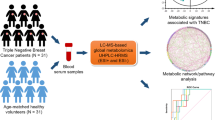
Abstract
Introduction
Metabolomics has recently emerged as a tool for understanding comprehensive tumor-associated metabolic dysregulation. However, only limited application of this technology has been introduced into the clinical setting of breast cancer.
Objectives
The aim of this study was to determine the feasibility of metabolome analysis using routine CNB/VAB samples from breast cancer patients and to elucidate metabolic signatures using metabolic profiling.
Methods
After breast cancer screenings, 20 consecutive patients underwent CNB/VAB, and diagnosed with benign, DCIS and IDC by histology. Metabolome analysis was performed using CE–MS. Differential metabolites were then analyzed and evaluated with MetaboAnalyst 4.0.
Results
We measured 116-targeted metabolites involved in energy metabolism. Principal component analysis and unsupervised hierarchical analysis revealed a distinct metabolic signature unique to namely “pure” IDC samples, whereas that of DCIS was similar to benign samples. Pathway analysis unveiled the most affected pathways of the “pure” IDC metabotype, including “pyrimidine,” “alanine, aspartate, and glutamate” and “arginine and proline” pathways.
Conclusions
Our proof-of-concept study demonstrated that CE–MS-based CNB/VAB metabolome analysis is feasible for implementation in routine clinical settings. The most affected pathways in this study may contribute to improved breast cancer stratification and precision medicine.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aittokallio, T., & Schwikowski, B. (2006). Graph-based methods for analysing networks in cell biology. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 7(3), 243–255. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbl022.
Allred, D. C. (2010). Ductal carcinoma in situ: Terminology, classification, and natural history. Journal of the National Cancer Institute Monographs, 2010(41), 134–138. https://doi.org/10.1093/jncimonographs/lgq035.
Amelio, I., Cutruzzolá, F., Antonov, A., Agostini, M., & Melino, G. (2014). Serine and glycine metabolism in cancer. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 39(4), 191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.004.
Brown, K. K., Spinelli, J. B., Asara, J. M., & Toker, A. (2017). Adaptive reprogramming of de novopyrimidine synthesis is a metabolic vulnerability in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Discovery, 7(4), 391–399. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0611.
Casasent, A. K., Schalck, A., Gao, R., Sei, E., Long, A., Pangburn, W., et al. (2018). Multiclonal invasion in breast tumors identified by topographic single cell sequencing. Cell, 172(1–2), 205–217.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.007.
Chong, J., & Xia, J. (2018). MetaboAnalystR: An R package for flexible and reproducible analysis of metabolomics data. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 34(24), 4313–4314. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty528.
Ehinger, J. K., Piel, S., Ford, R., Karlsson, M., Sjövall, F., Frostner, E. Å., et al. (2016). Cell-permeable succinate prodrugs bypass mitochondrial complex I deficiency. Nature Communications, 7(1), 12317. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12317.
Erbas, B., Provenzano, E., Armes, J., & Gertig, D. (2006). The natural history of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: A review. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 97(2), 135–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9101-z.
Hirayama, A., Kami, K., Sugimoto, M., Sugawara, M., Toki, N., Onozuka, H., et al. (2009). Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Cancer Research, 69(11), 4918–4925. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4806.
Islami, F., Siegel, R. L., & Jemal, A. (2017). Global cancer in women: Burden and trends. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention, 26(4), 444–457. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0858.
Kami, K., Fujimori, T., Sato, H., Sato, M., Yamamoto, H., Ohashi, Y., et al. (2013). Metabolomic profiling of lung and prostate tumor tissues by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Metabolomics, 9(2), 444–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0452-2.
Kaste, S. C., Snyder, S. E., Metzger, M. L., Sandlund, J. T., Howard, S. C., Krasin, M., et al. (2017). Comparison of11C-methionine and18F-FDG PET/CT for staging and follow-up of pediatric lymphoma. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 58(3), 419–424. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.178640.
Katz, S. J., Jagsi, R., & Morrow, M. (2018). Reducing overtreatment of cancer with precision medicine. JAMA, 319(11), 1091. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.0018.
Koppenol, W. H., Bounds, P. L., & Dang, C. V. (2011). Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nature Reviews Cancer, 11(5), 325–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3038.
Kremer, J. C., Prudner, B. C., Lange, S. E. S., Bean, G. R., Schultze, M. B., Brashears, C. B., et al. (2017). Arginine deprivation inhibits the Warburg effect and upregulates glutamine anaplerosis and serine biosynthesis in ASS1-deficient cancers. Cell Reports, 18(4), 991–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.077.
Lane, A. N., & Fan, T. W. M. (2015). Regulation of mammalian nucleotide metabolism and biosynthesis. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(4), 2466–2485. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv047.
Loayza-Puch, F., Rooijers, K., Buil, L. C. M., Zijlstra, J., Vrielink, J. F. O., Lopes, R., et al. (2016). Tumour-specific proline vulnerability uncovered by differential ribosome codon reading. Nature, 530(7591), 490–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16982.
Moriya, T., Kasami, M., Akiyama, F., Ichihara, S., Kurosumi, M., Tsuda, H., et al. (2000). A proposal for the histopathological diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Breast Cancer, 7(4), 321–325.
Ramautar, R., Somsen, G. W., & de Jong, G. J. (2016). CE-MS for metabolomics: Developments and applications in the period 2014-2016. Electrophoresis, 38(1), 190–202. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201600370.
Sato, K., Miyashita, M., Ishida, T., Suzuki, A., Tada, H., Watanabe, G., et al. (2016). Prognostic significance of the progesterone receptor status in Ki67-high and -low luminal B-like HER2-negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer, 23(2), 310–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-014-0575-6.
Shah, C., Wobb, J., Manyam, B., Kundu, N., Arthur, D., Wazer, D., et al. (2016). Management of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. JAMA Oncology, 2(8), 1083–1088. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.0525.
Soga, T., Ikeda, S., Ishikawa, T., Robert, M., & Nishioka, T. (2006). Differential metabolomics reveals ophthalmic acid as an oxidative stress biomarker indicating hepatic glutathione consumption. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(24), 16768–16776. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M601876200.
Soga, T., Soga, T., Ohashi, Y., Ohashi, Y., Ueno, Y., Ueno, Y., et al. (2003). Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Journal of Proteome Research, 2(5), 488–494.
Wishart, D. S. (2016). Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 15(7), 473–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.32.
Xia, J., & Sinelnikov, I. V. (2015). MetaboAnalyst 3.0–making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(W1), W251–W257. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv380.
Xia, J., & Wishart, D. S. (2011). Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nature Protocols, 6(6), 743–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.319.
Yoon, H., Yoon, D., Yun, M., Choi, J. S., Park, V. Y., Kim, E.-K., et al. (2016). Metabolomics of breast cancer using high-resolution magic angle spinning magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Correlations with 18F-FDG Positron emission tomography-computed tomography, dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted imaging MRI. PLoS ONE, 11(7), e0159949. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159949.
Zheng, Z.-G., Xu, H., Suo, S.-S., Xu, X.-L., Ni, M.-W., Gu, L.-H., et al. (2016). The essential role of H19 contributing to cisplatin resistance by regulating glutathione metabolism in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26093.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research Grants from the Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NH-S and TI conceived the study. NH-S and TS contributed to the study design. NH-S, HT, MM, GW, YH, AS, TS, AS and TI carried out the sample collections. NH-S, MH and TS performed the data analysis. NH-S, MH and TI drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest in relation to this manuscript for any of the authors listed above.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harada-Shoji, N., Soga, T., Tada, H. et al. A metabolic profile of routine needle biopsies identified tumor type specific metabolic signatures for breast cancer stratification: a pilot study. Metabolomics 15, 147 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1610-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1610-6