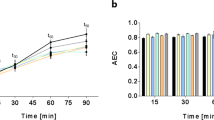
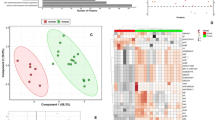
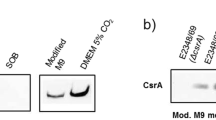
Abstract
Streptococcus intermedius, S. constellatus, and S. anginosus comprise the Streptococcus Milleri/Anginosus group (SMG). They are facultative anaerobic bacteria that asymptomatically colonize the upper respiratory, gastrointestinal and urogenital tracts. They are also common pathogens in pyogenic invasive infections, as well as pulmonary and urinary tract infections. Most SMG infections are polymicrobial and associated with co-infecting obligate anaerobic bacteria. To better understand the effect of oxygen on the growth and physiology of these organisms, we compared the global metabolomic and transcriptomic profiles of S. intermedius strain B196 under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The largest transcriptional changes were associated with induction of oxidative stress response genes under aerobic conditions. Modest changes in expression of genes associated with primary metabolism were observed under the two conditions. Intracellular and extracellular metabolites were measured using HILIC–LCMS. Differences in the abundance of specific metabolites were correlated with observed transcription changes in genes associated with their metabolism, implying that metabolism is primarily regulated at the transcriptional level. Rather than a large shift in primary metabolism under anaerobic conditions our results suggest a modest tuning of metabolism to support the accelerated growth rate of S. intermedius strain B196 in the absence of oxygen. For example, under anaerobic conditions, purine metabolism, pyrimidine de novo synthesis and pyrimidine salvage pathways were up-regulated at metabolic and transcriptional levels. This study provides a better understanding of differences between S. intermedius anaerobic and aerobic metabolism. The results reflect the organism’s predilection for anaerobic growth consistent with its pathogenic association with anaerobes in polymicrobial infections.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, S.-J., Ahn, S.-J., Browngardt, C. M., & Burne, R. A. (2009). Changes in biochemical and phenotypic properties of Streptococcus mutans during growth with aeration. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 75(8), 2517–2527.
Ahn, S.-J., Wen, Z. T., & Burne, R. A. (2007). Effects of oxygen on virulence traits of Streptococcus mutans. Journal of Bacteriology, 189(23), 8519–8527. doi:10.1128/JB.01180-07.
Asam, D., & Spellerberg, B. (2014). Molecular pathogenicity of Streptococcus anginosus. Mol Oral Microbiol, 29(4), 145–155.
Bassit, N., Boquien, C.-Y., Picque, D., & Georges, C. (1993). Effect of initial oxygen concentration on diacetyl and acetoin production by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 59(6), 1893–1897.
Brittan, J. L., Buckeridge, T. J., Finn, A., Kadioglu, A., & Jenkinson, H. F. (2012). Pneumococcal neuraminidase A: An essential upper airway colonization factor for Streptococcus pneumoniae. Molecular Oral Microbiology, 27(4), 270–283.
Broadhurst, D. I., & Kell, D. B. (2006). Statistical strategies for avoiding false discoveries in metabolomics and related experiments. Metabolomics, 2(4), 171–196.
Caspi, R., Altman, T., Billington, R., Dreher, K., Foerster, H., Fulcher, C. A., et al. (2014). The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(D1), D459–D471.
Choi, K.-H., Heath, R. J., & Rock, C. O. (2000). β-Ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III (FabH) is a determining factor in branched-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Journal of Bacteriology, 182(2), 365–370.
Coman, G., Pânzaru, C., Diculencu, D., Gotia, D., Cârlan, M., Dahorea, C., & Butnaru, F. (1995). Pyogenic infections with different locations caused by Streptococcus anginosus alone or in association with anaerobic bacteria. Revista Medico-Chirurgicala A Societatii de Medici si Naturalisti din Iasi, 99(3–4), 215–219.
Cotter, P. D., & Hill, C. (2003). Surviving the acid test: Responses of gram-positive bacteria to low pH. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 67(3), 429–453.
Creek, D. J., Dunn, W. B., Fiehn, O., Griffin, J. L., Hall, R. D., Lei, Z., et al. (2014). Metabolite identification: Are you sure? And how do your peers gauge your confidence? Metabolomics, 10(3), 350–353.
Crow, V. L., & Pritchard, G. G. (1977). Fructose 1,6-diphosphate-activated l-lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus lactis: Kinetic properties and factors affecting activation. Journal of Bacteriology, 131(1), 82–91.
Cusumano, Z. T., & Caparon, M. G. (2015). Citrulline protects Streptococcus pyogenes from acid stress using the arginine deiminase pathway and the F1F0-ATPase. Journal of Bacteriology, 197(7), 1288–1296.
Cusumano, Z. T., Watson, M. E., & Caparon, M. G. (2014). Streptococcus pyogenes arginine and citrulline catabolism promotes infection and modulates innate immunity. Infection and Immunity, 82(1), 233–242.
Derré-Bobillot, A., Cortes-Perez, N. G., Yamamoto, Y., Kharrat, P., Couvé, E., Da Cunha, V., et al. (2013). Nuclease A (Gbs0661), an extracellular nuclease of Streptococcus agalactiae, attacks the neutrophil extracellular traps and is needed for full virulence. Molecular Microbiology, 89(3), 518–531.
Fei, F., Bowdish, D. M. E., & McCarry, B. E. (2014). Comprehensive and simultaneous coverage of lipid and polar metabolites for endogenous cellular metabolomics using HILIC-TOF-MS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406(15), 3723–3733.
Filkins, L. M., Hampton, T. H., Gifford, A. H., Gross, M. J., Hogan, D. A., Sogin, M. L., et al. (2012). Prevalence of streptococci and increased polymicrobial diversity associated with cystic fibrosis patient stability. Journal of Bacteriology, 194(17), 4709–4717.
Fozo, E. M., & Quivey, R. G. (2004). The fabM gene product of Streptococcus mutans is responsible for the synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids and is necessary for survival at low pH. Journal of Bacteriology, 186(13), 4152–4158.
Gossling, J. (1988). Occurrence and pathogenicity of the Streptococcus milleri group. Reviews of Infectious Diseases, 10(2), 257–285.
Gruening, P., Fulde, M., Valentin-Weigand, P., & Goethe, R. (2006). Structure, regulation, and putative function of the arginine deiminase system of Streptococcus suis. Journal of Bacteriology, 188(2), 361–369.
Gupta, R., Yang, J., Dong, Y., Swiatlo, E., Zhang, J.-R., Metzger, D. W., & Bai, G. (2013). Deletion of arcD in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 impairs its capsule and attenuates virulence. Infection and Immunity, 81(10), 3903–3911.
Higuchi, M. (1984). The effect of oxygen on the growth and mannitol fermentation of Streptococcus mutans. Journal of General Microbiology, 130(7), 1819–1826.
Higuchi, M., Yamamoto, Y., & Kamio, Y. (2000). Molecular biology of oxygen tolerance in lactic acid bacteria: Functions of NADH oxidases and Dpr in oxidative stress. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 90(5), 484–493.
Hirai, T., Kimura, S., & Mori, N. (2005). Head and neck infections caused by Streptococcus milleri group: An analysis of 17 cases. Auris, Nasus, Larynx, 32(1), 55–58.
Hocken, D. B., & Dussek, J. E. (1985). Streptococcus milleri as a cause of pleural empyema. Thorax, 40(8), 626–628.
Hytönen, J., Haataja, S., & Finne, J. (2006). Use of flow cytometry for the adhesion analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes mutant strains to epithelial cells: Investigation of the possible role of surface pullulanase and cysteine protease, and the transcriptional regulator Rgg. BMC Microbiology, 6(1), 18.
Imlay, J. A. (2013). The molecular mechanisms and physiological consequences of oxidative stress: Lessons from a model bacterium. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 11(7), 443–454.
Jakubovics, N. S., Smith, A. W., & Jenkinson, H. F. (2002). Oxidative stress tolerance is manganese (Mn(2+)) regulated in Streptococcus gordonii. Microbiology, 148(Pt10), 3255–3263.
Kuhl, C., Tautenhahn, R., Böttcher, C., Larson, T.R., & Neumann, S. (2015). CAMERA: An integrated strategy for compound spectra extraction and annotation of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data sets. Analytical Chemistry, 84(1), 283–289.
Laupland, K. B., Ross, T., Church, D. L., & Gregson, D. B. (2006). Population-based surveillance of invasive pyogenic streptococcal infection in a large Canadian region. Clinical Microbiology & Infection, 12(3), 224–230.
Lee, E. Y., Khatwa, U., McAdam, A. J., Bastos, M. Almeida, Mahmood, S. A., Ervoes, J. P., & Boiselle, P. M. (2010). Streptococcus milleri group pleuropulmonary infection in children: Computed tomographic findings and clinical features. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 34(6), 927–932.
Marquis, R. E., Bender, G. R., Murray, D. R., & Wong, A. (1987). Arginine deiminase system and bacterial adaptation to acid environments. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 53(1), 198–200.
Marraffini, L. A., & Sontheimer, E. J. (2010). CRISPR interference: RNA-directed adaptive immunity in bacteria and archaea. Nature Reviews Genetics, 11(3), 181–190.
Marrakchi, H., Zhang, Y.-M., & Rock, C. O. (2002). Mechanistic diversity and regulation of Type II fatty acid synthesis. Biochemical Society Transactions, 30(part 6), 1050–1055.
Midon, M., Schäfer, P., Pingoud, A., Ghosh, M., Moon, A. F., Cuneo, M. J., et al. (2011). Mutational and biochemical analysis of the DNA-entry nuclease EndA from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(2), 623–634.
Olson, A. B., Kent, H., Sibley, C. D., Grinwis, M. E., Mabon, P., Ouellette, C., et al. (2013). Phylogenetic relationship and virulence inference of Streptococcus anginosus group : Curated annotation and whole-genome comparative analysis support distinct species designation. BMC Genomics, 14, 895.
Parkhomchuk, D., Borodina, T., Amstislavskiy, V., Banaru, M., Hallen, L., Krobitsch, S., et al. (2009). Transcriptome analysis by strand-specific sequencing of complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 37(18), e123.
Parkins, M. D., Sibley, C. D., Surette, M. G., & Rabin, H. R. (2008). The Streptococcus milleri group—an unrecognized cause of disease in cystic fibrosis: A case series and literature review. Pediatric Pulmonology, 43(5), 490–497.
Portela, C. A. F., Smart, K. F., Tumanov, S., Cook, G. M., & Villas-Bôas, S. G. (2014). Global metabolic response of Enterococcus faecalis to oxygen. Journal of Bacteriology, 196(11), 2012–2022.
Prüb, B. M., Nelms, J. M., Park, C., & Wolfe, A. J. (1994). Mutations in NADH: Ubiquinone oxidoreductase. Journal of Bacteriology, 176(8), 2143–2150.
Ripley, R. T., Cothren, C. C., Moore, E. E., Long, J., Johnson, J. L., & Haenel, J. B. (2006). Streptococcus milleri infections of the pleural space: Operative management predominates. American Journal of Surgery, 192(6), 817–821.
Rogers, A. H., Zilm, P. S., & Gully, N. J. (1987). Influence of arginine on the coexistence of Streptococcus mutans and S. milleri in glucose-limited mixed continuous culture. Microbial Ecology, 14(3), 193–202.
Ruoff, K. L. (1988). Streptococcus anginosus (“Streptococcus milleri”): the unrecognized pathogen. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 1(1), 102–108.
Sapranauskas, R., Gasiunas, G., Fremaux, C., Barrangou, R., Horvath, P., & Siksnys, V. (2011). The Streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR/Cas system provides immunity in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(21), 9275–9282.
Serbanescu, M. A., Cordova, M., Krastel, K., Flick, R., Beloglazova, N., Latos, A., et al. (2015). Role of the Streptococcus mutans CRISPR-Cas systems in immunity and cell physiology. Journal of Bacteriology, 197(4), 749–761.
Sezonov, G., Joseleau-Petit, D., & D’Ari, R. (2007). Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. Journal of Bacteriology, 189(23), 8746–8749.
Shinzato, T., & Saito, A. (1994). A mechanism of pathogenicity of “Streptococcus milleri group” in pulmonary infection: Synergy with an anaerobe. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 40, 118–123.
Shinzato, T., & Saito, A. (1995). The Streptococcus milleri group as a cause of pulmonary infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 21(Supplement 3), S238–S243.
Sibley, C. D., Church, D. L., Surette, M. G., Dowd, S. E., & Parkins, M. D. (2012). Pyrosequencing reveals the complex polymicrobial nature of invasive pyogenic infections: Microbial constituents of empyema, liver abscess, and intracerebral abscess. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 31(10), 2679–2691.
Sibley, C. D., Parkins, M. D., Rabin, H. R., Duan, K., Norgaard, J. C., & Surette, M. G. (2008). A polymicrobial perspective of pulmonary infections exposes an enigmatic pathogen in cystic fibrosis patients. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(39), 15070–15075.
Siegman-Igra, Y., Azmon, Y., & Schwartz, D. (2012). Milleri group streptococcus—a stepchild in the viridans family. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 31(9), 2453–2459.
Smith, C. A., Want, E. J., O’Maille, G., Abagyan, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Analytical Chemistry, 78(3), 779–787.
Stadelmann, B., Hanevik, K., Andersson, M. K., Bruserud, O., & Svärd, S. G. (2013). The role of arginine and arginine-metabolizing enzymes during Giardia—host cell interactions in vitro. BMC Microbiology, 13, 256.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis chemical analysis working group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics, 3(3), 211–221.
Trapnell, C., Roberts, A., Goff, L., Pertea, G., Kim, D., Kelley, D. R., et al. (2012). Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nature Protocols, 7(3), 562–578.
Trotter, E. W., Rolfe, M. D., Hounslow, A. M., Craven, C. J., Williamson, M. P., Sanguinetti, G., et al. (2011). Reprogramming of Escherichia coli K-12 metabolism during the initial phase of transition from an anaerobic to a micro-aerobic environment. PLoS One, 6(9), e25501.
Van der Auwera, P. (1985). Clinical significance of Streptococcus milleri. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 4(4), 386–390.
Whiley, R. A. A., Beighton, D., Winstanley, T. G. G., Fraser, H. Y. Y., & Hardie, J. M. M. (1992). Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus (the Streptococcus milleri group): association with different body sites and clinical infections. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 30(1), 243–244.
Wong, C. A., Donald, F., & Macfarlane, J. T. (1995). Streptococcus milleri pulmonary disease: A review and clinical description of 25 patients. Thorax, 50(10), 1093–1096.
Xia, J., Sinelnikov, I. V., Han, B., & Wishart, D. S. (2015). MetaboAnalyst 3.0–making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(W1), W251–W257.
Zheng, L., T’Kind, R., Decuypere, S., von Freyend, S. J., Coombs, G. H., & Watson, D. G. (2010). Profiling of lipids in Leishmania donovani using hydrophilic interaction chromatography in combination with Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 24, 2074–2082.
Zúñiga, M., Pérez, G., & González-Candelas, F. (2002). Evolution of arginine deiminase (ADI) pathway genes. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 25(3), 429–444.
Acknowledgments
This work is dedicated to the late Prof. Brian McCarry (1946–2013). FF was supported by an Ontario Graduate Scholarship. MGS and DMEB are supported by the CIHR and hold Canada Research Chairs. Work in the Bowdish laboratory is supported by the McMaster Immunology Research Centre (MIRC) and work in the Bowdish and Surette labs are supported by the M.G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research (IIDR). The authors would like to thank the Center for Microbial Chemical Biology (CMCB) at McMaster for access to the LC–MS. This study was funded by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to DMEB and MGS (Grant # 108032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Human and animal informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the author.
Additional information
Fan Fei, and Michelle L. Mendonca have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fei, F., Mendonca, M.L., McCarry, B.E. et al. Metabolic and transcriptomic profiling of Streptococcus intermedius during aerobic and anaerobic growth. Metabolomics 12, 46 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-0966-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-0966-0