Abstract
Introduction
The metabolic alterations accompanying the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are complex, not coherently understood and only partially represented by conventional clinical tests like the oral glucose tolerance test. Changes in plasma metabolite concentrations preceding insulin resistance or overt T2DM may help understand the etiology of metabolic disorders and they are potential predictive risk markers.
Objectives
Here, we describe a non-targeted metabolomics platform based on UPLC-UHR-QToF-MS(/MS) for the assessment of plasma non-polar metabolites.
Methods
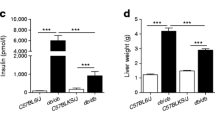
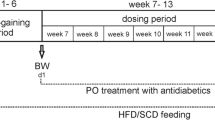
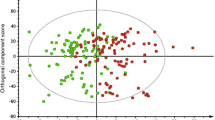
This method was applied to a longitudinal mouse obesity study comparing mice on control and high fat diet (HFD), respectively. Plasma metabolites were assessed 2, 4, 8 and 16 weeks after initiation of feeding. Multivariate analysis of the metabolite dataset showed clear differentiation of the feeding groups after 8 weeks when the HFD-fed mice exhibited clear signs of insulin resistance.
Results
The discrimination of the groups was due to changes in various metabolic pathways including, among others, glycerophospholipid, sphingolipid and cholesterol metabolism.
Conclusion
From 81 compounds with a p-value lower than 0.05, a total of 19 metabolites could be putatively identified due to their accurate mass, isotope and fragmentation pattern. Thirteen of these observed metabolites are known key metabolites to diabetes or its secondary diseases like diabetic nephropathy and neuropathy (Meiss, Werner, John, Scheja, Herbach, Heeren, Fischer 2015). The compounds putatively identified here may provide valuable starting points for further investigations and developments of clinical diagnostics and prediagnostics for T2DM and related diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrutkar, M., et al. (2015). Genetic disruption of protein kinase stk25 ameliorates metabolic defects in a diet-induced type 2 diabetes model. Diabetes, 64, 2791–2804. doi:10.2337/db15-0060.
An, Y., et al. (2013). High-fat diet induces dynamic metabolic alterations in multiple biological matrices of rats. Journal of Proteome Research, 12, 3755–3768. doi:10.1021/pr400398b.
Bartelt, A., et al. (2013). Effects of adipocyte lipoprotein lipase on de novo lipogenesis and white adipose tissue browning. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1831, 934–942. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.11.011.
Cao, H., Gerhold, K., Mayers, J. R., Wiest, M. M., Watkins, S. M., & Hotamisligil, G. S. (2008). Identification of a lipokine, a lipid hormone linking adipose tissue to systemic metabolism. Cell, 134, 933–944. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.048.
Dutta, T., et al. (2012). Concordance of changes in metabolic pathways based on plasma metabolomics and skeletal muscle transcriptomics in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, 61, 1004–1016. doi:10.2337/db11-0874.
Eisinger, K., Liebisch, G., Schmitz, G., Aslanidis, C., Krautbauer, S., & Buechler, C. (2014). Lipidomic analysis of serum from high fat diet induced obese mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15, 2991–3002. doi:10.3390/ijms15022991.
Godzien, J., et al. (2011). Metabolomic approach with LC-QTOF to study the effect of a nutraceutical treatment on urine of diabetic rats. Journal of Proteome Research, 10, 837–844. doi:10.1021/pr100993x.
Guo, X., et al. (2012). Palmitoleate induces hepatic steatosis but suppresses liver inflammatory response in mice. PLoS One, 7, e39286. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039286.
Ha, C. Y., et al. (2011). The association of specific metabolites of lipid metabolism with markers of oxidative stress, inflammation and arterial stiffness in men with newly diagnosed type 2 Diabetes. Clinical Endocrinology (Oxf). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04244.x.
Hotamisligil, G. S. (2006). Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature, 444, 860–867. doi:10.1038/nature05485.
Huang, Q., et al. (2011). Method for liver tissue metabolic profiling study and its application in type 2 diabetic rats based on ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B, 879, 961–967. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.03.009.
IDF (2015). IDF Diabetes Atlas. 7th Edition.
Kim, H. J., et al. (2011). Metabolomic analysis of livers and serum from high-fat diet induced obese mice. Journal of Proteome Research, 10, 722–731.
Kleemann, R., et al. (2010). Time-resolved and tissue-specific systems analysis of the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. PLoS One, 5, e8817. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008817.
Laguzzi, F., et al. (2016). Cross-sectional relationships between dietary fat intake and serum cholesterol fatty acids in a Swedish cohort of 60-year-old men and women. Journal of human nutrition and dietetics, 29, 325–337. doi:10.1111/jhn.12336.
Lappas, M., et al. (2015). The prediction of type 2 diabetes in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus using lipidomics. Diabetologia, 58, 1436–1442. doi:10.1007/s00125-015-3587-7.
Li, Y., Li, J. J., Wen, X. D., Pan, R., He, Y. S., & Yang, J. (2014). Metabonomic analysis of the therapeutic effect of Potentilla discolor in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Molecular BioSystems, 10, 2898–2906. doi:10.1039/c4mb00278d.
Loftus, N., Miseki, M., Iida, J., Gika, H. G., Theodoridis, T., & Wilson, I. D. (2008). Profiling and biomarker identification in plasma from different Zucker rat strains via high mass accuracy multistage mass spectrometric analysis using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with a quadrupole ion trap-time of flight mass spectrometer. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 22, 2547–2554.
Meiss, E., et al. (2016). Metabolite targeting: Development of a comprehensive targeted metabolomics platform for the assessment of diabetes and its complications. Metabolomics, 12, 52. doi:10.1007/s11306-016-0958-0.
Oresic, M., et al. (2008). Dysregulation of lipid and amino acid metabolism precedes islet autoimmunity in children who later progress to type 1 diabetes. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 205, 2975–2984. doi:10.1084/jem.20081800.
Pallares-Mendez, R., Aguilar-Salinas, C. A., Cruz-Bautista, I., & Del Bosque-Plata, L. (2016). Metabolomics in diabetes, a review. Annals of Medicine, 48, 89–102. doi:10.3109/07853890.2015.1137630.
Pereira, T. J., et al. (2015). Maternal obesity characterized by gestational diabetes increases the susceptibility of rat offspring to hepatic steatosis via a disrupted liver metabolome. The Journal of Physiology, 593, 3181–3197. doi:10.1113/JP270429.
Psychogios, N., et al. (2011). The human serum metabolome. PLoS One, 6, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016957.
Renner, S., et al. (2012). Changing metabolic signatures of amino acids and lipids during the prediabetic period in a pig model with impaired incretin function and reduced beta-cell mass. Diabetes, 61, 2166–2175. doi:10.2337/db11-1133.
Rhee, E. P., et al. (2011). Lipid profiling identifies a triacylglycerol signature of insulin resistance and improves diabetes prediction in humans. Journal of Clinical Investigation. doi:10.1172/JCI44442.
Rubio-Aliaga, I., et al. (2011). Alterations in hepatic one-carbon metabolism and related pathways following a high-fat dietary intervention. Physiological Genomics, 43, 408–416.
Scheja, L., et al. (2008). Liver TAG transiently decreases while PL n-3 and n-6 fatty acids are persistently elevated in insulin resistant mice. Lipids, 43, 1039–1051. doi:10.1007/s11745-008-3220-3.
Schmelzer, K., Fahy, E., Subramaniam, S., & Dennis, E. A. (2007). The lipid maps initiative in lipidomics. Methods in Enzymology, 432, 171–183.
Stahlman, M., et al. (2013). Dyslipidemia, but not hyperglycemia and insulin resistance, is associated with marked alterations in the HDL lipidome in type 2 diabetic subjects in the DIWA cohort: Impact on small HDL particles. Biochimica et Biophysica acta, 1831, 1609–1617. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.07.009.
Tchernof, A., & Despres, J. P. (2013). Pathophysiology of human visceral obesity: An update. Physiological Reviews, 93, 359–404. doi:10.1152/physrev.00033.2011.
Tsutsui, H., et al. (2011). Biomarker discovery in biological specimens (plasma, hair, liver and kidney) of diabetic mice based upon metabolite profiling using ultra-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clinica Chimica Acta, 412, 861–872. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2010.12.023.
Ugarte, M., M. Brown, K. A. Hollywood, G. J. Cooper, P. N. Bishop, W. B. Dunn (2012). Metabolomic analysis of rat serum in streptozotocin-induced diabetes and after treatment with oral triethylenetetramine (TETA). Genome Medicine, 4, 35. doi:10.1186/gm334.
Wahl, S., et al. (2012). Childhood obesity is associated with changes in the serum metabolite profile. Obesity Facts, 5, 660–670. doi:10.1159/000343204.
Yang, J., et al. (2004). Discrimination of type 2 diabetic patients from healthy controls by using metabonomics method based on their serum fatty acid profiles. Journal of Chromatography B, 813, 53–58.
Zhao, X., et al. (2010). Metabonomic fingerprints of fasting plasma and spot urine reveal human pre-diabetic metabolic traits. Metabolomics, 6, 362–374. doi:10.1007/s11306-010-0203-1.
Zhu, Y., et al. (2013). Effect of metformin on the urinary metabolites of diet-induced-obese mice studied by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-TOF/MS). Journal of chromatography, 925, 110–116. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.02.040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Philipp Werner and Ernst Meiss contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Werner, P., Meiss, E., Scheja, L. et al. Metabolite profiling: development and application of an UHR-QTOF-MS(/MS) method approach for the assessment of metabolic changes in high fat diet fed mice. Metabolomics 13, 44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1181-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1181-3