Abstract
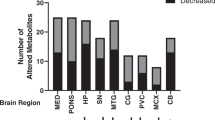
Using a novel metabolomics approach the current study aimed to further characterize the functional attributes of alpha-synuclein that mediate its involvement in neurodegeneration. The metabolic profiles of alpha-synuclein knockout and A53T mutant overexpressing mouse brains were studied using proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC/MS). Gene deletion and mutation were both associated with significant alterations in brain energy metabolism when compared with their respective wild-type controls. These changes indicated deficiencies in key metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and significant differences in the concentrations of small molecules including adenine nucleotides, taurine, NAD+ and glutamine. Analysis of the metabolic pathways affected by both knockout and mutation further indicated involvement of alpha-synuclein in metabolic pathways of energy metabolism, cellular redox status and glycerophospholipid metabolism. As such, our data identify novel functions of alpha-synuclein, validate previous reports describing its contribution to energy metabolism and lipid synthesis and support the use of metabolomic analysis as a fundamental technique in defining the effect of protein expression and mutation in genetic models.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich, A., Schmitz, Y., Fariñas, I., Choi-Lundberg, D., Ho, W. H., & Castillo, P. E. (2000). Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron, 25, 239–252.
Barceló-Coblijn, G., Golovko, M., Weinhofer, I., Berger, J., & Murphy, E. (2007). Brain neutral lipids mass is increased in alpha-synuclein gene-ablated mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 101(1), 132–141. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04348.x.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of Royal Statistics Society: Series B, 57, 289–300.
Block, W., Traber, F., Flacke, S., Jessen, F., Pohl, C., Schild, H., et al. (2002). In-vivo proton MR-spectroscopy of the human brain: assessment of N-acetylaspartate (NAA) reduction as a marker for neurodegeneration. Amino Acids, 23(1–3), 317–323.
Bocker, S., Letzel, M. C., Liptak, Z., & Pervukhin, A. (2008). SIRIUS: Decomposing isotope patterns for metabolite identification. Bioinformatics. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btn603.
Bourgeron, T., Rustin, P., Chretien, D., Birch-Machin, M., Bourgeois, M., Viegas-Pequignot, E., et al. (1995). Mutation of a nuclear succinate dehydrogenase gene results in mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiency. Nature Genetics, 11(2), 144–149. doi:10.1038/ng1095-144.
Burri, R., Steffen, C., & Herschkowitz, N. (1991). N-acetyl-l-aspartate is a major source of acetyl groups for lipid synthesis during rat brain development. Developmental Neuroscience, 16(6), 403–411.
Cabin, D. E., Shimazu, K., Murphy, D. D., Cole, N. B., Gottschalk, W., McIlwain, K. L., et al. (2002). Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. Journal of Neuroscience, 22(20), 8797–8807.
Chandra, S., Gallardo, G., Fernández-Chacón, R., Schlüter, O. M., & Südhof, T. C. (2005). Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell, 123(3), 383–396. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.028.
Cookson, M. R., & Bandmann, O. (2010). Parkinson’s disease: Insights from pathways. Human Molecular Genetics, 19(R1), R21–R27. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq167.
De Meyer, T., Sinnaeve, D., Van Gasse, B., Tsiporkova, E., Rietzschel, E. R., De Buyzere, M. L., et al. (2008). NMR-based characterization of metabolic alterations in hypertension using an adaptive, intelligent binning algorithm. Analytical Chemistry, 80(10), 3783–3790. doi:10.1021/ac7025964.
Devi, L., Raghavendran, V., Prabhu, B. M., Avadhani, N. G., & Anandatheerthavarada, H. K. (2008). Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(14), 9089–9100. doi:10.1074/jbc.M710012200.
Dieterle, F., Ross, A., Schlotterbeck, G., & Senn, H. (2006). Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78(13), 4281–4290. doi:10.1021/ac051632c.
Dodson, M. W., & Guo, M. (2007). Pink1, Parkin, DJ-1 and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 17(3), 331–337. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2007.04.010.
Edwards, L. M., Lawler, N. G., Nikolic, S. B., Peters, J. M., Horne, J., Wilson, R., et al. (2012). Metabolomics reveals increased isoleukotoxin diol (12,13-DHOME) in human plasma after acute intralipid infusion. Journal of Lipid Research, 53(9), 1979–1986. doi:10.1194/jlr.P027706.
Edwards, L. M., Musgrove, R., King, A., DeMeyer, T., Horne, J., & Dickson, T. (2011). Exometabolomics reveals increased glycolysis in cultured neurons lacking alpha-synuclein. In 7th International Metabolomics Society Conference.
Ellis, C. E., Murphy, E. J., Mitchell, D. C., Golovko, M. Y., Scaglia, F., Barcelo-Coblijn, G. C., et al. (2005). Mitochondrial lipid abnormality and electron transport chain impairment in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 25(22), 10190–10201. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.22.10190-10201.2005.
Giasson, B. I., Duda, J. E., Quinn, S. M., Zhang, B., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Lee, V. M. (2002). Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron, 34(4), 521–533.
Gibson, G., & Blass, J. P. (1976). A relation between (NAD+)/(NADH) potentials and glucose utilization in rat brain slices. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 251(13), 4127–4130.
Gispert, S., Del Turco, D., Garrett, L., Chen, A., Bernard, D. J., Hamm-Clement, J., et al. (2003). Transgenic mice expressing mutant A53T human alpha-synuclein show neuronal dysfunction in the absence of aggregate formation. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 24(2), 419–429.
Golovko, M., Rosenberger, T., Feddersen, S., Faergeman, N., & Murphy, E. (2007). Alpha-synuclein gene ablation increases docosahexaenoic acid incorporation and turnover in brain phospholipids. Journal of Neurochemistry, 101(1), 201–211. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04357.x.
Graham, D. R., & Sidhu, A. (2010). Mice expressing the A53T mutant form of human alpha-synuclein exhibit hyperactivity and reduced anxiety-like behavior. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 88(8), 1777–1783. doi:10.1002/jnr.22331.
Iwai, A., Masliah, E., Yoshimoto, M., Ge, N., Flanagan, L., de Silva, H. A., et al. (1995). The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron, 14(2), 467–475.
Klivenyi, P., Siwek, D., Gardian, G., Yang, L., Starkov, A., Cleren, C., et al. (2006). Mice lacking alpha-synuclein are resistant to mitochondrial toxins. Neurobiology of Diseases, 21(3), 541–548. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2005.08.018.
Kuchel, P. (2010). Models of the human metabolic network: Aiming to reconcile metabolomics and genomics. Genome Medicine, 2(7), 46. doi:10.1186/gm167.
Le Belle, J. E., Harris, N. G., Williams, S. R., & Bhakoo, K. K. (2002). A comparison of cell and tissue extraction techniques using high-resolution 1H NMR spectroscopy. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(1), 37–44.
Lee, M. K., Stirling, W., Xu, Y., Xu, X., Qui, D., Mandir, A. S., et al. (2002). Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson’s disease-linked Ala-53-Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(13), 8968–8973. doi:10.1073/pnas.132197599.
Li, W. W., Yang, R., Guo, J. C., Ren, H. M., Zha, X. L., Cheng, J. S., et al. (2007). Localization of alpha-synuclein to mitochondria within midbrain of mice. Neuroreport, 18(15), 1543–1546. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e3282f03db4.
Liu, G., Zhang, C., Yin, J., Li, X., Cheng, F., Li, Y., et al. (2009). Alpha-synuclein is differentially expressed in mitochondria from different rat brain regions and dose-dependently down-regulates complex I activity. Neuroscience Letters, 454(3), 187–192. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.02.056.
Lowry, O. H., Passonneau, J. V., Hasselberger, F. X., & Schulz, D. W. (1964). Effect of ischemia on known substrates and cofactors of the glycolytic pathway in brain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 239(1), 18–30.
Martin, L. (2006). Parkinson’s disease-synuclein transgenic mice develop neuronal mitochondrial degeneration and cell death. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(1), 41–50. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4308-05.2006.
Maskri, L., Zhu, X., Fritzen, S., Kuhn, K., Ullmer, C., Engels, P., et al. (2004). Influence of different promoters on the expression pattern of mutated human alpha-synuclein in transgenic mice. Neurodegenerative Diseases, 1(6), 255–265. doi:10.1159/000085064.
Moffett, J. R., Ross, B., Arun, P., Madhavarao, C. N., & Namboodiri, A. M. (2007). N-Acetylaspartate in the CNS: From neurodiagnostics to neurobiology. Progress in Neurobiology, 81(2), 89–131.
Murphy, D. D., Rueter, S. M., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Lee, V. M. (2000). Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alpha-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 20(9), 3214–3220.
Nemani, V. M., Lu, W., Berge, V., Nakamura, K., Onoa, B., Lee, M. K., et al. (2010). Increased expression of alpha-synuclein reduces neurotransmitter release by inhibiting synaptic vesicle reclustering after endocytosis. Neuron, 65(1), 66–79. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2009.12.023.
Oaks, A. W., Frankfurt, M., Finkelstein, D. I., & Sidhu, A. (2013). Age-dependent effects of A53T alpha-synuclein on behavior and dopaminergic function. PLoS One, 8(4), e60378. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060378.
Pluskal, T., Castillo, S., Villar-Briones, A., & Oresic, M. (2010). MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 395. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-395.
Polymeropoulos, M. H., Lavedan, C., Leroy, E., Ide, S. E., Dehejia, A., Dutra, A., et al. (1997). Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science, 276(5321), 2045–2047.
Salek, R. M., Xia, J., Innes, A., Sweatman, B. C., Adalbert, R., Randle, S., et al. (2010). A metabolomic study of the CRND8 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochemistry International, 56, 937–947.
Saransaari, P., & Oja, S. S. (2000). Taurine and neural cell damage. Amino Acids, 19(3–4), 509–526.
Signoretti, S., Marmarou, A., Tavazzi, B., Lazzarino, G., Beaumont, A., & Vagnozzi, R. (2001). N-Acetylaspartate reduction as a measure of injury severity and mitochondrial dysfunction following diffuse traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 18(10), 991–997.
Smith, C. A., Want, E. J., O’Maille, G., Abagyan, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Analytical Chemistry, 78(3), 779–787. doi:10.1021/ac051437y.
Spillantini, M. G., Schmidt, M. L., Lee, V. M., Trojanowski, J. Q., Jakes, R., & Goedert, M. (1997). Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature, 388(6645), 839–840.
Surmeier, D. J. (2010). Alpha-synuclein at the synaptic gate. Neuron, 65(1), 3–4. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2009.12.030.
Wilhelm, F., & Hirrlinger, J. (2012). Multifunctional roles of NAD+ and NADH in astrocytes. Neurochemical Research,. doi:10.1007/s11064-012-0760-y.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Reza Salek for helpful comments and advice. Funding sources include the NHMRC (Project Grant and Career Development Fellowship to TD) and the Tasmanian Masonic Centenary Medical Research Foundation. We thank Dr. Tim De Meyer for his donation of Matlab scripts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lindsay M. Edwards and Tracey C. Dickson are the joint senior authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Musgrove, R.E., Horne, J., Wilson, R. et al. The metabolomics of alpha-synuclein (SNCA) gene deletion and mutation in mouse brain. Metabolomics 10, 114–122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0561-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0561-6