Abstract
Introduction
Genotype and metabolomic variation are important for bacterial survival and adaptation to environmental changes.
Objectives
In this study, we compared the relationship among Klebsiella pneumoniae strains based on their genotypic and metabolic profiles. In addition, we also evaluated the association of the relationship with beta-lactamase production.
Methods
A total of 53 K. pneumoniae strains isolated in 2013–2014 from a tertiary teaching hospital in Malaysia were subjected to antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) via disk diffusion method and beta-lactamase production confirmation. The bacterial strains were also typed genotypically and metabolically via REP-PCR and 1H-NMR spectroscopy respectively. The concordance of the matrices derived based on genotypic and metabolic characterization was measured based on Spearman’s rank correlation.
Results
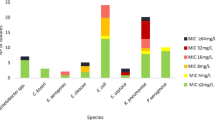
Spearman’s correlation rank showed that there is a weak but significant negative correlation between the genetic fingerprints and metabolic profiles of K. pneumoniae. Specifically, K. pneumoniae strains were clustered into five major clusters based on REP-PCR where most of the carbapenem resistant K. pneumoniae (CRKP) strains made up the major cluster. In contrast, metabolic patterns of the three groups (i.e. CRKP, extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing K. pneumoniae (ESBL), susceptible) of K. pneumoniae were clearly differentiated on PLS-DA score plots derived from 1H-NMR spectroscopy.
Conclusion
Overall, this study showed that metabolomic profiling using 1H-NMR spectroscopy is able to discriminate K. pneumoniae strains based on their beta-lactamase production status.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, N., Hashim, R., Shukor, S., Khalid, K. N. M., Shamsudin, F., & Hussin, H. (2013). Characterization of the first isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae carrying New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase and other extended spectrum beta-lactamase genes fr Malaysia. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 62, 804–806. doi:10.1099/Jmm.0.050781-0.
Al-Marzooq, F., Yusof, M. Y. M., & Tay, S. T. (2015). Molecular analysis of antibiotic resistance determinants and plasmids in Malaysian isolates of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE, 10(7), e0133654. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0133654.
Bratu, S., Landman, D., Haag, R., Recco, R., Eramo, A., Alam, M., et al. (2005). Rapid spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in New York City: A new threat to our antibiotic armamentarium. Archives of Internal Medicine, 165, 1430–1435. doi:10.1001/archinte.165.12.1430.
Bundy, J. G., Willey, T. L., Castell, R. S., Ellar, D. J., & Brindle, K. M. (2005). Discrimination of pathogenic clinical isolates and laboratory strains of Bacillus cereus by NMR-based metabolomic profiling. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 242, 127–136. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2004.10.048.
Casadesus, J., & Low, D. A. (2013). Programmed heterogeneity: Epigenetic mechanisms in bacteria. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(20), 13929–13935. doi:10.1074/jbc.R113.472274.
Cascioferro, S., & Schillaci, D. (2014). The future of antibiotic: from the magic bullet to the smart bullet. Microbial & Biochemical Technology, 6(5), 1000e118. doi:10.4172/1948-5948.1000e118.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Office of the Associate Director for Communication, Digital Media Branch, Division of Public Affairs. (2013). Antibiotic resistance threats in the US. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved May 21, 2016, from http://www.cdc.gov/features/AntibioticResistanceThreats/index.html.
Cepni, E., & Gürel, F. (2012). Variation in extragenic repetitive DNA sequences in Pseudomonas syringae and potential use of modified REP primers in identification of closely related isolates. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 35(3), 650–656. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572012005000040.
Chen, P., Seth, A. K., Abercrombie, J. J., Mustoe, T. A., & Leung, K. P. (2014). Activity of imipenem against Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 58(2), 1208–1213. doi:10.1128/AAC.01353-13.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. (2016). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 26th edn. CLSI supplement M100S, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
Ding, Y., Liu, X., Chen, F., Di, H., Xu, B., Zhou, L., et al. (2014). Metabolic sensor governing bacteria virulence Staphlococcus aureus. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(46), E4981–E4990. doi:10.1073/pnas.1411077111.
Fang, H., Ataker, F., Hedin, G., & Dornbusch, K. (2008). Molecular epidemiology of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases among Escherichia coli isolates collected in a Swedish hospital and its associated health care facilities from 2001 to 2006. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 46(2), 707–712. doi:10.1128/Jcm.01943-07.
Fiehn, O. (2002). Metabolomics: The link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Molecular Biology, 48, 155–171.
Foster, P. L. (2005). Stress responses and genetic variation in bacteria. Mutation Research, 569, 3–11. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.07.017.
Fuchs, T. M., Eisenreich, W., Heesemann, J., & Goeble, W. (2011). Metabolic adaptation of human pathogenic and unrelated nonpathogenic bacteria to extra- and intracellular habitats. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 36(2), 435–462. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00301.x.
Gibney, E. R., & Nolan, C. M. (2010). Epigenetics and gene expression. Heredity, 105(1), 4–13. doi:10.1038/hdy.2010.54.
Guo, L., An, J. N., Ma, Y. N., Ye, L. Y., Luo, Y. P., Tao, C. M., et al. (2016a). Nosocomial outbreak of OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese Hospital: Clonal transmission of ST147 and ST383. PLoS ONE, 11(8), e0160754. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0160754.
Guo, Y. M., Zhou, H. J., Qin, L. Y., Pang, Z. Z., Qin, T., Ren, H. Y., et al. (2016b). Frequency, antimicrobial resistance and genetic diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in food samples. PLoS ONE, 11(4), e0153561. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0153561.
Halouska, S., Zhang, B., Gaupp, R., Lei, S., Snell, E., Fenton, R. J., et al. (2013). Revisiting protocols for the NMR analysis of bacterial metabolomes. Journal of Integrated OMICS, 3(2), 120–137. doi:10.5584/jiomics.v3i2.139.
Hamzan, N. I., Yean, C. Y., Rahman, R. A., Hasan, H., & Rahman, Z. A. (2015). Detection of blaIMP4 and blaNDM1 harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a university hospital in Malaysia. Emerging Health Threats Journal, 8, 26011. doi:10.3402/ehtj.v8.26011.
Helmi, U. M., Desa, M. N. M., Taib, N. M., Jamaluddin, T. Z. M. T., & Masri, S. N. (2016). Multiple ambler class A ESBL genes among Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a Malaysian district hospital. Tropical Biomedicine, 33(1), 109–119.
Jacobs, D. M., Deltimple, N., van Velzen, E., van Dorsten, F. A., Bingham, M., Vaughan, E. E., et al. (2008). (1)H-NMR metabolite profiling of feces as a tool to assess the impact of nutrition on the human microbiome. NMR in Biomedicine, 21, 615–626. doi:10.1002/nbm.1233.
Kane, A. L., Brutinel, E. D., Joo, H., Maysonet, R., VanDrisse, C. M., Kotloski, N. J., et al. (2016). Formate metabolism in Shewanella oneidensis generates proton motive force and prevents growth without an electron acceptor. Journal of Bacteriology, 198(8), 1337–1346. doi:10.1128/JB.00927-15.
Korvin, D., Graydon, C., McNeil, L., & Mroczek, M. (2014). Banding profile of Rep-PCR experiments differs with varying extension times and annealing temperatures. Journal of Experimental Microbiology and Immunology, 18, 146–149.
Lee, M. Y., Ko, K. S., Kang, C. I., Chung, D. R., Peck, K. R., & Song, J. H. (2011). High prevalence of CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in Asian countries: Diverse clones and clonal dissemination. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 38, 160–163. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.03.020.
Li, J., Huang, C., Zheng, D., Wang, Y., & Yuan, Z. (2012). CcpA-mediated enhancement of sugar and amino acid metabolism in Lysinibacillus sphaericus by NMR-based metabolomics. Journal of Proteome Research, 11, 4654–4661. doi:10.1021/pr300469v.
Lina, T. T., Khajanchi, B. K., Azmi, I. J., Islam, M. A., Mahmood, B., Akter, M., et al. (2014). Phenotypic and molecular characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE, 9(10), e108735. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0108735.
Lobel, L., & Herskovits, A. A. (2016). Systems level analyses reveal multiple regulatory activities of CodY controlling metabolism, motility and virulence Listeria monocytogenes. PLoS Genetics, 12(2), e1005870. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005870.
Louis, P., Scott, K. P., Duncan, S. H., & Flint, H. J. (2007). Understanding the effects of diet on bacterial metabolism in the large intestine. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 102, 1197–1208. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03322.x.
Lu, W., Du, J., Schwarzer, N. J., Gerbig-Smentek, E., Einsle, O., & Andrade, S. L. A. (2012). The formate channel FocA exports the products of mixed-acid fermentation. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(3), 13254–13259. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204201109.
Martin, F. P. J., Sprenger, N., Yap, I. K. S., Wang, Y. L., Bibiloni, R., Rochat, F., et al. (2009). Panorganismal gut microbiome-host metabolic crosstalk. Journal of Proteome Research, 8(4), 2090–2105. doi:10.1021/pr801068x.
Mohsen, S. M. Y., Hamzah, H. A., Al-Deen, M. M. I., & Baharudin, R. (2016). Antimicrobial susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli with extended-spectrum-lactamase associated genes in Hospital Tengku Ampuan Afzan, Kuantan, Pahang. The Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, 23(2), 14–20.
Navarro Llorens, J. M., Tormo, A., & Martinez-Garcia, E. (2010). Stationary phase in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 34(4), 476–495. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00213.x.
Navia, M. M., Capitano, L., Ruiz, J., Vargas, M., Urassa, H., Schellemberg, D., et al. (1999). Typing and characterization of mechanisms of resistance of Shigella spp. isolated from feces of children under 5 years of age from Ifakara, Tanzania. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 37(10), 3113–3117.
Odén, A., & Wedel, H. (1975). Arguments for Fisher’s permutation test. The Annals of Statistics, 3(2), 518–520.
Parter, M., Kashtan, N., & Alon, U. (2007). Environmental variability and modularity of bacterial metabolic networks. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 7(169), 1–8. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-169.
Rampadarath, S., Puchooa, D., & Bal, S. (2015). Repetitive element palindromic PCR (rep-PCR) as a genetic tool to study interspecific diversity in Euphorbiaceae family. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 18, 412–417. doi:10.1016/j.ejbt.2015.09.003.
Richards, C. L., Bossdorf, O., & Pigliucci, M. (2010). What role does heritable epigenetic variation play in phenotypic evolution? BioScience, 60(3), 232–237. doi:10.1525/bio.2010.60.3.9.
Rohmer, L., Hocquet, D., & Miller, S. I. (2011). Are pathogenic bacteria just looking for food? Metabolism and microbial pathogenesis. Trends in Microbiology, 19(7), 341–348. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2011.04.003.
Sawers, R. G., & Clark, D. P. (2004). Fermentative pyruvate and acetyl-coenzyme A metabolism. EcoSal Plus, 1(1). doi:10.1128/ecosalplus.3.5.3.
Smits, W. K., Kuipers, O. P., & Veening, J. W. (2006). Phenotypic variation in bacteria: The role of feedback regulation. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 4(4), 259–271. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1381.
Somerville, G. A., & Proctor, R. A. (2009). At the crossroads of bacterial metabolism and virulence factor synthesis Staphylococci. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 73(2), 233–248. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00005-09.
Spencer, S., Gugliotta, A., Godecke, N., Hauser, H., & Wirth, D. (2016). Epigenetic modulations rendering cell-to-cell variability and phenotypic metastability. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 43(8), 503–511. doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2016.05.008.
Teh, C. S. J., Thong, K. L., Osawa, R., & Chue, K. H. (2011). Comparative PCR-based fingerprinting of Vibrio cholerae isolated in Malaysia. Journal of General Applied Microbiology, 57(1), 19–26.
Wilharm, G., & Heider, C. (2014). Interrelationship between type three secretion system and metabolism in pathogenic bacteria. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 4(150), 1–10. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2014.00150.
Wolfe, A. J. (2005). The acetate switch. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 69(1), 12–50. doi:10.1128/MMBR.69.1.12-50.2005.
Wong, M. S., Wu, S., Causey, T. B., Bennett, G. N., & San, K. Y. (2008). Reduction of acetate accumulation in Escherichia coli cultures for increased recombinant protein production. Metabolic Engineering, 10(2), 97–108. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2007.10.003.
Xu, Y. L., Gu, B., Huang, M., Liu, H. Y., Xu, T., Xia, W. Y., et al. (2015). Epidemiology of carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) during 2000–2012 in Asia. Journal of Thoracic Disease, 7(3), 376–385. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.12.33.
Yap, I. K., Kho, M. T., Lim, S. H., Ismail, N. H., Yam, W. K., & Chong, C. W. (2015). Acclimatisation-induced stress influenced host metabolic and gut microbial composition change. Molecular Biosystems, 11(1), 297–306. doi:10.1039/c4mb00463a.
Yap, I. K., Li, J. V., Saric, J., Martin, F. P., Davies, H., Wang, Y., et al. (2008). Metabonomic and microbiological analysis of the dynamic effect of vancomycin-induced gut microbiota modification in the mouse. Journal of Proteome Research, 7(9), 3718–3728. doi:10.1021/pr700864x.
Yap, I. K. S., Angley, M., Veselkov, K. A., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2010). Urinary metabolic phenotyping differentiates children with autism from their unaffected siblings and age-matched controls. Journal of Proteome Research, 9(6), 2996–3004. doi:10.1021/pr901188e.
Zhang, X., Jantama, K., Shanmugam, K. T., & Ingram, L. O. (2009). Reengineering Escherichia coli for succinate production in mineral salts medium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(24), 7807–7813. doi:10.1128/AEM.01758-09.
Funding
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) from the Ministry of Education, Malaysia (Grant Number: FP023-2014A), University of Malaya Research Grant (UMRG) from University of Malaya (Grant Number: RP014B-14HTM) and Postgraduate Research Grant (PPP) from University of Malaya (Grant Number: PG028-2014B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ye Mun Low, Ivan Kok Seng Yap, Kartini Abdul Jabar, Mohd Yasim Md Yusof, Chun Wie Chong and Cindy Shuan Ju Teh declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11306_2017_1201_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 1 Mean growth profiles (mean ± standard deviation) of the three groups of K. pneumoniae; CRKP, ESBL and susceptible. (TIF 143 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Low, Y.M., Yap, I.K.S., Abdul Jabar, K. et al. Genotypic and metabolic approaches towards the segregation of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains producing different antibiotic resistant enzymes. Metabolomics 13, 65 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1201-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1201-3