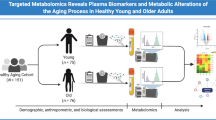
Abstract
Aging is a multifaceted process involving the accumulation of diverse deleterious changes in biological systems over time, so significant alterations in cellular metabolism are detected throughout aging. In the present study, the metabolic processes relevant to the normal aging process were investigated via non-targeted metabolomics using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. To exclude physiological and environmental differences, the metabolic profiles and the relevant metabolic pathways were analyzed in plasma from two separate study groups comprising two distinctly aged cohorts of healthy individuals, the elderly and the younger. The first group was recruited from an urban hospital, and the second group was recruited from a rural community. Alterations in fatty acid beta-oxidation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, and sphingolipid metabolism were identified as significant metabolic pathways relevant to normal aging. It was also found that sphingosine in sphingolipid metabolism, long-chain acylcarnitines in beta-oxidation, and lysophosphatidylcholines (LysoPCs) in glycerophospholipid metabolism could be critical candidate metabolites in the aging process. These results suggest that the metabolic profile of the healthiest individuals could be associated with the normal function of mitochondria, the primary organelle of redox homeostasis, as indicated by their low acylcarnitine to l-carnitine ratio and low levels of LysoPCs and sphingosine in plasma. The present study provides a critical contribution to the entire picture of the aging process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beekman, M., Blanche, H., Perola, M., Hervonen, A., Bezrukov, V., Sikora, E., et al. (2013). Genome-wide linkage analysis for human longevity: Genetics of Healthy Aging Study. Aging Cell, 12(2), 184–193. doi:10.1111/acel.12039.
Bruunsgaard, H., Pedersen, M., & Pedersen, B. K. (2001). Aging and proinflammatory cytokines. Current Opinion in Hematology, 8(3), 131–136.
Bylesjo, M., Eriksson, D., Sjodin, A., Jansson, S., Moritz, T., & Trygg, J. (2007). Orthogonal projections to latent structures as a strategy for microarray data normalization. BMC Bioinformatics, 8, 207. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-8-207.
Chalmers, R. A., Roe, C. R., Stacey, T. E., & Hoppel, C. L. (1984). Urinary excretion of l-carnitine and acylcarnitines by patients with disorders of organic acid metabolism: Evidence for secondary insufficiency of l-carnitine. Pediatric Research, 18(12), 1325–1328.
Choe, M., Jackson, C., & Yu, B. P. (1995). Lipid peroxidation contributes to age-related membrane rigidity. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 18(6), 977–984.
Chung, H. Y., Cesari, M., Anton, S., Marzetti, E., Giovannini, S., Seo, A. Y., et al. (2009). Molecular inflammation: Underpinnings of aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Research Reviews, 8(1), 18–30. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2008.07.002.
Cooper, R. A. (1978). Influence of increased membrane cholesterol on membrane fluidity and cell function in human red blood cells. Journal of Supramolecular Structure, 8(4), 413–430. doi:10.1002/jss.400080404.
D’Adamo, P., Ulivi, S., Beneduci, A., Pontoni, G., Capasso, G., Lanzara, C., et al. (2010). Metabonomics and population studies: Age-related amino acids excretion and inferring networks through the study of urine samples in two Italian isolated populations. Amino Acids, 38(1), 65–73. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0205-8.
Dunn, W. B., Broadhurst, D., Begley, P., Zelena, E., Francis-McIntyre, S., Anderson, N., et al. (2011). Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 6(7), 1060–1083. doi:10.1038/nprot.2011.335.
Edsall, L. C., Van Brocklyn, J. R., Cuvillier, O., Kleuser, B., & Spiegel, S. (1998). N,N-dimethylsphingosine is a potent competitive inhibitor of sphingosine kinase but not of protein kinase C: Modulation of cellular levels of sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide. Biochemistry, 37(37), 12892–12898. doi:10.1021/bi980744d.
Findeisen, H. M., Pearson, K. J., Gizard, F., Zhao, Y., Qing, H., Jones, K. L., et al. (2011). Oxidative stress accumulates in adipose tissue during aging and inhibits adipogenesis. PLoS ONE, 6(4), e18532. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018532.
Fouque, D., Holt, S., Guebre-Egziabher, F., Nakamura, K., Vianey-Saban, C., Hadj-Aissa, A., et al. (2006). Relationship between serum carnitine, acylcarnitines, and renal function in patients with chronic renal disease. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 16(2), 125–131. doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2006.01.004.
Gelinas, D. S., & McLaurin, J. (2005). PPAR-alpha expression inversely correlates with inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and TNF-alpha in aging rats. Neurochemical Research, 30(11), 1369–1375. doi:10.1007/s11064-005-8341-y.
Gika, H. G., Macpherson, E., Theodoridis, G. A., & Wilson, I. D. (2008a). Evaluation of the repeatability of ultra-performance liquid chromatography–TOF-MS for global metabolic profiling of human urine samples. Journal of Chromatography, B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 871(2), 299–305. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.05.048.
Gika, H. G., Theodoridis, G. A., Earll, M., & Wilson, I. D. (2012). A QC approach to the determination of day-to-day reproducibility and robustness of LC–MS methods for global metabolite profiling in metabonomics/metabolomics. Bioanalysis, 4(18), 2239–2247. doi:10.4155/bio.12.212.
Gika, H. G., Theodoridis, G. A., & Wilson, I. D. (2008b). Liquid chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry fingerprinting of human urine: Sample stability under different handling and storage conditions for metabonomics studies. Journal of Chromatography A, 1189(1–2), 314–322. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.10.066.
Gika, H. G., Theodoridis, G. A., Wingate, J. E., & Wilson, I. D. (2007). Within-day reproducibility of an HPLC–MS-based method for metabonomic analysis: Application to human urine. Journal of Proteome Research, 6(8), 3291–3303. doi:10.1021/pr070183p.
Gonzalez-Covarrubias, V., Beekman, M., Uh, H. W., Dane, A., Troost, J., Paliukhovich, I., et al. (2013). Lipidomics of familial longevity. Aging Cell, 12(3), 426–434. doi:10.1111/acel.12064.
Gregersen, N. (1985). The acyl-CoA dehydrogenation deficiencies. Recent advances in the enzymic characterization and understanding of the metabolic and pathophysiological disturbances in patients with acyl-CoA dehydrogenation deficiencies. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation. Supplementum, 174, 1–60.
Grolleau-Julius, A., Ray, D., & Yung, R. L. (2010). The role of epigenetics in aging and autoimmunity. Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology, 39(1), 42–50. doi:10.1007/s12016-009-8169-3.
Harman, D. (1956). Aging: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. The Journal of Gerontology, 11(3), 298–300.
Hiona, A., & Leeuwenburgh, C. (2008). The role of mitochondrial DNA mutations in aging and sarcopenia: Implications for the mitochondrial vicious cycle theory of aging. Experimental Gerontology, 43(1), 24–33. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2007.10.001.
Hong, S. E., Heo, H. S., Kim, D. H., Kim, M. S., Kim, C. H., Lee, J., et al. (2010). Revealing system-level correlations between aging and calorie restriction using a mouse transcriptome. Age, 32(1), 15–30. doi:10.1007/s11357-009-9106-3.
Knight, J. A. (2000). The biochemistry of aging. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 35, 1–62.
Kregel, K. C., & Zhang, H. J. (2007). An integrated view of oxidative stress in aging: Basic mechanisms, functional effects, and pathological considerations. American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 292(1), R18–R36. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00327.2006.
Kristal, B. S., & Shurubor, Y. I. (2005). Metabolomics: Opening another window into aging. Science of Aging Knowledge Environment, 2005(26), pe19. doi:10.1126/sageke.2005.26.pe19.
Lai, L., Michopoulos, F., Gika, H., Theodoridis, G., Wilkinson, R. W., Odedra, R., et al. (2010). Methodological considerations in the development of HPLC–MS methods for the analysis of rodent plasma for metabonomic studies. Molecular Biosystems, 6(1), 108–120. doi:10.1039/b910482h.
Lawton, K. A., Berger, A., Mitchell, M., Milgram, K. E., Evans, A. M., Guo, L., et al. (2008). Analysis of the adult human plasma metabolome. Pharmacogenomics, 9(4), 383–397. doi:10.2217/14622416.9.4.383.
Lehmann, R., Zhao, X., Weigert, C., Simon, P., Fehrenbach, E., Fritsche, J., et al. (2010). Medium chain acylcarnitines dominate the metabolite pattern in humans under moderate intensity exercise and support lipid oxidation. PLoS ONE, 5(7), e11519. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011519.
Leslie, C. C. (1997). Properties and regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272(27), 16709–16712.
Moyes, K. M., Drackley, J. K., Morin, D. E., Bionaz, M., Rodriguez-Zas, S. L., Everts, R. E., et al. (2009). Gene network and pathway analysis of bovine mammary tissue challenged with Streptococcus uberis reveals induction of cell proliferation and inhibition of PPARgamma signaling as potential mechanism for the negative relationships between immune response and lipid metabolism. BMC Genomics, 10, 542. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-542.
Pearson, K. (1909). Determination of the coefficient of correlation. Science, 30(757), 23–25. doi:10.1126/science.30.757.23.
Pellkofer, R., & Sandhoff, K. (1980). Halothane increases membrane fluidity and stimulates sphingomyelin degradation by membrane-bound neutral sphingomyelinase of synaptosomal plasma membranes from calf brain already at clinical concentrations. Journal of Neurochemistry, 34(4), 988–992.
Pohjantahti-Maaroos, H., Palomaki, A., Kankkunen, P., Laitinen, R., Husgafvel, S., & Oksanen, K. (2010). Circulating oxidized low-density lipoproteins and arterial elasticity: Comparison between men with metabolic syndrome and physically active counterparts. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 9, 41. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-9-41.
Psihogios, N. G., Gazi, I. F., Elisaf, M. S., Seferiadis, K. I., & Bairaktari, E. T. (2008). Gender-related and age-related urinalysis of healthy subjects by NMR-based metabonomics. NMR in Biomedicine, 21(3), 195–207. doi:10.1002/nbm.1176.
Qin, Z. X., Zhu, H. Y., & Hu, Y. H. (2009). Effects of lysophosphatidylcholine on beta-amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 30(4), 388–395. doi:10.1038/aps.2009.25.
Rebouche, C. J., & Seim, H. (1998). Carnitine metabolism and its regulation in microorganisms and mammals. Annual Review of Nutrition, 18, 39–61. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.18.1.39.
Sacket, S. J., Chung, H. Y., Okajima, F., & Im, D. S. (2009). Increase in sphingolipid catabolic enzyme activity during aging. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 30(10), 1454–1461. doi:10.1038/aps.2009.136.
Sangster, T., Major, H., Plumb, R., Wilson, A. J., & Wilson, I. D. (2006). A pragmatic and readily implemented quality control strategy for HPLC–MS and GC–MS-based metabonomic analysis. The Analyst, 131(10), 1075–1078. doi:10.1039/b604498k.
Sheikh, A. M., & Nagai, A. (2011). Lysophosphatidylcholine modulates fibril formation of amyloid beta peptide. The FEBS Journal, 278(4), 634–642. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07984.x.
Slupsky, C. M., Rankin, K. N., Wagner, J., Fu, H., Chang, D., Weljie, A. M., et al. (2007). Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Analytical Chemistry, 79(18), 6995–7004. doi:10.1021/ac0708588.
Steinbrecher, U. P., Parthasarathy, S., Leake, D. S., Witztum, J. L., & Steinberg, D. (1984). Modification of low density lipoprotein by endothelial cells involves lipid peroxidation and degradation of low density lipoprotein phospholipids. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 81(12), 3883–3887.
Suhre, K., & Gieger, C. (2012). Genetic variation in metabolic phenotypes: Study designs and applications. Nature Reviews Genetics, 13(11), 759–769. doi:10.1038/nrg3314.
Sung, B., Park, S., Yu, B. P., & Chung, H. Y. (2006). Amelioration of age-related inflammation and oxidative stress by PPARgamma activator: Suppression of NF-kappaB by 2,4-thiazolidinedione. Experimental Gerontology, 41(6), 590–599. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2006.04.005.
Wick, G., & Grubeck-Loebenstein, B. (1997). Primary and secondary alterations of immune reactivity in the elderly: Impact of dietary factors and disease. Immunological Reviews, 160, 171–184.
Wick, G., Huber, L. A., Xu, Q. B., Jarosch, E., Schonitzer, D., & Jurgens, G. (1991). The decline of the immune response during aging: The role of an altered lipid metabolism. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 621, 277–290.
Won, J. S., & Singh, I. (2006). Sphingolipid signaling and redox regulation. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 40(11), 1875–1888. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.01.035.
Woodward, M., Rumley, A., Lowe, G. D., & Tunstall-Pedoe, H. (2003). C-reactive protein: Associations with haematological variables, cardiovascular risk factors and prevalent cardiovascular disease. British Journal of Haematology, 122(1), 135–141.
Wu, D., Ren, Z., Pae, M., Guo, W., Cui, X., Merrill, A. H., et al. (2007). Aging up-regulates expression of inflammatory mediators in mouse adipose tissue. Journal of Immunology, 179(7), 4829–4839.
Xia, J., Mandal, R., Sinelnikov, I. V., Broadhurst, D., & Wishart, D. S. (2012). MetaboAnalyst 2.0—A comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(Web Server issue), W127–W133. doi:10.1093/nar/gks374.
Xing, J., Chen, X., Sun, Y., Luan, Y., & Zhong, D. (2005). Interaction of baicalin and baicalein with antibiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 57(6), 743–750. doi:10.1211/0022357056244.
Yu, B. P., Suescun, E. A., & Yang, S. Y. (1992). Effect of age-related lipid peroxidation on membrane fluidity and phospholipase A2: Modulation by dietary restriction. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 65(1), 17–33.
Yu, Z., Zhai, G., Singmann, P., He, Y., Xu, T., Prehn, C., et al. (2012). Human serum metabolic profiles are age dependent. Aging Cell, 11(6), 960–967. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00865.x.
Zou, Y., Kim, D. H., Jung, K. J., Heo, H. S., Kim, C. H., Baik, H. S., et al. (2009). Lysophosphatidylcholine enhances oxidative stress via the 5-lipoxygenase pathway in rat aorta during aging. Rejuvenation Research, 12(1), 15–24. doi:10.1089/rej.2008.0807.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Creative Fusion Research Program through the Creative Allied Project funded by the Korea Research Council of Fundamental Science and Technology (CAP-12-1), the Bio-Synergy Research Project (NRF-2013M3A9C4078145) of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST). We would like to especially thank Prof. Hyun Ok Kim (Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea) for her help with the serum biochemical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Both Soo Hyun Lee and Sungha Park contributed equally to this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.H., Park, S., Kim, HS. et al. Metabolomic approaches to the normal aging process. Metabolomics 10, 1268–1292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0663-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0663-9