Abstract
Background
Liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) is a popular approach for metabolomics data acquisition and requires many data processing software tools. The FAIR Principles – Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reusability – were proposed to promote open science and reusable data management, and to maximize the benefit obtained from contemporary and formal scholarly digital publishing. More recently, the FAIR principles were extended to include Research Software (FAIR4RS).
Aim of review
This study facilitates open science in metabolomics by providing an implementation solution for adopting FAIR4RS in the LC-HRMS metabolomics data processing software. We believe our evaluation guidelines and results can help improve the FAIRness of research software.
Key scientific concepts of review
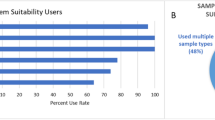
We evaluated 124 LC-HRMS metabolomics data processing software obtained from a systematic review and selected 61 software for detailed evaluation using FAIR4RS-related criteria, which were extracted from the literature along with internal discussions. We assigned each criterion one or more FAIR4RS categories through discussion. The minimum, median, and maximum percentages of criteria fulfillment of software were 21.6%, 47.7%, and 71.8%. Statistical analysis revealed no significant improvement in FAIRness over time. We identified four criteria covering multiple FAIR4RS categories but had a low %fulfillment: (1) No software had semantic annotation of key information; (2) only 6.3% of evaluated software were registered to Zenodo and received DOIs; (3) only 14.5% of selected software had official software containerization or virtual machine; (4) only 16.7% of evaluated software had a fully documented functions in code. According to the results, we discussed improvement strategies and future directions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adusumilli, R., & Mallick, P. (2017). Data Conversion with ProteoWizard msConvert. Methods in Molecular Biology. (Clifton N J), 1550, 339–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6747-6_23.
Aghamohammadi, A., Mirian-Hosseinabadi, S. H., & Jalali, S. (2021). Statement frequency coverage: a code coverage criterion for assessing test suite effectiveness. Information and Software Technology, 129, 106426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2020.106426.
Agrawal, S., Kumar, S., Sehgal, R., George, S., Gupta, R., Poddar, S., Jha, A., & Pathak, S. (2019). El-MAVEN: A Fast, Robust, and User-Friendly Mass Spectrometry Data Processing Engine for Metabolomics. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1978, 301–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9236-2_19
Alonso, A., Julià, A., Beltran, A., Vinaixa, M., Díaz, M., Ibañez, L., Correig, X., & Marsal, S. (2011). AStream: an R package for annotating LC/MS metabolomic data. Bioinformatics, 27(9), 1339–1340. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr138.
Analytica Chimica Acta | Journal | ScienceDirect.com by Elsevier. (n.d.). Retrieved September 16, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/analytica-chimica-acta
Barker, M., Chue Hong, N. P., Katz, D. S., Lamprecht, A. L., Martinez-Ortiz, C., Psomopoulos, F., Harrow, J., Castro, L. J., Gruenpeter, M., Martinez, P. A., & Honeyman, T. (2022). Introducing the FAIR principles for research software. Scientific Data, 9(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01710-x.
Berrios, D. C., Beheshti, A., & Costes, S. V. (n.d.). FAIRness and Usability for Open-access Omics Data Systems. 10.
Broeckling, C. D., Afsar, F. A., Neumann, S., Ben-Hur, A., & Prenni, J. E. (2014). RAMClust: a Novel feature clustering method enables spectral-matching-based annotation for Metabolomics Data. Analytical Chemistry, 86(14), 6812–6817. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac501530d.
Brunius, C., Shi, L., & Landberg, R. (2016). Large-scale untargeted LC-MS metabolomics data correction using between-batch feature alignment and cluster-based within-batch signal intensity drift correction. Metabolomics: Official Journal of the Metabolomic Society, 12(11), 173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1124-4.
Bueschl, C., Kluger, B., Neumann, N. K. N., Doppler, M., Maschietto, V., Thallinger, G. G., Meng-Reiterer, J., Krska, R., & Schuhmacher, R. (2017). MetExtract II: a Software suite for stable isotope-assisted untargeted metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 89(17), 9518–9526. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02518.
Cai, Y., Weng, K., Guo, Y., Peng, J., & Zhu, Z. J. (2015). An integrated targeted metabolomic platform for high-throughput metabolite profiling and automated data processing. Metabolomics, 11(6), 1575–1586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0809-4.
Capellades, J., Navarro, M., Samino, S., Garcia-Ramirez, M., Hernandez, C., Simo, R., Vinaixa, M., & Yanes, O. (2016). geoRge: a computational Tool to detect the Presence of stable isotope labeling in LC/MS-Based untargeted metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 88(1), 621–628. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03628.
Chokkathukalam, A., Jankevics, A., Creek, D. J., Achcar, F., Barrett, M. P., & Breitling, R. (2013). mzMatch–ISO: an R tool for the annotation and relative quantification of isotope-labelled mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics, 29(2), 281–283. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts674.
Chong, J., & Xia, J. (2018). MetaboAnalystR: an R package for flexible and reproducible analysis of metabolomics data. Bioinformatics, 34(24), 4313–4314. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty528.
Chue Hong, N. P., Katz, D. S., Barker, M., Lamprecht, A. L., Martinez, C., Psomopoulos, F. E., Harrow, J., Castro, L. J., Gruenpeter, M., Martinez, P. A., Honeyman, T., Struck, A., Lee, A., Loewe, A., van Werkhoven, B., Jones, C., Garijo, D., Plomp, E., & Genova, F. (2022). … WG, R. F. FAIR Principles for Research Software (FAIR4RS Principles). https://doi.org/10.15497/RDA00068
Clasquin, M. F., Melamud, E., & Rabinowitz, J. D. (2012). LC-MS Data Processing with MAVEN: A Metabolomic Analysis and Visualization Engine. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics / Editoral Board, Andreas D. Baxevanis … et Al.], 0 14, Unit14.11. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi1411s37
Considine, E. C., & Salek, R. M. (2019). A Tool to encourage Minimum Reporting Guideline Uptake for Data Analysis in Metabolomics. Metabolites, 9(3), E43. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9030043.
Covidence—Better systematic review management. (n.d.). Covidence. Retrieved April 6, from https://www.covidence.org/
Creek, D. J., Jankevics, A., Burgess, K. E. V., Breitling, R., & Barrett, M. P. (2012). IDEOM: an Excel interface for analysis of LC-MS-based metabolomics data. Bioinformatics (Oxford England), 28(7), 1048–1049. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts069.
Davidson, R. L., Weber, R. J. M., Liu, H., Sharma-Oates, A., & Viant, M. R. (2016). Galaxy-M: a Galaxy workflow for processing and analyzing direct infusion and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. GigaScience, 5(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13742-016-0115-8.
De Livera, A. M., Olshansky, G., Simpson, J. A., & Creek, D. J. (2018). NormalizeMets: assessing, selecting and implementing statistical methods for normalizing metabolomics data. Metabolomics, 14(5), 54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1347-7.
De Vos, R. C., Moco, S., Lommen, A., Keurentjes, J. J., Bino, R. J., & Hall, R. D. (2007). Untargeted large-scale plant metabolomics using liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 2(4), https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.95.
Decan, A., Mens, T., Claes, M., & Grosjean, P. (2015). On the Development and Distribution of R Packages: An Empirical Analysis of the R Ecosystem. Proceedings of the 2015 European Conference on Software Architecture Workshops, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1145/2797433.2797476
DeFelice, B. C., Mehta, S. S., Samra, S., Čajka, T., Wancewicz, B., Fahrmann, J. F., & Fiehn, O. (2017). Mass Spectral feature list optimizer (MS-FLO): a Tool to minimize false positive peak reports in untargeted liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectroscopy (LC-MS) data Processing. Analytical Chemistry, 89(6), 3250–3255. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04372.
Del Carratore, F., Schmidt, K., Vinaixa, M., Hollywood, K. A., Greenland-Bews, C., Takano, E., Rogers, S., & Breitling, R. (2019). Integrated Probabilistic Annotation: a bayesian-based annotation method for metabolomic profiles integrating biochemical connections, isotope patterns, and Adduct Relationships. Analytical Chemistry, 91(20), 12799–12807. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02354.
Directorate-General for Research and Innovation (European Commission). (2018). Turning FAIR into reality: final report and action plan from the European Commission expert group on FAIR data. Publications Office of the European Union. https://doi.org/10.2777/1524.
Du, X., Aristizabal-Henao, J. J., Garrett, T. J., Brochhausen, M., Hogan, W. R., & Lemas, D. J. (2022). A checklist for reproducible computational analysis in clinical Metabolomics Research. Metabolites, 12(1), https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010087.
Dührkop, K., Fleischauer, M., Ludwig, M., Aksenov, A. A., Melnik, A. V., Meusel, M., Dorrestein, P. C., Rousu, J., & Böcker, S. (2019). SIRIUS 4: a rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nature Methods, 16(4), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0344-8. Article 4.
Fiehn, O., Sumner, L. W., Rhee, S. Y., Ward, J., Dickerson, J., Lange, B. M., Lane, G., Roessner, U., Last, R., & Nikolau, B. (2007). Minimum reporting standards for plant biology context information in metabolomic studies. Metabolomics, 3(3), 195–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0068-0.
fillPeaks-methods: Integrate areas of missing peaks in xcms: LC-MS and GC-MS Data Analysis. (n.d.). Retrieved April 6, from https://rdrr.io/bioc/xcms/man/fillPeaks-methods.html
Fischer, D., Panse, C., & Laczko, E. (2022). cosmiq: Cosmiq - COmbining Single Masses Into Quantities (1.28.0). Bioconductor version: Release (3.14). https://doi.org/10.18129/B9.bioc.cosmiq
Franceschi, P., Mylonas, R., Shahaf, N., Scholz, M., Arapitsas, P., Masuero, D., Weingart, G., Carlin, S., Vrhovsek, U., Mattivi, F., & Wehrens, R. (2014). MetaDB a Data Processing Workflow in untargeted MS-Based Metabolomics experiments. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2, 72. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2014.00072.
Gatto, L., Gibb, S., & Rainer, J. (2021). MSnbase, efficient and elegant R-Based Processing and visualization of raw Mass Spectrometry Data. Journal of Proteome Research, 20(1), 1063–1069. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00313.
Georgeson, P., Syme, A., Sloggett, C., Chung, J., Dashnow, H., Milton, M., Lonsdale, A., Powell, D., Seemann, T., & Pope, B. (2019). Bionitio: demonstrating and facilitating best practices for bioinformatics command-line software. GigaScience, 8, giz109. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giz109.
Giacomoni, F., Le Corguillé, G., Monsoor, M., Landi, M., Pericard, P., Pétéra, M., Duperier, C., Tremblay-Franco, M., Martin, J. F., Jacob, D., Goulitquer, S., Thévenot, E. A., & Caron, C. (2015). Workflow4Metabolomics: a collaborative research infrastructure for computational metabolomics. Bioinformatics, 31(9), 1493–1495. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu813.
Goodacre, R., Broadhurst, D., Smilde, A. K., Kristal, B. S., Baker, J. D., Beger, R., Bessant, C., Connor, S., Capuani, G., Craig, A., Ebbels, T., Kell, D. B., Manetti, C., Newton, J., Paternostro, G., Somorjai, R., Sjöström, M., Trygg, J., & Wulfert, F. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics, 3(3), 231–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0081-3.
Goodman, S. N., Fanelli, D., & Ioannidis, J. P. A. (2016). What does research reproducibility mean? Science Translational Medicine, 8(341), 341ps12-341ps12.
Guo, J., Shen, S., Xing, S., & Huan, T. (2021). DaDIA: Hybridizing Data-Dependent and Data-Independent Acquisition Modes for Generating High-Quality Metabolomic Data.Analytical Chemistry, 93(4),2669–2677. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05022
Hao, L., Wang, J., Page, D., Asthana, S., Zetterberg, H., Carlsson, C., Okonkwo, O. C., & Li, L. (2018). Comparative evaluation of MS-based Metabolomics Software and its application to preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. Scientific Reports, 8(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27031-x.
Hasselbring, W., Carr, L., Hettrick, S., Packer, H., & Tiropanis, T. (2020). From FAIR research data toward FAIR and open research software. It - Information Technology, 62(1), 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1515/itit-2019-0040.
Heil, B. J., Hoffman, M. M., Markowetz, F., Lee, S. I., Greene, C. S., & Hicks, S. C. (2021). Reproducibility standards for machine learning in the life sciences. Nature Methods, 18(10), 1132–1135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01256-7.
Helmus, R., ter Laak, T. L., van Wezel, A. P., de Voogt, P., & Schymanski, E. L. (2021). patRoon: open source software platform for environmental mass spectrometry based non-target screening. Journal of Cheminformatics, 13(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-020-00477-w.
Huan, T., & Li, L. (2015a). Counting missing values in a metabolite-intensity data set for measuring the analytical performance of a metabolomics platform. Analytical Chemistry, 87(2), 1306–1313. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5039994.
Huan, T., & Li, L. (2015b). Quantitative metabolome analysis based on Chromatographic Peak Reconstruction in Chemical isotope labeling liquid chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 87(14), 7011–7016. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01434.
Huang, X., Chen, Y. J., Cho, K., Nikolskiy, I., Crawford, P. A., & Patti, G. J. (2014). X13CMS: Global Tracking of Isotopic Labels in untargeted metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 86(3), 1632–1639. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac403384n.
Huber, C., Nijssen, R., Mol, H., Philippe Antignac, J., Krauss, M., Brack, W., Wagner, K., Debrauwer, L., Vitale, M., Price, C. J., Klanova, E., Molina, J. G., Leon, B., Pardo, N., Fernández, O., Szigeti, S. F., Középesy, T., Šulc, S., Čupr, L., & Lommen, P., A (2022). A large scale multi-laboratory suspect screening of pesticide metabolites in human biomonitoring: from tentative annotations to verified occurrences. Environment International, 168, 107452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2022.107452.
Huber, F., Ridder, L., Verhoeven, S., Spaaks, J. H., Diblen, F., Rogers, S., & van der Hooft, J. J. J. (2021). Spec2Vec: improved mass spectral similarity scoring through learning of structural relationships. PLOS Computational Biology, 17(2), e1008724. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008724.
Huber, F., van der Burg, S., van der Hooft, J. J. J., & Ridder, L. (2021). MS2DeepScore: a novel deep learning similarity measure to compare tandem mass spectra. Journal of Cheminformatics, 13(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-021-00558-4.
Hughes, G., Cruickshank-Quinn, C., Reisdorph, R., Lutz, S., Petrache, I., Reisdorph, N., Bowler, R., & Kechris, K. (2014). MSPrep—Summarization, normalization and diagnostics for processing of mass spectrometry–based metabolomic data. Bioinformatics, 30(1), 133–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt589.
Hunter-Zinck, H., de Siqueira, A. F., Vásquez, V. N., Barnes, R., & Martinez, C. C. (2021). Ten simple rules on writing clean and reliable open-source scientific software. PLOS Computational Biology, 17(11), e1009481. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009481.
Ison, J., Ienasescu, H., Chmura, P., Rydza, E., Ménager, H., Kalaš, M., Schwämmle, V., Grüning, B., Beard, N., Lopez, R., Duvaud, S., Stockinger, H., Persson, B., Vařeková, R. S., Raček, T., Vondrášek, J., Peterson, H., Salumets, A., Jonassen, I., & Brunak, S. (2019). The bio.tools registry of software tools and data resources for the life sciences. Genome Biology, 20(1), 164. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1772-6.
Jaitly, N., Mayampurath, A., Littlefield, K., Adkins, J. N., Anderson, G. A., & Smith, R. D. (2009). Decon2LS: an open-source software package for automated processing and visualization of high resolution mass spectrometry data. Bmc Bioinformatics, 10(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-87.
Ji, H., Xu, Y., Lu, H., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Deep MS/MS-Aided structural-similarity scoring for unknown metabolite identification. Analytical Chemistry, 91(9), 5629–5637. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05405.
Ji, H., Zeng, F., Xu, Y., Lu, H., & Zhang, Z. (2017). KPIC2: an effective Framework for Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics using pure Ion Chromatograms. Analytical Chemistry, 89(14), 7631–7640. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01547.
Jiménez, R. C., Kuzak, M., Alhamdoosh, M., Barker, M., Batut, B., Borg, M., Capella-Gutierrez, S., Chue Hong, N., Cook, M., Corpas, M., Flannery, M., Garcia, L., Gelpí, J. L., Gladman, S., Goble, C., González Ferreiro, M., Gonzalez-Beltran, A., Griffin, P. C., Grüning, B., & Crouch, S. (2017). Four simple recommendations to encourage best practices in research software. F1000Research, 6, ELIXIR-876. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.11407.1
de Jonge, N. F., Louwen, J. R., Chekmeneva, E., Camuzeaux, S., Vermeir, F. J., Jansen, R. S., Huber, F., & van der Hooft, J. J. J. (2022). MS2Query: Reliable and Scalable MS2 Mass Spectral-based Analogue Search (p. 2022.07.22.501125). bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.22.501125
Kantz, E. D., Tiwari, S., Watrous, J. D., Cheng, S., & Jain, M. (2019). Deep neural networks for classification of LC-MS spectral peaks. Analytical Chemistry, 91(19), 12407–12413. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02983.
Karimzadeh, M., & Hoffman, M. M. (2018). Top considerations for creating bioinformatics software documentation. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 19(4), 693–699. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw134.
Kasalica, V., Schwämmle, V., Palmblad, M., Ison, J., & Lamprecht, A. L. (2021). APE in the Wild: Automated Exploration of Proteomics Workflows in the bio.tools Registry. Journal of Proteome Research, 20(4), 2157–2165. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00983.
Katz, D. S., Barker, M., Chue Hong, N. P., Castro, L. J., & Martinez, P. A. (2021, June 28). The FAIR4RS team: Working together to make research software FAIR. 2021 Collegeville Workshop on Scientific Software - Software Teams (Collegeville2021). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5037157
Katz, D. S., Gruenpeter, M., & Honeyman, T. (2021). Taking a fresh look at FAIR for research software. Patterns, 2(3), 100222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2021.100222.
Kuhl, C., Tautenhahn, R., Böttcher, C., Larson, T. R., & Neumann, S. (2012). CAMERA: an Integrated strategy for compound Spectra extraction and annotation of Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Data Sets. Analytical Chemistry, 84(1), 283–289. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac202450g.
Kutuzova, S., Colaianni, P., Röst, H., Sachsenberg, T., Alka, O., Kohlbacher, O., Burla, B., Torta, F., Schrübbers, L., Kristensen, M., Nielsen, L., Herrgård, M. J., & McCloskey, D. (2020). SmartPeak automates targeted and quantitative Metabolomics Data Processing. Analytical Chemistry, 92(24), 15968–15974. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03421
Lamprecht, A.-L., Garcia, L., Kuzak, M., Martinez, C., Arcila, R., Martin Del Pico,E., Dominguez Del Angel, V., van de Sandt, S., Ison, J., Martinez, P. A., McQuilton,P., Valencia, A., Harrow, J., Psomopoulos, F., Gelpi, J. L., Chue Hong, N., Goble,C., & Capella-Gutierrez, S. (2020). Towards FAIR principles for research software.Data Science, 3(1), 37–59. https://doi.org/10.3233/DS-190026
Lamprecht, A. L., Palmblad, M., Ison, J., Schwämmle, V., Manir, M. S. A., Altintas, I., Baker, C. J. O., Amor, A. B. H., Capella-Gutierrez, S., Charonyktakis, P., Crusoe, M. R., Gil, Y., Goble, C., Griffin, T. J., Groth, P., Ienasescu, H., Jagtap, P., Kalaš, M., Kasalica, V., & Wolstencroft, K. (2021). Perspectives on automated composition of workflows in the life sciences (10:897). F1000Research. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.54159.1
Lee, B. D. (2018). Ten simple rules for documenting scientific software. PLOS Computational Biology, 14(12), e1006561. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006561.
Leprevost, F. V., Barbosa, V. C., Francisco, E. L., Perez-Riverol, Y., & Carvalho, P. C. (2014). On best practices in the development of bioinformatics software. Frontiers in Genetics, 5, 199. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00199.
Li, B., Tang, J., Yang, Q., Li, S., Cui, X., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Xue, W., Li, X., & Zhu, F. (2017). NOREVA: normalization and evaluation of MS-based metabolomics data. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(W1), W162–W170. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx449.
Li, Z., Lu, Y., Guo, Y., Cao, H., Wang, Q., & Shui, W. (2018). Comprehensive evaluation of untargeted metabolomics data processing software in feature detection, quantification and discriminating marker selection. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1029, 50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.001.
Liberati, A., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gøtzsche, P. C., Ioannidis, J. P. A., Clarke, M., Devereaux, P. J., Kleijnen, J., & Moher, D. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. Bmj, 339, b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700.
Libiseller, G., Dvorzak, M., Kleb, U., Gander, E., Eisenberg, T., Madeo, F., Neumann, S., Trausinger, G., Sinner, F., Pieber, T., & Magnes, C. (2015). IPO: a tool for automated optimization of XCMS parameters. Bmc Bioinformatics, 16(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0562-8.
Liggi, S., Hinz, C., Hall, Z., Santoru, M. L., Poddighe, S., Fjeldsted, J., Atzori, L., & Griffin, J. L. (2018). KniMet: a pipeline for the processing of chromatography–mass spectrometry metabolomics data. Metabolomics, 14(4), 52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1349-5.
Liu, Q., Walker, D., Uppal, K., Liu, Z., Ma, C., Tran, V., Li, S., Jones, D. P., & Yu, T. (2020). Addressing the batch effect issue for LC/MS metabolomics data in data preprocessing. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 13856. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70850-0.
Lommen, A. (2009). MetAlign: Interface-Driven, Versatile Metabolomics Tool for Hyphenated full-scan Mass Spectrometry Data Preprocessing. Analytical Chemistry, 81(8), 3079–3086. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac900036d.
Loos, M. (2016). enviPick: Peak Picking for High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Data (1.5). https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=enviPick
Mahieu, N. G., Spalding, J. L., & Patti, G. J. (2016). Warpgroup: increased precision of metabolomic data processing by consensus integration bound analysis. Bioinformatics, 32(2), 268–275. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv564.
Malone, J., Brown, A., Lister, A. L., Ison, J., Hull, D., Parkinson, H., & Stevens, R. (2014). The Software Ontology (SWO): a resource for reproducibility in biomedical data analysis, curation and digital preservation. Journal of Biomedical Semantics, 5(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.1186/2041-1480-5-25.
Mayer, G., Montecchi-Palazzi, L., Ovelleiro, D., Jones, A. R., Binz, P. A., Deutsch, E. W., Chambers, M., Kallhardt, M., Levander, F., Shofstahl, J., Orchard, S., Vizcaíno, J. A., Hermjakob, H., Stephan, C., Meyer, H. E., Eisenacher, M., & HUPO-PSI Group. (2013). &. The HUPO proteomics standards initiative- mass spectrometry controlled vocabulary. Database: The Journal of Biological Databases and Curation, 2013, bat009. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bat009
Mayer, G., Müller, W., Schork, K., Uszkoreit, J., Weidemann, A., Wittig, U., Rey, M., Quast, C., Felden, J., Glöckner, F. O., Lange, M., Arend, D., Beier, S., Junker, A., Scholz, U., Schüler, D., Kestler, H. A., Wibberg, D., Pühler, A., & Turewicz, M. (2021). Implementing FAIR data management within the German Network for Bioinformatics infrastructure (de.NBI) exemplified by selected use cases. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 22(5), bbab010. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbab010.
Mendez, K. M., Pritchard, L., Reinke, S. N., & Broadhurst, D. I. (2019). Toward collaborative open data science in metabolomics using Jupyter Notebooks and cloud computing. Metabolomics, 15(10), 125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1588-0.
Menke, J., Roelandse, M., Ozyurt, B., Martone, M., & Bandrowski, A. (2020). The rigor and transparency Index Quality Metric for assessing Biological and Medical Science Methods. IScience, 23(11), 101698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101698.
Misra, B. B. (2018). New tools and resources in metabolomics: 2016–2017. ELECTROPHORESIS, 39(7), 909–923. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201700441.
Misra, B. B. (2021). New software tools, databases, and resources in metabolomics: updates from 2020. Metabolomics, 17(5), 49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01796-1.
Misra, B. B., Fahrmann, J. F., & Grapov, D. (2017). Review of emerging metabolomic tools and resources: 2015–2016. ELECTROPHORESIS, 38(18), 2257–2274. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201700110.
Misra, B. B., & Mohapatra, S. (2019). Tools and resources for metabolomics research community: a 2017–2018 update. ELECTROPHORESIS, 40(2), 227–246. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201800428.
Müller, E., Huber, C. E., Brack, W., Krauss, M., & Schulze, T. (2020). Symbolic aggregate approximation improves gap filling in high-resolution Mass Spectrometry Data Processing. Analytical Chemistry, 92(15), 10425–10432. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00899.
Olivon, F., Elie, N., Grelier, G., Roussi, F., Litaudon, M., & Touboul, D. (2018). MetGem Software for the generation of Molecular Networks based on the t-SNE algorithm. Analytical Chemistry, 90(23), 13900–13908. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03099.
O’Shea, K., & Misra, B. B. (2020). Software tools, databases and resources in metabolomics: updates from 2018 to 2019. Metabolomics, 16(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-020-01657-3.
Palarea-Albaladejo, J., Mclean, K., Wright, F., & Smith, D. G. E. (2018). MALDIrppa: quality control and robust analysis for mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics, 34(3), 522–523. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx628.
Palmblad, M., Lamprecht, A. L., Ison, J., & Schwämmle, V. (2019). Automated workflow composition in mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Bioinformatics, 35(4), 656–664. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty646.
Pang, Z., Chong, J., Zhou, G., de Lima Morais, D. A., Chang, L., Barrette, M., Gauthier, C., Jacques, P., Li, S., & Xia, J. (2021). MetaboAnalyst 5.0: narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(W1), W388–W396. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab382.
Pluskal, T., Castillo, S., Villar-Briones, A., & Orešič, M. (2010). MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. Bmc Bioinformatics, 11(1), 395. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-395.
Protsyuk, I., Melnik, A. V., Nothias, L. F., Rappez, L., Phapale, P., Aksenov, A. A., Bouslimani, A., Ryazanov, S., Dorrestein, P. C., & Alexandrov, T. (2018). 3D molecular cartography using LC-MS facilitated by Optimus and ’ili software. Nature Protocols, 13(1), 134–154. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2017.122.
Rainer, J., Vicini, A., Salzer, L., Stanstrup, J., Badia, J. M., Neumann, S., Stravs, M. A., Hernandes, V., Gatto, V., Gibb, L., S., & Witting, M. (2022). A modular and expandable ecosystem for Metabolomics Data Annotation in R. Metabolites, 12(2), https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020173. Article 2.
Ram, K. (2013). Git can facilitate greater reproducibility and increased transparency in science. Source Code for Biology and Medicine, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0473-8-7.
Referencing and citing content. (n.d.). GitHub Docs. Retrieved December 30, from https://ghdocs-prod.azurewebsites.net/en/repositories/archiving-a-github-repository/referencing-and-citing-content
Review checklist—JOSS documentation. (n.d.). Retrieved April 28, from https://joss.readthedocs.io/en/latest/review_checklist.html
RforMassSpectrometry. (n.d.). Retrieved January 14, from https://www.rformassspectrometry.org/
Ridder, L., van der Hooft, J. J. J., Verhoeven, S., de Vos, R. C. H., van Schaik, R., & Vervoort, J. (2012). Substructure-based annotation of high-resolution multistage MSn spectral trees. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 26(20), 2461–2471. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.6364.
Rocca-Serra, P., & Sansone, S. A. (2019). Experiment design driven FAIRification of omics data matrices, an exemplar. Scientific Data, 6(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0286-0.
Romano, J. D., & Moore, J. H. (2020). Ten simple rules for writing a paper about scientific software. PLOS Computational Biology, 16(11), e1008390. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008390.
Ross, D. H., Cho, J. H., Zhang, R., Hines, K. M., & Xu, L. (2020). LiPydomics: a Python Package for Comprehensive Prediction of lipid Collision Cross sections and Retention Times and Analysis of Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics Data. Analytical Chemistry, 92(22), 14967–14975. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02560.
Röst, H. L., Sachsenberg, T., Aiche, S., Bielow, C., Weisser, H., Aicheler, F., Andreotti, S., Ehrlich, H. C., Gutenbrunner, P., Kenar, E., Liang, X., Nahnsen, S., Nilse, L., Pfeuffer, J., Rosenberger, G., Rurik, M., Schmitt, U., Veit, J., Walzer, M., & Kohlbacher, O. (2016). OpenMS: a flexible open-source software platform for mass spectrometry data analysis. Nature Methods, 13(9), 741–748. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3959.
Ruttkies, C., Schymanski, E. L., Wolf, S., Hollender, J., & Neumann, S. (2016). MetFrag relaunched: incorporating strategies beyond in silico fragmentation. Journal of Cheminformatics, 8(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-016-0115-9.
Savoi, S., Arapitsas, P., Duchêne, É., Nikolantonaki, M., Ontañón, I., Carlin, S., Schwander, F., Gougeon, R. D., Ferreira, A. C. S., Theodoridis, G., Töpfer, R., Vrhovsek, U., Adam-Blondon, A. F., Pezzotti, M., & Mattivi, F. (2021). Grapevine and wine metabolomics-based guidelines for FAIR data and Metadata Management. Metabolites, 11(11), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11110757.
Schober, P., Boer, C., & Schwarte, L. A. (2018). Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 126(5), 1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864.
Seemann, T. (2013). Ten recommendations for creating usable bioinformatics command line software. GigaScience, 2(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-217X-2-15.
Senington, R., Pataki, B., & Wang, X. V. (2018). Using docker for factory system software management: experience report. Procedia CIRP, 72, 659–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.03.173.
Shen, X., Wang, R., Xiong, X., Yin, Y., Cai, Y., Ma, Z., Liu, N., & Zhu, Z. J. (2019). Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics. Nature Communications, 10(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09550-x.
Smith, C. A., Want, E. J., O’Maille, G., Abagyan, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). Matching, and Identification. Analytical Chemistry, 78(3), 779–787. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac051437y. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment,.
Snyder, M., Mias, G., Stanberry, L., & Kolker, E. (2014). Metadata Checklist for the Integrated Personal OMICS Study: Proteomics and Metabolomics experiments. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 18(1), 81–85. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2013.0148.
Spicer, R., Salek, R. M., Moreno, P., Cañueto, D., & Steinbeck, C. (2017). Navigating freely-available software tools for metabolomics analysis. Metabolomics: Official Journal of the Metabolomic Society, 13(9), 106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1242-7.
Stanstrup, J., Broeckling, C. D., Helmus, R., Hoffmann, N., Mathé, E., Naake, T., Nicolotti, L., Peters, K., Rainer, J., Salek, R. M., Schulze, T., Schymanski, E. L., Stravs, M. A., Thévenot, E. A., Treutler, H., Weber, R. J. M., Willighagen, E., Witting, M., & Neumann, S. (2019). The metaRbolomics Toolbox in Bioconductor and beyond. Metabolites, 9(10), https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100200. Article 10.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., Fan, T. W. M., Fiehn, O., Goodacre, R., Griffin, J. L., Hankemeier, T., Hardy, N., Harnly, J., Higashi, R., Kopka, J., Lane, A. N., Lindon, J. C., Marriott, P., Nicholls, A. W., & Viant, M. R. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics: Official Journal of the Metabolomic Society, 3(3), 211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2.
Tautenhahn, R., Patti, G. J., Rinehart, D., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). XCMS Online: a web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Analytical Chemistry, 84(11), 5035–5039. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac300698c.
Teo, G., Chew, W. S., Burla, B. J., Herr, D., Tai, E. S., Wenk, M. R., Torta, F., & Choi, H. (2020). MRMkit: Automated Data Processing for large-scale targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 92(20), 13677–13682. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03060.
Tsugawa, H., Cajka, T., Kind, T., Ma, Y., Higgins, B., Ikeda, K., Kanazawa, M., VanderGheynst, J., Fiehn, O., & Arita, M. (2015). MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nature Methods, 12(6), 523–526. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3393.
Tsugawa, H., Kind, T., Nakabayashi, R., Yukihira, D., Tanaka, W., Cajka, T., Saito, K., Fiehn, O., & Arita, M. (2016). Hydrogen rearrangement rules: computational MS/MS fragmentation and structure elucidation using MS-FINDER Software. Analytical Chemistry, 88(16), 7946–7958. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00770.
Uppal, K., Soltow, Q. A., Strobel, F. H., Pittard, W. S., Gernert, K. M., Yu, T., & Jones, D. P. (2013). xMSanalyzer: automated pipeline for improved feature detection and downstream analysis of large-scale, non-targeted metabolomics data. Bmc Bioinformatics, 14(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-15.
Uppal, K., Walker, D. I., & Jones, D. P. (2017). xMSannotator: an R Package for Network-Based annotation of high-resolution Metabolomics Data. Analytical Chemistry, 89(2), 1063–1067. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01214.
van de Sandt, S., Nielsen, L. H., Ioannidis, A., Muench, A., Henneken, E., Accomazzi, A., Bigarella, C., Lopez, J. B. G., & Dallmeier-Tiessen, S. (2019). Practice meets Principle: Tracking Software and Data Citations to Zenodo DOIs (arXiv:1911.00295). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1911.00295
Vesteghem, C., Brøndum, R. F., Sønderkær, M., Sommer, M., Schmitz, A., Bødker, J. S., Dybkær, K., El-Galaly, T. C., & Bøgsted, M. (2020). Implementing the FAIR Data Principles in precision oncology: review of supporting initiatives. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 21(3), 936–945. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbz044.
Vitale, C. M., Lommen, A., Huber, C., Wagner, K., Garlito Molina, B., Nijssen, R., Price, E. J., Blokland, M., van Tricht, F., Mol, H. G. J., Krauss, M., Debrauwer, L., Pardo, O., Leon, N., Klanova, J., & Antignac, J. P. (2022). Harmonized Quality Assurance/Quality control provisions for nontargeted measurement of urinary pesticide biomarkers in the HBM4EU Multisite SPECIMEn Study. Analytical Chemistry, 94(22), 7833–7843. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00061.
Weber, R. J. M., & Viant, M. R. (2010). MI-Pack: increased confidence of metabolite identification in mass spectra by integrating accurate masses and metabolic pathways. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 104(1), 75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2010.04.010.
Wilkinson, M. D., Dumontier, M., Aalbersberg, I. J., Appleton, G., Axton, M., Baak, A., Blomberg, N., Boiten, J. W., da Silva Santos, L. B., Bourne, P. E., Bouwman, J., Brookes, A. J., Clark, T., Crosas, M., Dillo, I., Dumon, O., Edmunds, S., Evelo, C. T., Finkers, R., & Mons, B. (2016). The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data, 3(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18
Wilkinson, M. D., Dumontier, M., Sansone, S. A., Bonino da Silva Santos, L. O., Prieto, M., Batista, D., McQuilton, P., Kuhn, T., Rocca-Serra, P., Crosas, M., & Schultes, E. (2019). Evaluating FAIR maturity through a scalable, automated, community-governed framework. Scientific Data, 6(1), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0184-5.
Wolf, M., Logan, J., Mehta, K., Jacobson, D., Cashman, M., Walker, A. M., Eisenhauer, G., Widener, P., & Cliff, A. (2021). Reusability First: Toward FAIR Workflows. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (CLUSTER), 444–455. https://doi.org/10.1109/Cluster48925.2021.00053
Yu, T., Park, Y., Johnson, J. M., & Jones, D. P. (2009). ApLCMS—adaptive processing of high-resolution LC/MS data. Bioinformatics, 25(15), 1930–1936. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp291.
Zhang, X., Li, Q., Xu, Z., & Dou, J. (2020). Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in health and medical science: a systematic review. RSC Advances, 10(6), 3092–3104. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA08985C.
Zhao, J., Gómez-Pérez, J., Belhajjame, K., Klyne, G., García-Cuesta, E., Garrido, A., Hettne, K., Roos, M., Roure, D. D., & Goble, C. (2012). Why workflows break—Understanding and combating decay in Taverna workflows. 2012 IEEE 8th International Conference on E-Science. https://doi.org/10.1109/eScience.2012.6404482
Zheng, C. L., Ratnakar, V., Gil, Y., & McWeeney, S. K. (2015). Use of semantic workflows to enhance transparency and reproducibility in clinical omics. Genome Medicine, 7(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-015-0202-y.
Zhou, B., Xiao, J. F., Tuli, L., & Ressom, H. W. (2012). LC-MS-based metabolomics. Molecular BioSystems, 8(2), 470–481. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1mb05350g.
Zhou, R., Tseng, C. L., Huan, T., & Li, L. (2014). IsoMS: automated processing of LC-MS data generated by a chemical isotope labeling metabolomics platform. Analytical Chemistry, 86(10), 4675–4679. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5009089.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Biswapriya Misra, Ph.D., for his constructive remarks and useful suggestions for the study. The authors also sincerely thank Bailey Ballard and Jianming (Jennifer) Wang for their help in the process of title-abstract screening. We would like to express a special thank to all software authors that took the time out of their busy schedule to respond our emails and provide thoughtful feedback regarding the annotation of software functions.
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported by the University of Florida Informatics Institute Fellowship Program. Research reported in this publication was also supported by Southeast Center for Integrated Metabolomics at the University of Florida, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (K01DK115632), the University of Florida Clinical and Translational Science Institute (UL1TR001427). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views the University of Florida Informatics Institute, Southeast Center for Integrated Metabolomics at the University of Florida, University of Florida Clinical and Translational Science Institute, or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XD conceived the idea, designed the study, participated in the paper review, participated in software evaluation, participated in designing software evaluation criteria and assigning criteria to corresponding FAIR4RS categories as a major contributor, drafted the original version of the categorization and description of LC-HRMS metabolomics data processing steps, performed and programmed for all analysis and visualization, interpreted results, prepared the original draft, and revised the manuscript. FD participated in the paper review and software evaluation. HY provided literature search terms and databases, participated in designing software evaluation criteria and assigned criteria to corresponding FAIR4RS categories. TJL provided expertise regarding study design, revised the categorization and description of LC-HRMS metabolomics data processing steps, and revised the manuscript. MAD participated in designing software evaluation criteria and assigning criteria to corresponding FAIR4RS categories. ML provided expertise regarding statistical analysis. WRH revised the manuscript. MB revised the manuscript. DJL conceived the idea, provided expertise regarding study design, provided expertise regarding data analysis and visualization, interpreted results, and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Dastmalchi, F., Ye, H. et al. Evaluating LC-HRMS metabolomics data processing software using FAIR principles for research software. Metabolomics 19, 11 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-01974-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-023-01974-3