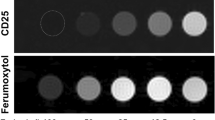
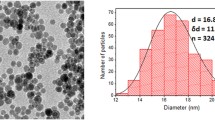
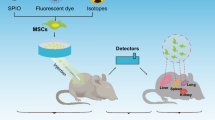
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose is to address the problem in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of contrast agent dilution.
Procedures
In situ magnetic labeling of cells and MRI were used to assess distribution and growth of human hepatic stem cells (hHpSCs) transplanted into severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)/non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. It was done with commercially available magnetic microbeads coupled to an antibody to a surface antigen, epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), uniquely expressed in the liver by hepatic progenitors.
Results
We validated the microbead connection to cells and related MRI data to optical microscopy observations in order to develop a means to quantitatively estimate cell numbers in the aggregates detected. Cell counts of hHpSCs at different times post-transplantation revealed quantifiable evidence of cell engraftment and expansion.
Conclusions
This magnetic labeling methodology can be used with any antibody coupled to a magnetic particle to target any surface antigen that distinguishes transplanted cells from host cells, thus facilitating studies that define methods and strategies for clinical cell therapy programs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFP:
-
α-Fetoprotein
- ALB:
-
Albumin
- CK:
-
Cytokeratin
- EpCAM:
-
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule
- HDM:
-
Hormonally defined medium
- hHB:
-
Human hepatoblast
- hHpSC:
-
Human hepatic stem cell
- KM:
-
Kubota’s medium
- MACS:
-
Magnetically activated cell sorting
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Susick R, Moss N, Kubota H et al (2002) Hepatic progenitors and strategies for liver cell therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 943:398–419
Ito M, Nagata H, Miyakawa S, Fox IJ (2009) Review of hepatocyte transplantation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16:97–100
Khan AA, Shaik MV, Parveen N et al (2010) Human fetal liver-derived stem cell transplantation as supportive modality in the management of end-stage decompensated liver cirrhosis. Cell Transpl, in press
Bulte JW, Douglas T, Witwer B et al (2001) Magnetodendrimers allow endosomal magnetic labeling and in vivo tracking of stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 19:1141–1147
Lewin M, Carlesso N, Tung CH et al (2000) Tat peptide-derivatized magnetic nanoparticles allow in vivo tracking and recovery of progenitor cells. Nat Biotechnol 18:410–414
Gubin AN, Reddy B, Njoroge JM, Miller JL (1997) Long-term, stable expression of green fluorescent protein in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236:347–350
Song S, Witek RP, Lu Y et al (2004) Ex vivo transduced liver progenitor cells as a platform for gene therapy in mice. Hepatology 40:918–924
Gambhir SS, Barrio JR, Herschman HR, Phelps ME (1999) Assays for noninvasive imaging of reporter gene expression. Nucl Med Biol 26:481–490
Gupta S, Inada M, Joseph B, Kumaran V, Benten D (2004) Emerging insites into liver-directed cell therapy for genetic and acquired disorders. Transpl Immunol 12:289–302
Wang LJ, Chen YM, George D et al (2002) Engraftment assessment in human and mouse liver tissue after sex-mismatched liver cell transplantation by real-time quantitative PCR for Y chromosome sequences. Liver Transpl 8:822–828
Mahieu-Caputo D, Allain J, Branger J et al (2004) Repopulation of athymic mouse liver by cryopreserved early human fetal hepatoblasts. Human Gene Therapy 15:1219–1228
Turner R, Gerber D, Reid LM (2010) Transplantation of cells from solid organs requires grafting protocols. Transplantation, in press
Schmelzer E, Zhang L, Bruce A et al (2007) Human hepatic stem cells from fetal and postnatal donors. J Exp Med 204:1973–1987, the authors are equal contributors
Wang Y, Yao H-l, Barbier C et al (2010) Lineage-dependent epithelial–mesenchymal paracrine signals dictate growth versus differentiation of human hepatic stem cells to adult fates. Hepatology, in press
Schmelzer E, Wauthier E, Reid LM (2006) Phenotypes of pluripotent human hepatic progenitors. Stem Cell 24:1852–1858
Sicklick JK, Li YX, Melhem A et al (2006) Hedgehog signaling maintains resident hepatic progenitors throughout life. [co-senior authors]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G859–G870
Schmelzer E, Reid LM (2009) Telomerase activity in human hepatic stem cells, hepatoblasts and hepatocytes from neonatal, pediatric, adult and geriatric donors. Eur J Hepatol Gastroenterol 21:1191–1198
Schmelzer E, Wauthier E, Melhem A et al (2006) Hepatic stem cells. In: Potten C, Clarke R, Wilson J, Renehan A (eds) Tissue stem cells. Taylor & Francis, NY, pp 161–214
Zhang L, Theise N, Chua M, Reid LM (2008) Human hepatic stem cells and hepatoblasts: symmetry between liver development and liver regeneration. Hepatology 48:1598–1607
Turner WS, Seagle C, Galanko J et al (2008) Metabolomic footprinting of human hepatic stem cells and hepatoblasts cultured in engineered hyaluronan-matrix hydrogel scaffolds. Stem Cell 26:1547–1555
Kubota H, Reid LM (2000) Clonogenic hepatoblasts, common precursors for hepatocytic and biliary lineages, are lacking classical major histocompatibility complex class I antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12132
McClelland R, Wauthier E, Zhang L et al (2008) Ex vivo conditions for self-replication of human hepatic stem cells. Tissue Eng 14:1–11
Wauthier E, McClelland R, Turner W et al (2008) Hepatic stem cells and hepatoblasts: identification, isolation and ex vivo maintenance. Methods Cell Biol, Methods for Stem Cells 86:137–225
Kubota H, Yao H, Reid LM (2007) Identification and characterization of vitamin A-storing cells in fetal liver. Stem Cell 25:2339–2349
Taylor AE, Granger DW (1984) Exchange of macromolecules across microcapillaries. In: Rankin EM, Michel CC (eds) Section 2. The cardiovascular system, microcirulation: Part 1. Handbook of physiology, vol 4. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, pp 467–520
Yamashita Y, Ji J, Budhu A et al (2009) Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates cancer initiating cells (EpCAM+ AFP+) with stem cell features and metastatic activities in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 136:1012–1024
Wicha MS, Liu S, Dontu G (2006) Cancer stem cells: an old idea—a paradigm shift. Cancer Res 66:1883–1890
Benhaj K, Akcali KC, Ozturk M (2006) Redundant expression of canonical Wnt ligands in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 15:701–707
Schmelzer E, Reid LM (2008) EpCAM expression in normal, non-pathological tissues. Frontiers Biosci 13:3096–3100
Bulte JW, Duncan ID, Frank JA (2002) In vivo magnetic resonance tracking of magnetically labeled cells after transplantation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:899–907
Hill JM, Ma MR, Dick AJ et al (2003) Serial cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of injected mesenchymal stem cells. Circulation 108:1009–1014
Walter GA, Cahill KS, Huard J et al (2004) Noninvasive monitoring of stem cell transfer for muscle disorders. Magn Reson Med 51:273–277
Maxwell DJ, Bonde J, Hess DA et al (2008) Fluorophore-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticle labeling and analysis of engrafting human hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells 26:517–524
Walczak P, Kedziorek DA, Gilad AA, Lin S, Bulte JWM (2005) Instant MR labeling of stem cells using magnetoelectroporation. Magn Reson Med 54:769–774
Partlow KC, Chen J, Brant JA et al (2007) 19F magnetic resonance imaging for stem/progenitor cell tracking with multiple unique perfluorcarbon nanobeacons. FASEB J 21:1647–1654
Modo M, Cash D, Mellodew K et al (2007) Tracking transplanted stem cell migration using bifunctional, contrast agent enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 17:803–811
Naldini L, Blomer U, Gallay P, Gage FH, Verma IM, Trono D (1996) In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of postmitotic cells by a lentiviral vector. Science 272:263–267
Gropp M, Itsykson P, Singer O et al (2003) Stable genetic modification of human embryonic stem cells by lentiviral vectors. Mol Ther 7:281–287
Blaese R (2007) What is the status of gene therapy for primary immunodeficiency? Immunol Res 38:274–284
Jansen JF, Shamblott MJ, van Zijl PC et al (2006) Stem cell profiling by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Res Med 56:666–670
Holmes E, Foxall PJD, Spraul M, Duncan Farrant R, Nicholson JK, Lindon JC (1997) 750 MHz 1H NMR spectroscopy characterisation of the complex metabolic pattern of urine from patients with inborn errors of metabolism: 2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria and maple syrup urine disease. J Pharm Biomed Anal 15:1647–1659
Cohen BH, Buiy E, Packer RJ, Sutton LN, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA (1989) Gadolinium–DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in childhood brain tumors. Neurology 39:1178
Schafer R, Kehlbach R, Wiskirchen J et al (2007) Transferrin receptor upregulation: in vitro labeling of rat mesenchymal stem cells with superparametic iron oxide. Radiology 244:514–523
Ji J, Yamashita T, Budhu A et al (2009) Identification of a conserved microRNA-181 family by genome-wide screening as a critical player in hepatic cancer stem cell. Hepatology 50:880–892
Acknowledgements
Technical and administrative support was provided by Lucendia English, Victoria Morgan, and Dr. Claire Barbier. The microscopy was done in the Michael Hooker Confocal Microscope Facility at UNC (Dr. Michael Chua, director) and the electron microscopy in the Microscope Facility (Dr. Robert Bagnell, director). We thank Dr. Sharon Lubkin for a critical evaluation of the paper and Dr. Claire Barbier for editing the figures.
This work was funded primarily by a US Department of Energy (DOE) grant (DE-FG02-02ER-63477). It derived also from grants from the North Carolina Biotechnology Center, Vesta Therapeutics (Bethesda, MD), the National Institutes of Health (NIH; AA014243 and IP30-DK065933), the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (DK34987), and the National Cancer Institute (CA016086). All of the imaging was done in the Duke Center for In Vivo Microscopy (Dr. G.A. Johnson, director), an NIH/National Center for Research Resources Biomedical Technology Resource Center (P41 RR005959) and Small Animal Imaging Resource Program (U24 CA092656).
Conflict of Interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Significance:
We have developed a novel method for post-transplantation magnetic labeling of cells. The technique overcomes the problem of fading MRI contrast that occurs with transplanting pre-labeled cells.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McClelland, R., Wauthier, E., Tallheden, T. et al. In Situ Labeling and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Transplanted Human Hepatic Stem Cells. Mol Imaging Biol 13, 911–922 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-010-0422-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-010-0422-x