correlated with cognitive dysfunction. In hierarchical linear regression analysis, measures of obstructive sleep apnea severity explained 5.5% of the variance in cognitive dysfunction (n.s.). After including sTNF-R1, percentage of variance explained by the full model increased more than threefold to 19.6% (F = 2.84, df = 3, 36, p = 0.05). Only sTNF-R1 had a significant individual relationship with cognitive dysfunction (β = 0.376 t = 2.48, p = 0.02).
Conclusions
sTNF-R1 as a marker of chronic inflammation may be associated with diminished neuropsychological functioning in patients with OSA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheshire K, Engleman H, Deary I, Shapiro C, Douglas NJ (1992) Factors impairing daytime performance in patients with sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Arch Intern Med 152:538–541
Newman AB, Nieto FJ, Guidry U, Lind BK, Redline S, Pickering TG, Quan SF, Sleep Heart Health Study Research Group (2001) Relation of sleep-disordered breathing to cardiovascular disease risk factors: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Epidemiol 154:50–59
Aloia MS, Arnedt JT, Davis JD, Riggs RL, Byrd D (2004) Neuropsychological sequelae of obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome: a critical review. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 10:772–785
Beebe DW, Groesz L, Wells C, Nichols A, McGee K (2003) The neuropsychological effects of obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis of norm-referenced and case-controlled data. Sleep 26:298–307
Gay P, Weaver R, Loube D, Iber C (2006) Evaluation of positive airway pressure treatment for sleep related breathing disorders in adults. Sleep 29:381–401
Bardwell WA, Ancoli-Israel S, Berry CC, Dimsdale JE (2001 July) Neuropsychological effects of one-week continuous positive airway pressure treatment in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a placebo-controlled study. Psychosom Med 63:579–584
Lim W, Bardwell WA, Loredo JS, Kim E, Ancoli-Israel S, Morgan EE, Heaton R, Dimsdale JE (2007) Effects of 2-week continuous positive airway pressure treatment vs. oxygen supplementation on neuropsychological functioning in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Sleep Med 3:380–386
Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1991) Blood to brain transport of interleukin links the immune and central nervous systems. Life Sci 48:117–121
Maier S, Watkins LR (1998) Cytokines for psychologists: implications for bidirectional immune-to-brain communication for understanding behavior, mood, and cognition. Psychol Rev 105:83–107
Tracey KJ (2002) The inflammatory reflex. Nature 420:853–859
Yaffe K, Lindquist K, Penninx BW, Simonsick EM, Pahor M, Kritchevsky S, Launer L, Kuller L, Rubin S, Harris T (2003) Inflammatory markers and cognition in well-functioning African–American and white elders. Neurology 61:76–80
De Luigi A, Fragiacomo C, Lucca U, Quadri P, Tettamanti M, Grazia De Simoni M (2001) Inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease and multi-infarct dementia. Mech Ageing Dev 122:1985–1995
Marsland AL, Petersen KL, Sathanoori R, Muldoon MF, Neumann SA, Ryan C, Flory JD, Manuck SB (2006) Interleukin-6 covaries inversely with cognitive performance among middle-aged community volunteers. Psychosom Med 68:895–903
Weaver JD, Huang MH, Albert M, Harris T, Rowe JW, Seeman TE (2002) Interleukin-6 and risk of cognitive decline. Neurology 59:371–378
Wilson CJ, Finch CE, Cohen JH (2002) Cytokines and cognition—the case for a head-to-toe inflammatory paradigm. J Am Geriatr Soc 50:2041–2056
Shamsuzzaman AS, Winnicki M, Lanfranchi P, Wolk R, Kara T, Accurso V, Somers VK (2002) Elevated C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 105:2462–2464
Vgontzas AN, Papanicolaou DA, Bixler EO, Kales A, Tyson K, Chrousos GP (1997) Elevation of plasma cytokines in disorders of excessive daytime sleepiness: role of sleep disturbance and obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:1313–1316
Ciftci TU, Kokturk O, Bukan N, Bilgihan A (2004) The relationship between serum cytokine levels with obesity and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Cytokine 17:87–91
Lavie P (2004) Pro: sleep apnea causes cardiovascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169:147–148
Metropolitan Life Insurance Company (1983) Metropolitan height and weight tables. Stat Bull Metrop Life Found 64:3–9
Rechtshaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standard terminology: techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. UCLA Brain Information Service/Brain Research Institute, Los Angeles
Loredo JS, Ancoli-Israel S, Dimsdale JE (1999) Effect of continuous positive airway pressure vs. placebo continuous positive airway pressure on sleep quality in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 116:1545–1549
Wechsler D (1997) Wechsler adult intelligence scale—III. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Benedict RH (1997) Brief visuospatial memory test-revised. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Benedict RH, Schretlen D, Groninger L, Brandt J (1998) Hopkins verbal learning test-revised: normative data and analysis of inter-form and test–retest reliability. Clin Neuropsychol 12:43–55
Heaton RK, Miller SW, Taylor MJ, Grant I (2004) Revised comprehensive norms for an expanded Halstead-Reitan battery: demographic adjusted norms for African American and Caucasian adults. Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc, Lutz
Lewis RF (1995) Digit vigilance test. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Golden CJ (1978) Stroop color and word test. Stoelting Co., Chicago
Lezak MD (1995) Neuropsychological assessment. Oxford University Press, New York
Heaton RK, Taylor MJ, Manly J (2003) Demographic effects and use of demographically corrected norms with the WAIS-III and WMS-III. In: Tulsky DS, Saklaeske DH, Heaton EK, Bornstein R, Ledbetter ME (eds) Clinical interpretation of the WAIS-III and WMS-III. Academic, San Diego, pp 181–210
Benton AL (1968) Differential behavioral effects of frontal lobe disease. Neuropsychologia 6:53–60
Radloff LS (1977) The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 1:385–401
Schulberg HC, Saul M, McClelland M, Ganguli M, Christy W, Frank R (1985) Assessing depression in primary medical and psychiatric practices. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42:1164–1170
Cockram A, Judd FK, Mijch A, Norman T (1999) The evaluation of depression in inpatients with HIV disease. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 33:344–352
Hann D, Winter K, Jacobsen P (1999) Measurement of depressive symptoms in cancer patients: evaluation of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D). J Psychosom Res 46:437–443
Bardwell WA, Berry CC, Ancoli-Israel S, Dimsdale JE (1999) Psychological correlates of sleep apnea. J Psychosom Res 47:583–596
Bardwell WA, Moore P, Ancoli-Israel S, Dimsdale JE (2000) Does obstructive sleep apnea confound sleep architecture findings in subjects with depressive symptoms? Biol Psychiatry 48:1001–1009
Bardwell WA, Moore P, Ancoli-Israel S, Dimsdale JE (2003) Fatigue in obstructive sleep apnea: driven by depressive symptoms instead of apnea severity? Am J Psychiatry 160:350–355
Carey CL, Woods SP, Gonzalez R, Conover E, Marcotte TD, Grant I, Heaton RK, the HNRC Group (2004) Predictive validity of Global Deficit Scores in detecting neuropsychological impairment in HIV infection. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 26:307–319
Aderka D (1996) The potential biological and clinical significance of the soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 7:231–240
Diez-Ruiz A, Tilz GP, Zangerle R, Baier-Bitterlich G, Wachter H, Fuchs D (1995) Soluble receptors for tumour necrosis factor in clinical laboratory diagnosis. Eur J Haematol 54:1–8
Haack M, Schuld A, Kraus T, Pollmächer T (2001) Effects of sleep on endotoxin-induced host responses in healthy men. Psychosom Med 63:568–578
Mullington J, Korth C, Hermann DM, Orth A, Galanos C, Holsboer F, Pollmächer T (2000) Dose-dependent effects of endotoxin on human sleep. Am J Physiol 278:R947–R955
Haack M, Pollmächer T, Mullington JM (2004) Diurnal and sleep–wake dependent variations of soluble TNF- and IL-2 receptors in healthy volunteers. Brain Behavior Immunity 18:361–367
Shearer WT, Reuben JM, Mullington JM, Price NJ, Lee BN, Smith EO, Szuba MP, Van Dongen HP, Dinges DF (2001) Soluble TNF-α receptor 1 and IL-6 plasma levels in humans subjected to the sleep deprivation model of spaceflight. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:165–170
Entzian P, Linnemann K, Schlaak M, Zabel P (1996) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and circadian rhythms of hormones and cytokines. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:1080–1086
Reichenberg A, Yirmiya R, Schuld A, Kraus T, Haack M, Morag A, Pollmächer T (2001) Cytokine-associated emotional and cognitive disturbances in human. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:445–452
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants HL044915, RR00827, and AG08415 and by the grant PBBSB115117 from the Swiss National Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haensel, A., Bardwell, W.A., Mills, P.J. et al. Relationship between inflammation and cognitive function in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 13, 35–41 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-008-0198-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-008-0198-2