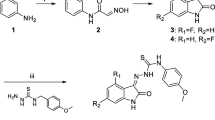
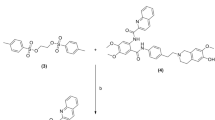
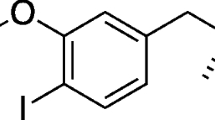
Abstract
Purpose
The plasma membrane P-glycoprotein (Pgp) is an efflux transporter involved in multidrug resistance and in the onset of neurodegenerative disease. Its function and most mechanisms of action are still under investigation. We developed a C-11-labeled 2-arylethylphenylamine-([11C]AEPH) derivative for positron emission tomography (PET), as a novel probe to better understand the activity and the function of Pgp in vivo.
Procedures
The synthetic procedure and the quality control of the selected lead compound, [11C]AEPH-1, were set up and optimized. The biodistribution and the dynamic extraction in target organs of [11C]AEPH-1 were studied in vivo by PET in healthy rats at baseline and after pre-treatment with a Pgp inhibitor (tariquidar).
Results
In vivo dynamic imaging was consistent with the results of ex vivo extraction on explanted organs. An adequate stability for in vivo studies, as well as a high activity of [11C]AEPH-1 in intestine and barrier tissues, has been demonstrated. Results of the blockade study showed a decrease of uptake after the pre-treatment, indicating a behavior attributable to a Pgp ligand.
Conclusions
The suitable pharmacokinetics and the specificity tested in the pre-treated animals have indicated the potentiality of this AEPH derivative to act as Pgp ligand, providing new opportunities for further studies on expression and function of this important efflux transporter in the fields of neurology and oncology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deeley R, Westlake C, Cole SPC (2006) Transmembrane transport of endo- and xenobiotics by mammalian ATP-binding cassette multidrug resistance proteins. Physiol Rev 86:849–899
Ambudkar SV, Dey S, Hrycyna AC et al (1999) Biochemical cellular and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:361–398
Leslie EM, Deeley RG, Cole SP (2005) Multi drug resistance proteins: role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204:216–237
Löscher W, Potschka H (2005) Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases. Prog Neurobiol 76:22–765
Higgins CF, Gottesman MM (1992) Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem Sci 17:18–21
Sharom FJ (2014) Complex Interplay between the P-glycoprotein multidrug efflux pump and the membrane: its role in modulating protein function. Front Oncol 4(41):1–19
Ambudkar SV, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Sauna ZE et al (2003) P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene 22:7468–7485
Gottesman MM, Ling V (2006) The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: the early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS Lett 580:998–1009
Beaulieu E, Demeule M, Ghitescu L et al (1997) P-glycoprotein is strongly expressed in the luminal membranes of the endothelium of blood vessels in the brain. Biochem J 326:539–544
Melaine N, Liénard MO, Dorval I et al (2002) Multidrug resistance genes and P-glycoprotein in the testis of the rat, mouse, guinea pig, and human. Biol Reprod 67:1699–1707
Edwards JE, Alcorn J, Savolainen J et al (2005) Role of P-glycoprotein in distribution of nelfinavir across the blood-mammary tissue barrier and blood-brain barrier. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:1626–1628
Fromm MF (2004) Importance of P-glycoprotein at blood-tissue barriers. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:423–429
Demeule M, Labelle M, Regina A et al (2001) Isolation of endothelial cells from brain, lung, and kidney: expression of the multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein isoforms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:827–834
Sharom FJ (2008) ABC multidrug transporters: structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics 9:105–127
Meissner K, Sperker B, Karsten C et al (2002) Expression and localization of P-glycoprotein in human heart: effects of cardiomyopathy. J Histochem Cytochem 50(10):1351–1356
Auzmendi J, Merelli A, Girardi E et al (2014) Progressive heart P-glycoprotein (P-gp) overexpression after experimental repetitive seizures (ERS) associated with fatal status epilepticus (FSE). Is it related with SUDEP? Mol Cell Epilepsy 1:43–51
Loscher W, Potschka H (2005) Drug resistance in brain diseases and the role of drug efflux transporters. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:591–602
Bartels AL, Willemsen ATM, Kortekaas R et al (2008) Decreased blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in the progression of Parkinson’s disease, PSP and MSA. J Neural Transm 115:1001–1009
Rapposelli S, Digiacomo M, Balsamo A (2009) P-gp transporter and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Top Med Chem 9(1):209–217
Vogelgesang S, Cascorbi I, Schroeder E et al (2002) Deposition of Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid is inversely correlated with P-glycoprotein expression in the brains of elderly non-demented humans. Pharmacogenetics 12(7):535–541
Van Assema D, Lubberink M, Rizzu P et al (2012) Blood–brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in healthy subjects and Alzheimer’s disease patients: effect of polymorphisms in the ABCB1 gene. EJNMMI Res 2:57
Aller SG, Yu J, Ward A et al (2009) Structure of P-glycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug dinding. Science 323(5922):1718–1722
Liu M, Hou T, Feng Z, Li Y (2013) The flexibility of P-glycoprotein for its poly-specific drug binding from molecular dynamics simulations. J Biomol Struct Dyn 31(6):612–629
Kerb R (2006) Implications of genetic polymorphisms in drug transporters for pharmacotherapy. Cancer Lett 234:4–33
Syvänen S, Eriksson J (2013) Advances in PET imaging of P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier. ACS Chem Neurosci 4:225–237
Hendrikse NH, de Vries EG, Eriks-Fluks L et al (1999) A new in vivo method to study P-glycoprotein transport in tumors and the blood–brain barrier. Cancer Res 59:2411–2416
Bart J, Willemsen AT, Groen HJ et al (2003) Quantitative assessment of P-glycoprotein function in the rat blood–brain barrier by distribution volume of [11C]verapamil measured with PET. Neuroimage 20:1775–1782
Dörner B, Kuntner C, Bankstahl JP et al (2009) Synthesis and small-animal positron emission tomography evaluation of [11C]-elacridar as a radiotracer to assess the distribution of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier. J Med Chem 52(19):6073–6082
Liow JS, Yasuno F et al (2008) 11C-loperamide and its N-desmethyl radiometabolite are avid substrates for brain permeability-glycoprotein efflux. J Nucl Med 49(4):649–656
Luurtsema G, Schuit RC, Klok RP et al (2009) Evaluation of [11C]laniquidar as a tracer of P-glycoprotein: radiosynthesis and biodistribution in rats. Nucl Med Biol 36(6):643–649
Lazarova N, Zoghbi SS, Hong J et al (2008) Synthesis and evaluation of [N-methyl-11C]N-desmethyl-loperamide as a new and improved PET radiotracer for imaging P-gp function. J Med Chem 51(19):6034–6043
Bauer F, Kuntner C, Bankstahl JP et al (2010) Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of [11C]tariquidar, a positron emission tomography radiotracer based on a third-generation P-glycoprotein inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem 18(15):5489–5497
Levchenko A, Mehta B, Lee J et al (2000) Evaluation of 11C-colchicine for PET imaging of multiple drug resistance. J Nucl Med 41:493–501
van Waarde A, Ramakrishnan NK, Rybczynska AA et al (2009) Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of novel PET probes for Pp-glycoprotein function and expression. J Med Chem 52(14):4524–4532
Shiue CY, Shiue GG, Mozley PD et al (1997) P-[18F]-MPPF: a potential radioligand for PET studies of 5-HT1A receptors in humans. Synapse 25(2):147–154
Mairinger S, Wanek T, Kuntner C et al (2012) Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of the radiolabeled P-glycoprotein inhibitor [11C]MC113. Nucl Med Biol 39:1219–1225
Bart J, Dijkers E, Wegman T et al (2005) New positron emission tomography tracer [11C]carvedilol reveals P-glycoprotein modulation kinetics. Br J Pharmacol 145(8):1045–1051
Eriks-Fluks E, Elsinga PH, Hendrikse NH et al (1998) Enzymatic synthesis of [4-methoxy-11C]daunorubicin for functional imaging of P-glycoprotein with PET. Appl Radiat Isot 49(7):811–813
Luurtsema G, Verbeek J, Lammertsma AA et al (2010) Carbon-11 labeled tracers for in vivo imaging of P-glycoprotein function: kinetics, advantages and disadvantages. Curr Top Med Chem 10:1820–1833
Colabufo NA, Berardi F, Perrone R et al (2006) Arylmethyloxyphenyl derivatives: small molecules displaying P-glycoprotein inhibition. J Med Chem 49:6607–6613
Colabufo NA, Berardi F, Perrone R et al (2008) 2-[(3-Methoxyphenylethyl)phenoxy]-based ABCB1 inhibitors: effect of different basic side-chains on their biological properties. J Med Chem 51:7602–7613
Colabufo NA, Berardi F, Perrone R et al (2008) Synthesis and biological evaluation of (hetero)arylmethyloxy- and arylmethylamine-phenyl derivatives as potent P-glycoprotein modulating agents. J Med Chem 51:1415–1422
Polli JW, Wring SA, Humphreys JE et al (2001) Huang rational use of in vitro P-glycoprotein assays in drug discovery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:620–628
Nesi G, Colabufo NA, Contino M et al (2014) SAR study on arylmethyloxyphenyl scaffold: looking for a P-gp nanomolar affinity. Eur J Med Chem 76:558–566
Larsen P, Ulin J, Dahlstrom K et al (1997) Synthesis of [11C]iodomethane by iodination of [11C]methane. Appl Radiat Isot 48:153–157
Link JM, Krohn KA, Clark JC (1997) Production of [11C]CH3I by single pass reaction of [11C]CH4 with I2. Nucl Med Biol 24:93–97
Petroni D, Berton B, Bettini B et al (2014) Performances of a TRACERlab FX C synthesis module using a Ni-nanopowder/molecular sieves mixed catalyst. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:2005–2011
Mistry P, Stewart AJ, Dangerfield W et al (2001) In vitro and in vivo reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by a novel potent modulator, XR9576. Cancer Res 61:749–758
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by the grant PRIN2009 (20097FJHPZ_003) from the Ministero dell’Istruzione dell’Università e della Ricerca (MIUR) Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The experimental protocol, which conformed to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 85–23, revised 1996), was approved by the Animal Care Committee of the Italian Ministry of Health (protocol no. 0000249/2014).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petroni, D., Bartoli, A., Rapposelli, S. et al. Synthesis and In Vivo Imaging of N-(3-[11C]Methoxybenzyl)-2-(3-Methoxyphenyl)ethylaniline as a Potential Targeting Agent for P-glycoprotein. Mol Imaging Biol 18, 916–923 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-016-0965-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-016-0965-6