Abstract
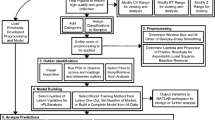
Metabolic footprinting has been applied as a non-invasive approach to study the behaviour and responses of cultured cells to a range of genetic and environmental perturbations. Gas chromatography interfaced with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-ToF-MS) has become a powerful tool for the analysis of metabolome-derived samples. Generally, two data analysis strategies are used to interrogate and understand the biological patterns within the multi-dimensional data. The first strategy, a commoner one, uses multivariate analysis after chromatographic and mass spectral deconvolution, and the second strategy directly employs multivariate analysis of non-deconvoluted data. Here, two strategies have been assessed for the separation and classification of metabolic footprints (exometabolomes) of two strains of Candida albicans grown on three different carbon sources (glycerol, glucose and galactose). We describe a semi-automated approach that simultaneously processes all samples using the chromatographic dimension data with principal components analysis (PCA), which can include data pre-processing before PCA analysis. The preprocessed and non-deconvoluted total ion chromatogram (TIC) data showed good separation of classes defined by growth on different carbon sources and when comparing the two strains grown on the same carbon source separation was achieved for strains grown on glucose and glycerol after preprocessing. The discrimination observed is greater for preprocessed and non-deconvoluted TIC data than for that of preprocessed and non-deconvoluted single ion chromatogram data. The results from the proposed approach with those produced by MZmine were compared. The results from MZmine data depicted separations in PCA space according to carbon source, but no separation was seen when studying strains grown on the same carbon source. Our research showed that the non-deconvoluted strategy is suitable for fast comparison of large sets of GC-MS data although it will not directly provide biological information. The non-deconvoluted strategy can avoid problems of analyzing complex samples using deconvolution software.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebersold, R., Anderson, L., Caprioli, R., Druker, B., Hartwell, L., & Smith, R. (2005). Perspective: A program to improve protein biomarker discovery for cancer. Journal of Proteome Research, 4, 1104–1109.
Allen, J., Davey, H. M., Broadhurst, D., Heald, J. K., Rowland, J. J., Oliver, S. G., et al. (2003). High-throughput classification of yeast mutants for functional genomics using metabolic footprinting. Nature Biotechnology, 21, 692–696.
Boernsen, K. O., Gatzek, S., & Imbert, G. (2005). Controlled protein precipitation in combination with chip-based nanospray infusion mass spectrometry. An approach for metabolomics profiling of plasma. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 7255–7264.
Bro, R., & Smilde, A. K. (2003). Centering and scaling in component analysis. Journal of Chemometrics, 17, 16–33.
Broadhurst, D. I., & Kell, D. B. (2006). Statistical strategies for avoiding false discoveries in metabolomics and related experiments. Metabolomics, 2, 171–196.
Brown, M., Dunn, W. B., Ellis, D. I., Goodacre, R., Handl, J., Knowles, J. D., et al. (2005). A metabolome pipeline: From concept to data to knowledge. Metabolomics, 1, 39–51.
Bundy, J. G., Willey, T. L., Castell, R. S., Ellar, D. J., & Brindle, K. M. (2005). Discrimination of pathogenic clinical isolates and laboratory strains of Bacillus cereus by NMR-based metabolomic profiling. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 242, 127–136.
Callister, S. J., Barry, R. C., Adkins, J. N., Johnson, E. T., Qian, W. J., Webb-Robertson, B. J. M., et al. (2006). Normalization approaches for removing systematic biases associated with mass spectrometry and label-free proteomics. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 277–286.
Deport, C., Ratel, J., Berdague, J. L., & Engel, E. (2006). Comprehensive combinatory standard correction: A calibration method for handling instrumental drifts of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry systems. Journal of Chromatography A, 1116, 248–258.
Dunn, W. B., Bailey, N. J. C., & Johnson, H. E. (2005). Measuring the metabolome: Current analytical technologies. Analyst, 130, 606–625.
Dunn, W. B., & Ellis, D. I. (2005). Metabolomics: Current analytical platforms and methodologies. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 24, 285–294.
Duran, A. L., Yang, J., Wang, L. J., & Sumner, L. W. (2003). Metabolomics spectral formatting, alignment and conversion tools (MSFACTs). Bioinformatics, 19, 2283–2293.
Edwards, J. L., Chisolm, C. N., Shackman, J. G., & Kennedy, R. T. (2006). Negative mode sheathless capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry for metabolite analysis of prokaryotes. Journal of Chromatography A, 1106, 80–88.
Eilers, P. H. C. (2004). Parametric time warping. Analytical Chemistry, 76, 404–411.
Ellis, D., Broadhurst, D., Kell, D., Rowland, J., & Goodacre, R. (2002). Rapid and quantitative detection of the microbial spoilage of meat by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and machine learning. Applied and environmental microbiology, 68, 2822–2828.
Fiehn, O. (2002). Metabolomics—the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Molecular Biology, 48, 155–171.
Goodacre, R. (2004). Metabolic profiling: Pathways in discovery. Drug Discovery Today, 9, 260–261.
Goodacre, R. (2007). Metabolomics of a superorganism. Journal of Nutrition, 137, 259S–266S.
Harrigan, G. G., & Goodacre, R. (Eds.). (2003). Metabolic profiling: Its role in biomarker discovery and gene function analysis. Boston: Kluwer Academic.
Harrison, B., Ellis, J., Broadhurst, D., Reid, K., Goodacre, R., & Priest, F. G. (2006). Differentiation of peats used in the preparation of malt for Scotch whisky production using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Journal of the Institute of Brewing, 112, 333–339.
Higgs, R. E., Knierman, M. D., Gelfanova, V., Butler, J. P., & Hale, J. E. (2005). Comprehensive label-free method for the relative quantification of proteins from biological samples. Journal of Proteome Research, 4, 1442–1450.
Himmelreich, U., Somorjai, R. L., Dolenko, B., Lee, O. C., Daniel, H.-M., Murray, R., et al. (2003). Rapid identification of Candida species by using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and a statistical classification strategy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69, 4566–4574.
Hollywood, K., Brison, D. R., & Goodacre, R. (2006). Metabolomics: Current technologies and future trends. Proteomics, 6, 4716–4723.
Hotelling, H. (1933). Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. Journal of Educational Psychology, 24, 417–441.
Huhman, D. V., & Sumner, L. W. (2002). Metabolic profiling of saponins in Medicago sativa and Medicago truncatula using HPLC coupled to an electrospray ion-trap mass spectrometer. Phytochemistry, 59, 347–360.
Idborg-Björkman, H., Edlund, P.-O., Kvalheim, O. M., Schuppe-Koistinen, I., & Jacobsson, S. P. (2003). Screening of biomarkers in rat urine using LC/electrospray ionization-MS and two-way data analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 75, 4784–4792.
Jarvis, R., Clarke, S., & Goodacre, R. (2006). Rapid analysis of microbiological systems using SERS. In K. Kneipp, M. Moskovits, & H. Kneipp (Eds.), Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: Physics and applications. Topics in Applied Physics (Vol. 103, pp. 397–408). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer Verlag. ISBN: 978-3-540-33566-5.
Jonsson, P., Gullberg, J., Nordstrom, A., Kusano, M., Kowalczyk, M., Sjöström, M., et al. (2004). A strategy for identifying differences in large series of metabolomic samples analyzed by GC/MS. Analytical Chemistry, 76, 1738–1745.
Jonsson, P., Johansson, A., Gullberg, J., Trygg, J., Jiye, A., Grung, B., et al. (2005). High-throughput data analysis for detecting and identifying differences between samples in GC/MS-based metabolomic analyses. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 5635–5642.
Kaderbhai, N. N., Broadhurst, D. I., Ellis, D. I., Goodacre, R., & Kell, D. B. (2003). Functional genomics via metabolic footprinting: Monitoring metabolite secretion by Escherichia coli tryptophan metabolism mutants using FT–IR and direct injection electrospray mass spectrometry. Comparative and Functional Genomics, 4, 376–391.
Katajamaa, M., Miettinen, J., & Oresic, M. (2006). MZmine: Toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics, 22, 634–636.
Katajamaa, M., & Orešič, M. (2005). Processing methods for differential analysis of LC/MS profile data. BMC Bioinformatics, 6, 179–190.
Kell, D. B., Brown, M., Davey, H. M., Dunn, W. B., Spasic, I., & Oliver, S. G. (2005). Metabolic footprinting and systems biology: The medium is the message. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 3, 557–565.
Kell, D. B., & Oliver, S. G. (2004). Here is the evidence, now what is the hypothesis? The complementary roles of inductive and hypothesis-driven science in the post-genomic era. Bioessays, 26, 99–105.
Kopka, J. (2006). Current challenges and developments in GC-MS based metabolite profiling technology. Journal of Biotechnology, 124, 312–322.
Li, B. Y., Hu, Y., Liang, Y. Z., Xie, P. S., & Du, Y. P. (2004). Quality evaluation of fingerprints of herbal medicine with chromatographic data. Analytica Chimica Acta, 514, 69–77.
Liang, Y. Z. (Ed.). (1996). White, grey and black multicomponent systems and their chemometric algorithms. Changsha, China: Hunan Publishing House of Science and technology.
Liang, Y. Z., Kvalheim, O. M., Rahmani, A., & Brereton, R. G. (1993). A 2-way procedure for background correction of chromatographic spectroscopic data by congruence analysis and least-squares fit of the zero-component regions—comparison with double-centering. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 18, 265–279.
Lu, H., Dunn, W. B., Shen, H., Kell, D. B., & Liang, Y. Z. (2008). Comparative evaluation of software for deconvolution of metabolomics data based on GC-TOF-MS. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27, 215–227.
Malmquist, G., & Danielsson, R. (1994). Alignment of chromatographic profiles for principal component analysis: A prerequisite for fingerprinting methods. Journal of Chromatography A, 687, 71–88.
Mashego, M. R., Rumbold, K., Mey, M. D., Vandamme, E., Soetaert, W., & Heijnen, J. J. (2007). Microbial metabolomics: Past, present and future methodologies. Biotechnology Letters, 29, 1–16.
Mulhern, S. M., Logue, M. E., & Butler, G. (2006). Candida albicans transcription factor Ace2 regulates metabolism and is required for filamentation in hypoxic conditions. Eukaryotic Cell, 5, 2001–2013.
Nicholson, J. K., & Wilson, I. D. (2003). Understanding ‘global’ systems biology: Metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2, 668–676.
Nielsen, N. P. V., Carstensen, J. M., & Smedsgaard, J. (1998). Aligning of single and multiple wavelength chromatographic profiles for chemometric data analysis using correlation optimised warping. Journal of Chromatography A, 805, 17–35.
O’Hagan, S. B., Dunn, W., Brown, M., Knowles, J. D., & Kell, D. B. (2005). Closed-loop, multiobjective optimization of analytical instrumentation: Gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry of the metabolomes of human serum and of yeast fermentations. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 290–303.
O’Hagan, S., Dunn, W. B., Knowles, J. D., Broadhurst, D., Williams, R., Ashworth, J. J., et al. (2007). Closed-loop, multiobjective optimization of two-dimensional gas chromatography/mass spectrometry for serum metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 79, 464–476.
Oliver, S. G. (2002). Functional genomics: Lessons from yeast. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 357, 17–23.
Oliver, S. G., Winson, M. K., Kell, D. B., & Baganz, F. (1998). Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends in Biotechnology, 16, 373–378.
Pace, N. R. (1997). A molecular view of microbial diversity and the biosphere. Science, 276, 734–740.
Pope, G. A., MacKenzie, D. A., Defemez, M., Aroso, M., Fuller, L. J., Mellon, F. A., et al. (2007). Metabolic footprinting as a tool for discriminating between brewing yeasts. Yeast, 24, 667–679.
Pravdova, V., Walczak, B., & Massart, D. L. (2002). A comparison of two algorithms for warping of analytical signals. Analytica Chimica Acta, 456, 77–92.
Raamsdonk, L. M., Teusink, B., Broadhurst, D., Zhang, N., Hayes, A., Walsh, M. C., et al. (2001). A functional genomics strategy that uses metabolome data to reveal the phenotype of silent mutations. Nature Biotechnology, 19, 45–50.
Rejtar, T., Chen, H. S., Andreev, V., Moskovets, E., & Karger, B. L. (2004). Increased identification of peptides by enhanced data processing of high-resolution MALDI TOF/TOF mass spectra prior to database searching. Analytical Chemistry, 76, 6017–6028.
Sadygov, R. G., Maroto, F. M., & Huhmer, A. F. R. (2006). ChromAlign: A two-step algorithmic procedure for time alignment of three-dimensional LC-MS chromatographic surfaces. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 8207–8217.
Sangster, T. P., Wingate, J. E., Burton, L., Teichert, F., & Wilson, I. D. (2007). Investigation of analytical variation in metabonomic analysis using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 21, 2965–2970.
Shao, X. G., Leung, A. K. M., & Chau, F. T. (2003). Wavelet: A new trend in chemistry. Accounts of Chemical Research, 36, 276–283.
Shen, H. L., Wang, J. H., Liang, Y. Z., Pettersson, K., Josefson, M., Gottfries, J., et al. (1997). Chemical rank estimation by multiresolution analysis for two-way data in the presence of background. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 37, 261–269.
Urbanczyk-Wochniak, E. (2003). Parallel analysis of transcript and metabolic profiles: A new approach in systems biology. EMBO Reports, 4, 989–993.
van den Berg, R. A., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Westerhuis, J. A., Smilde, A. K., & van der Werf, M. J. (2006). Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics, 7, 142–156.
van Winden, W. A., van Dam, J. C., Ras, C., Kleijn, R. J., Vinke, J. L., van Gulik, W. M., et al. (2005). Metabolic-flux analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK113-7D based on mass isotopomer measurements of 13C-labeled primary metabolites. FEMS Yeast Research, 5, 559–568.
Villas-Bôas, S. G., Roessner, U., Hansen, M. A. E., Smedsgaard, J., & Nielsen, J. (Eds.). (2007). Metabolome analysis: An introduction. New York: Wiley.
Vorsta, O., de Vosa, C. H. R., Lommena, A., Stapsa, R. V., Visser, R. G. F., Binoa, R. J., et al. (2005). A non-directed approach to the differential analysis of multiple LC–MS-derived metabolic profiles. Metabolomics, 1, 169–180.
Xu, C.-J., Liang, Y.-Z., Chau, F.-T., & Heyden, Y. V. (2006). Pretreatments of chromatographic fingerprints for quality control of herbal medicines. Journal of Chromatography A, 1134, 253–259.
Yevgeniya, I. S., Ugo, P., Boris, F. K., Wayne, R. M., & Bruce, S. K. (2005). Analytical precision, biological variation, and mathematical normalization in high data density metabolomics. Metabolomics, 1, 75–85.
Yi, L.-Z., He, J., Liang, Y.-Z., Yuan, D.-L., & Chau, F.-T. (2006). Plasma fatty acid metabolic profiling and biomarkers of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on GC/MS and PLS-LDA. FEBS Letters, 580, 6837–6845.
Acknowledgments
The MZmine program is downloaded free; details may be obtained from the website http://mzmine.sourceforge.net/. The experimental work was carried out in the Bioanalytical Sciences Group, Department of Chemistry, and Manchester Centre for Integrative Systems Biology, Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester. We are grateful to Warwick B. Dunn for helpful comments on the manuscript and Douglas B. Kell for his excellent scientific support. We thank Marie C. Brown and David Broadhurst for their helpful discussion. We also thank Siobhan Mulhern and Geraldine Butler of University College, Dublin for supplying the samples. This work was supported by grant China Partnering Award from BBSRC (grant PA 1479). H.L. also thanks National Natural Science Foundation of China for support of the projects (No. 20975115 and No. 20745005), China Hunan Provincial science and technology department for support of the project (No. 2009GK3095), Central South University for special support of the basic scientific research project (No. 2010QZZD007), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation for support of the project (No. 20100471230) and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Central South University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Gan, D., Zhang, Z. et al. Sample classification of GC-ToF-MS metabolomics data without the requirement for chromatographic deconvolution. Metabolomics 7, 191–205 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0247-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-010-0247-2