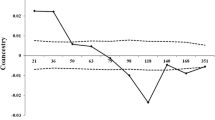
Abstract
Dipteryx alata is a Neotropical tree widely distributed throughout the Brazilian Cerrado biome and is popularly known as baru. In this study, we evaluated the mating system of D. alata and compared pollen dispersal patterns between the in situ and ex situ conditions. For this, we used 515 genotypes of adults, juveniles, and progeny from a natural population (in situ) in Orizona-GO, Brazil. In addition, we used 488 genotypes of adults and progeny from a germplasm collection (ex situ) located at the Federal University of Goiás. Both locations are situated in central Brazil. The genetic diversity, cross-pollination rates, and pollen dispersal distance under both conditions were estimated. Genetic diversity and polymorphism differed between the in situ and ex situ conditions. The average number of alleles found in situ (5.2) and ex situ (6.2) showed that the germplasm collection stores greater genetic diversity than the in situ condition. Cross-pollination detected among mother trees under both the in situ and ex situ conditions were high (tm = 0.815 and tm = 0.934, respectively), indicating that the species has a mixed reproductive system that was predominantly allogamous. The difference between tm and ts indicated that the in situ condition shows greater biparental inbreeding. Our results showed that, across generations, the ex situ condition preserved a larger number of alleles, confirming that the D. alata germplasm collection plays a role in conserving genetic diversity. The presence of self-fertilization suggests self-compatibility. Paternity correlation and the dispersal distance of the pollen donors were higher in the in situ condition, a maximum distance of 2.9 km of pollen flow. This can be explained by the number of pollinators and tree spatial distribution.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida SP de, Proença CEB, Sano SM, Ribeiro JF (1998) Cerrado: espécies vegetais úteis
Antiqueira LMOR, Kageyama PY (2015) Reproductive system and pollen flow in progenies of Qualea grandiflora mart., a typical species of the brazilian Cerrado. Rev Árvore 39:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-67622015000200013
Antiqueira LMOR, Kageyama PY (2014) Genetic diversity of four populations of Qualea grandiflora Mart. In fragments of the Brazilian Cerrado. Genetica 142:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-013-9750-5
Baldauf C, Ciampi-Guillardi M, Aguirra TJ, Corrêa CE, dos Santos FAM, de Souza AP, Sebbenn AM (2014) Genetic diversity, spatial genetic structure and realised seed and pollen dispersal of Himatanthus drasticus (Apocynaceae) in the Brazilian savanna. Conserv Genet 15:1073–1083. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-014-0600-5
de Barbosa AC, OF, Collevatti RG, Chaves LJ et al (2015) Range-wide genetic differentiation of Eugenia dysenterica (Myrtaceae) populations in Brazilian Cerrado. Biochem Syst Ecol 59:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2015.02.004
Bernardes V, dos Anjos DE, de Gondim SG, CA et al (2014) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in Byrsonima cydoniifolia (Malpighiaceae) and cross-amplification in B. crassifolia. Appl. Plant Sci 2:1400016. https://doi.org/10.3732/apps.1400016
Braga AC, Collevatti RG (2011) Temporal variation in pollen dispersal and breeding structure in a bee-pollinated Neotropical tree. Heredity (Edinb) 106:911–919. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2010.134
Chybicki IJ, Burczyk J (2009) Simultaneous estimation of null alleles and inbreeding coefficients. J Hered 100:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esn088
Collevatti RG, Estolano R, Garcia SF, Hay JD (2010) Short-distance pollen dispersal and high self-pollination in a bat-pollinated neotropical tree. Tree Genet Genomes 6:555–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0271-4
Collevatti RG, Olivatti AM, Telles MPC, Chaves LJ (2016) Gene flow among Hancornia speciosa (Apocynaceae) varieties and hybrid fitness. Tree Genet Genomes 12:74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1031-x
Collevatti RG, Telles MPC, Nabout JC, Chaves LJ, Soares TN (2013) Demographic history and the low genetic diversity in Dipteryx alata (Fabaceae) from Brazilian Neotropical savannas. Heredity (Edinb) 111:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2013.23
Corrêa GDC, Da Rocha MR, Naves RV (2000) Germinação de sementes e emergência de plântulas de baru (Dipteryx alata Vog.) nos cerrados do Estado de Goiás. Pesqui Agropecuária Trop 30:17–23. https://doi.org/10.5216/pat.v30i2.2580
Corrêa MP (1984) Dicionário de plantas úteis do Brasil e das exóticas cultivadas. In: Dicionário de plantas úteis do Brasil e das exóticas cultivadas. Imprensa Nacional Brasília
Costa CF, Collevatti RG, Chaves LJ, Lima JS, Soares TN, Telles MPC (2017) Genetic diversity and fine-scale genetic structure in Hancornia speciosa Gomes ( Apocynaceae ). Biochem Syst Ecol J 72:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2017.03.001
Cruz CD, Ferreira FM, Pessoni LA (2011) Biometria aplicada ao estudo da diversidade genética
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Earl DA, VonHold BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Ellstrand NC (2014) Is gene flow the most important evolutionary force in plants? Am J Bot 101:737–753. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1400024
Engels JMM, Visser L (2003) A guide to effective management of germplasm collections. IPGRI Handbooks for Genebanks, Maccarese Rome, Italy
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Felfili JM, Silva Júnior MC, Sevilha AC, et al (2004) Diversity, floristic and structural patterns of Cerrado vegetation in Central Brazil. Plant Ecol Former ‘Vegetation’ 175:37–46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VEGE.0000048090.07022.02
Feres JM, Sebbenn AM, Guidugli MC, Mestriner MA, Moraes MLT, Alzate-Marin AL (2012) Mating system parameters at hierarchical levels of fruits, individuals and populations in the Brazilian insect-pollinated tropical tree, Tabebuia roseo-alba (Bignoniaceae). Conserv Genet 13:393–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-011-0292-z
Gepts P (2006) Plant genetic resources conservation and utilization: the accomplishments and future of a societal insurance policy. Crop Sci 46:2278–2292. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.03.0169gas
Guimarães RA, Telles MPC, Antunes AM et al (2017) Discovery and characterization of new microsatellite loci in Dipteryx alata vogel (Fabaceae) using next-generation sequencing data. Genet Mol Res 16:1–6. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr16029639
Hoban S, Strand A (2015) Ex situ seed collections will benefit from considering spatial sampling design and species reproductive biology. Biol Conserv 187:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2015.04.023
Kalinowski ST, Taper ML, Marshall TC (2007) Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol Ecol 16:1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03089.x
Lewis PO, Zaykin D (2001) Genetic data analysis: computer program for the analysis of allelic data
Manoel RO, Alves PF, Dourado CL, Gaino APSC, Freitas MLM, Moraes MLT, Sebbenn AM (2012) Contemporary pollen flow, mating patterns and effective population size inferred from paternity analysis in a small fragmented population of the Neotropical tree Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. (Leguminosae-Caesalpinioideae). Conserv Genet 13:613–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-011-0311-0
Martins PS (1987) Estrutura populacional, fluxo gênico e conservação “in situ”. Ipef:71–78
Melo DB, Diniz-Filho JAF, Oliveira G, Santana LL, Soares TN, Chaves LJ, Naves RV, Collevatti RG, de Telles MP, C (2010) Optimizing sampling efforts for ex situ conservation of genetic variability of Dipteryx alata Vogel. BMC Proc 5:P18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1753-6561-5-S7-P18
de Moraes MLT, Sebbenn AM (2011) Pollen dispersal between isolated trees in the Brazilian savannah: a case study of the neotropical tree Hymenaea stigonocarpa. Biotropica 43:192–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7429.2010.00679.x
de Pineli LDL, O, de Carvalho MV, de Aguiar L, A, de Oliveira GT, Celestino SMC, Botelho RBA, Chiarello MD (2015) Use of baru (Brazilian almond) waste from physical extraction of oil to produce fl our and cookies. LWT - Food Sci Technol 60:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.09.035
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01758.x
Van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) MICRO - CHECKER: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol Ecol Notes 4:535–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2004.00684.x
Rabelo SG, Teixeira CF, Telles MPC, Collevatti RG (2011) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for Lychnophora ericoides, an endangered Cerrado shrub species. Conserv Genet Resour 3:741–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9447-y
Rajpurohit D, Jhang T (2015) In situ and ex situ conservation of plant genetic resources and traditional knowledge. In: Salgotra RK, Gupta BB (eds) Plant genetic resources and traditional knowledge for food security. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 137–162
Rao VR, Hodgkin T (2002) Genetic diversity and conservation and utilization of plant genetic resources. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 68:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013359015812
Richardson JL, Urban MC, Bolnick DI, Skelly DK (2014) Microgeographic adaptation and the spatial scale of evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 29:165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2014.01.002
Ritland K (2002) Extensions of models for the estimation of mating systems using n independent loci. Heredity 88:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6800029
Rodrigues EB, Collevatti RG, Chaves LJ, Moreira LR, Telles MPC (2016) Mating system and pollen dispersal in Eugenia dysenterica (Myrtaceae) germplasm collection: tools for conservation and domestication. Genetica 144:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-016-9884-3
Sano SM, Ribeiro JF, Brito MA (2004) Baru: biologia e uso. Embrapa cerrados -Brasilia DF
Santos-Filho PS (1995) Fragmentação de habitats: implicações para conservação in situ. Oecologia Bras 1:365–393
Santos AM, da Rosado SC, S, Oliveira AN (2014) Estimation of genetic parameters and verification of early selection efficiency in baru (Dipteryx alata). Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 14:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1590/1984-70332014v14n4a37
Scariot AO, Servilha AC (2007) Conservação in situ de recursos genéticos vegetais. In: Nass LL (ed) Recursos genéticos vegetais, 1a. Nass, Luciano Lourenço, Brasilia, DF, pp 473–502
Sebbenn AM (2002) Número de árvores matrizes e conceitos genéticos na coleta de sementes para reflorestamentos com espécies nativas. Rev do Inst Flor 14:115–132
Slatkin M (1987) Gene flow and the geographic structure of natural populations. Sci 236:787–792
Soares TN, Chaves LJ, de Telles M, CP et al (2008) Distribuição espacial da variabilidade genética intrapopulacional de Dipteryx alata. Pesqui Agropecuária Bras 43:1151–1158
Soares TN, Diniz-Filho JAF, Nabout JC, de Campos Telles MP, Terribile LC, Chaves LJ (2015) Patterns of genetic variability in central and peripheral populations of Dipteryx alata (Fabaceae) in the Brazilian Cerrado. Plant Syst Evol 301:1315–1324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-014-1155-0
Soares TN, Melo DB, Resende LV, Vianello RP, Chaves LJ, Collevatti RG, Telles MPC (2012) Development of microsatellite markers for the Neotropical tree species Dipteryx alata (Fabaceae). Am J Bot 99:e72–e73. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1100377
Tambarussi EV, Sebbenn AM, Vencovsky R et al (2017) Dipteryx alata Vogel (Fabaceae), a Neotropical tree with high levels of selfing: implications for conservation and breeding programs. Ann For Res. https://doi.org/10.15287/afr.2017.842
Tarazi R, Moreno MA, Gandara FB, Ferraz EM, Moraes MLT, Vinson CC, Ciampi AY, Vencovsky R, Kageyama PY (2010) High levels of genetic differentiation and selfing in the Brazilian Cerrado fruit tree Dipteryx alata Vog. (Fabaceae). Genet Mol Biol 33:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572010005000007
Vieira RF, de Ferreira T, SAC, Silva DB et al (2006) Frutas nativas da região centro-oeste do Brasil. Embrapa recursos genéticos e biotecnologia Brasília, DF
Wagner HW, Sefc KM (1999) IDENTITY 1.0 Centre for applied genetics
Williams CG (2017) How meso-scale pollen dispersal and its gene flow shape gene conservation decisions. New For 48:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-017-9574-8
Funding
Our research has been continuously supported by several grants and fellowships to the research network Núcleo de excelência em recursos genéticos vegetais do Cerrado (CERGEN) (PRONEX/FAPEG/CNPq, Proc. 201210267000802) and “Chamada pública 08/2014 Capes/FAPEG. Work by R. A. Guimarães and K. M. Corrêa was supported by a fellowship from CAPES, and work by M. P. C. Telles, L. J. Chaves, and T. N. Soares were also supported by productivity grants from CNPq. Current research is developed in the context of National Institutes for Science and Technology (INCT) in Ecology, Evolution and Biodiversity Conservation, supported by MCTIC/CNpq (proc. 465610/2014-5) and FAPEG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by J. Wright
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 197 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guimarães, R.A., Corrêa Miranda, K.M., Chaves, L.J. et al. Mating system and pollen dispersal in Dipteryx alata Vogel (Leguminosae): comparing in situ and ex situ conditions. Tree Genetics & Genomes 15, 28 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-019-1337-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-019-1337-6