Abstract
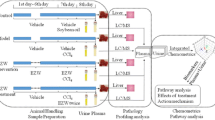
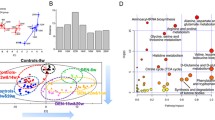
A key interest in clinical diagnosis and pharmaceutical industry is to have a repertoire of noninvasive biomarkers to—individually or in combination—be able to infer or predict the degree of liver injury caused by pathological conditions or drugs. Metabolomics—a comprehensive study of global metabolites—has become a highly sensitive and powerful tool for biomarker discovery thanks to recent technological advances. An ultra-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC/TOF MS/MS)-based metabolomics approach was employed to investigate sera from galactosamine-treated rats to find potential biomarkers for acute liver injury. Hepatic damage was quantified by determining serum transaminase activity and in situ liver histological lesions. Principal component analysis in combination with coefficient of correlation analysis was used for biomarker selection and identification. According to the data, serum levels of several metabolites including glucose, amino acids, and membrane lipids were significantly modified, some of them showing a high correlation with the degree of liver damage determined by histological examination of the livers. In conclusion, this study supports that UPLC-MS/MS based serum metabolomics in experimental animal models could be a powerful approach to search for biomarkers for drug- or disease-induced liver injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai, K., Lee, K., Berthiaume, F., Tompkins, R. G., & Yarmush, M. L. (2001). Intrahepatic amino acid and glucose metabolism in a d-galactosamine-induced rat liver failure model. Hepatology, 34, 360–371.
Barr, J., Vazquez-Chantada, M., Alonso, C., Perez-Cormenzana, M., Mayo, R., Galan, A., et al. (2010). Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based parallel metabolic profiling of human and mouse model serum reveals putative biomarkers associated with the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 4501–4512.
Boelsterli, U. A., & Lim, P. L. (2007). Mitochondrial abnormalities—a link to idiosyncratic drug hepatotoxicity? Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 220, 92–107.
Brindle, J. T., Antti, H., Holmes, E., Tranter, G., Nicholson, J. K., Bethell, H. W., et al. (2002). Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. Nature Medicine, 8, 1439–1444.
Cabrero, C., Duce, A. M., Ortiz, P., Alemany, S., & Mato, J. M. (1988). Specific loss of the high-molecular-weight form of S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthetase in human liver cirrhosis. Hepatology, 8, 1530–1534.
Chan, E. C., Yap, S. L., Lau, A. J., Leow, P. C., Toh, D. F., & Koh, H. L. (2007). Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry based metabolomics of raw and steamed Panax notoginseng. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 21, 519–528.
Chen, C., Gonzalez, F. J., & Idle, J. R. (2007). LC-MS-based metabolomics in drug metabolism. Drug Metabolism Reviews, 39, 581–597.
Clarke, C. J., & Haselden, J. N. (2008). Metabolic profiling as a tool for understanding mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicologic Pathology, 36, 140–147.
Coen, M. (2010). A metabonomic approach for mechanistic exploration of pre-clinical toxicology. Toxicology, 278, 326–340.
Coen, M., Hong, Y. S., Clayton, T. A., Rohde, C. M., Pearce, J. T., Reily, M. D., et al. (2007). The mechanism of galactosamine toxicity revisited; a metabonomic study. Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 2711–2719.
Coen, M., Want, E. J., Clayton, T. A., Rhode, C. M., Hong, Y. S., Keun, H. C., et al. (2009). Mechanistic aspects and novel biomarkers of responder and non-responder phenotypes in galactosamine-induced hepatitis. Journal of Proteome Research, 8, 5175–5187.
Dan, Y. Y., & Yeoh, G. C. (2008). Liver stem cells: A scientific and clinical perspective. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 23, 687–698.
Decker, K., & Keppler, D. (1972). Galactosamine induced liver injury. Progress in Liver Diseases, 4, 183–199.
Duarte, I. F., Stanley, E. G., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., Gil, A. M., Tang, H., et al. (2005). Metabolic assessment of human liver transplants from biopsy samples at the donor and recipient stages using high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 5570–5578.
El-Mofty, S. K., Scrutton, M. C., Serroni, A., Nicolini, C., & Farber, J. L. (1975). Early, reversible plasma membrane injury in galactosamine-induced liver cell death. The American Journal of Pathology, 79, 579–596.
Feng, B., Wu, S., Lv, S., Liu, F., Chen, H., Yan, X., et al. (2007). Metabolic profiling analysis of a d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse model of fulminant hepatic failure. Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 2161–2167.
Fernie, A. R., Trethewey, R. N., Krotzky, A. J., & Willmitzer, L. (2004). Metabolite profiling: From diagnostics to systems biology. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 5, 763–769.
Fox, L. M., Cox, D. G., Lockridge, J. L., Wang, X., Chen, X., Scharf, L., et al. (2009). Recognition of lyso-phospholipids by human natural killer T lymphocytes. PLoS Biology, 7, e1000228.
Gomez-Lechon, M. J., Castell, J. V., & Donato, M. T. (2008). An update on metabolism studies using human hepatocytes in primary culture. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism, 4, 837–854.
Kaplowitz, N. (2001). Drug-induced liver disorders: Implications for drug development and regulation. Drug Safety, 24, 483–490.
Keppler, D., Lesch, R., Reutter, W., & Decker, K. (1968). Experimental hepatitis induced by d-galactosamine. Experimental and Molecular Pathology, 9, 279–290.
Kitazawa, T., Tsujimoto, T., Kawaratani, H., & Fukui, H. (2009). Therapeutic approach to regulate innate immune response by Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist E5564 in rats with D-galactosamine-induced acute severe liver injury. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 24, 1089–1094.
Koff, R. S., Fitts, J. J., Sabesin, S. M., & Zimmerman, H. J. (1971). d-galactosamine hepatotoxicity II. Mechanism of fatty liver production. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 138, 89–92.
Komano, T., Egashira, Y., & Sanada, H. (2008). l-Gln and l-Ser suppress the d-galactosamine-induced IL-18 expression and hepatitis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 372, 688–690.
Kushnir, M. M., Rockwood, A. L., Bergquist, J. (2009). Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry applications in endocrinology. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 29, 480–502.
Lin, H. M., Barnett, M. P., Roy, N. C., Joyce, N. I., Zhu, S., Armstrong, K., et al. (2010). Metabolomic analysis identifies inflammatory and noninflammatory metabolic effects of genetic modification in a mouse model of Crohn’s disease. Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 1965–1975.
Lott, J. A., & Landesman, P. W. (1984). The enzymology of skeletal muscle disorders. Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences, 20, 153–190.
Lutz, U., Lutz, R. W., & Lutz, W. K. (2006). Metabolic profiling of glucuronides in human urine by LC-MS/MS and partial least-squares discriminant analysis for classification and prediction of gender. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4564–4571.
Lv, S., Wei, L., Wang, J. H., Wang, J. Y., & Liu, F. (2007). Identification of novel molecular candidates for acute liver failure in plasma of BALB/c murine model. Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 2746–2752.
Maezono, K., Kajiwara, K., Mawatari, K., Shinkai, A., Torii, K., & Maki, T. (1996). Alanine protects liver from injury caused by F-galactosamine and CCl4. Hepatology, 24, 185–191.
Major, H. J., Williams, R., Wilson, A. J., & Wilson, I. D. (2006). A metabonomic analysis of plasma from Zucker rat strains using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and pattern recognition. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 20, 3295–3302.
Mato, J. M., Martinez-Chantar, M. L., & Lu, S. C. (2008). Methionine metabolism and liver disease. Annual Review of Nutrition, 28, 273–293.
Medline, A., Schaffner, F., & Popper, H. (1970). Ultrastructural features in galactosamine-induced hepatitis. Experimental and Molecular Pathology, 12, 201–211.
Miller, T. J., Knapton, A., Adeyemo, O., Noory, L., Weaver, J., & Hanig, J. P. (2008). Cytochrome c: A non-invasive biomarker of drug-induced liver injury. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 28, 815–828.
Miyahara, M., Enzan, H., Shiraishi, N., Kawase, M., Yamamoto, M., Hara, H., et al. (1982). Mitochondrial damage in galactosamine-induced liver intoxication in rats. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 714, 505–515.
Muller, P. Y., & Dieterle, F. (2009). Tissue-specific, non-invasive toxicity biomarkers: Translation from preclinical safety assessment to clinical safety monitoring. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism, 5, 1023–1038.
Newsome, P. N., Plevris, J. N., Nelson, L. J., & Hayes, P. C. (2000). Animal models of fulminant hepatic failure: A critical evaluation. Liver Transplantation, 6, 21–31.
Nicholls, A. W., Mortishire-Smith, R. J., & Nicholson, J. K. (2003). NMR spectroscopic-based metabonomic studies of urinary metabolite variation in acclimatizing germ-free rats. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 16, 1395–1404.
Nicholson, J. K., & Wilson, I. D. (2003). Opinion: Understanding ‘global’ systems biology: Metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2, 668–676.
Nordstrom, A., O’Maille, G., Qin, C., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). Nonlinear data alignment for UPLC-MS and HPLC-MS based metabolomics: Quantitative analysis of endogenous and exogenous metabolites in human serum. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 3289–3295.
Novakova, L., Solichova, D., & Solich, P. (2006). Advantages of ultra performance liquid chromatography over high-performance liquid chromatography: Comparison of different analytical approaches during analysis of diclofenac gel. Journal of Separation Science, 29, 2433–2443.
Ozer, J., Ratner, M., Shaw, M., Bailey, W., & Schomaker, S. (2008). The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology, 245, 194–205.
Petkova, D. H., Momchilova, A. B., Markovska, T. T., & Koumanov, K. S. (1987). d-galactosamine induced changes in rat liver plasma membranes lipid composition and some enzyme activities. The International Journal of Biochemistry, 19, 289–291.
Schauer, N., & Fernie, A. R. (2006). Plant metabolomics: Towards biological function and mechanism. Trends in Plant Science, 11, 508–516.
Stramentinoli, G., Gualano, M., & Ideo, G. (1978). Protective role of S-adenosyl-l-methionine on liver injury induced by d-galactosamine in rats. Biochemical Pharmacology, 27, 1431–1433.
Tosti, E., Dahl, L., Endresen, M. J., & Henriksen, T. (1999). Endothelial degradation of extracellular lyso-phosphatidylcholine. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation, 59, 249–257.
Tunon, M. J., Alvarez, M., Culebras, J. M., & Gonzalez-Gallego, J. (2009). An overview of animal models for investigating the pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in acute hepatic failure. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15, 3086–3098.
Ulrich, R. G. (2007). Idiosyncratic toxicity: A convergence of risk factors. Annual Review of Medicine, 58, 17–34.
Yovchev, M. I., Grozdanov, P. N., Zhou, H., Racherla, H., Guha, C., & Dabeva, M. D. (2008). Identification of adult hepatic progenitor cells capable of repopulating injured rat liver. Hepatology, 47, 636–647.
Zhang, Q., Wang, G., Du, Y., Zhu, L., & Jiye, A. (2007). GC/MS analysis of the rat urine for metabonomic research. Journal of Chromatography B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 854, 20–25.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank B. Martínez de la Pera, C. Oceja, I. Iturriza and L. María for their technical assistance and FAES FARMA S.A. for its support with rat experimentation procedures and sample collection. This work was supported by grants from the Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (Institute of Health Carlos III, 06/0621 & PS09/00526 to J.M.F.P.); Program “Ramon y Cajal” of Spanish Ministry (to J.M.F.P); Diputación Foral de Bizkaia (612TK20100014); National Institute of Health Grant R01 AT004896 (to S.C.L. and J.M. M.); Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red en el Área temática de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBERehd) is funded by the Institute of Health Carlos III.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez, E., van Liempd, S., Conde-Vancells, J. et al. Serum UPLC-MS/MS metabolic profiling in an experimental model for acute-liver injury reveals potential biomarkers for hepatotoxicity. Metabolomics 8, 997–1011 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-011-0329-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-011-0329-9