Abstract
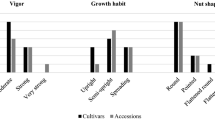
European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.), cultivated in several areas of the world including Europe, Anatolia, and the USA, is an economically important nut crop due to its high mineral, oleic acid, amino acid, and phenolic compound content and pleasant flavor. This study examined molecular genetic diversity and population structure of 54 wild accessions and 48 cultivars from the Slovenian national hazelnut collection using amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Eleven AFLP primer combinations and 49 SSR markers yielded 532 and 504 polymorphic fragments, respectively. As expected for a wind-pollinated, self-incompatible species, levels of genetic diversity were high with cultivars and wild accessions having mean dissimilarity values of 0.50 and 0.60, respectively. In general, cultivars and wild accessions clustered separately in dendrogram, principal coordinate, and population structure analyses with regional clustering of the wild material. The accessions were also characterized for ten nut and seven kernel traits and some wild accessions were shown to have breeding potential. Morphological principal component analysis showed distinct clustering of cultivars and wild accessions. An association mapping panel composed of 64 hazelnut cultivars and wild accessions had considerable variation for the nut and kernel quality traits. Morphological and molecular data were associated to identify markers controlling the traits. In all, 49 SSR markers were significantly associated with nut and kernel traits [P < 0.0001 and LD value (r 2) = 0.15–0.50]. This work is the first use of association mapping in hazelnut and has identified molecular markers associated with important quality parameters in this important nut crop.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdurakhmonov IY, Kohel RJ, Yu JZ, Pepper AE, Abdullaev AA, Kushanov FN, Abdukarimov A (2008) Molecular diversity and association mapping of fiber quality traits in exotic G. hirsutum L. germplasm. Genomics 92:478–487
Bacchetta L, Avanzato D, Di Giovanni B, Botta R, Boccacci P, Drogoudi P, Metzidakis I, Rovira M, Sarraquigne JP, Silva AP, Solar A, Spera D (2014) The reorganisation of European hazelnut genetic resources in the SAFENUT (AGRI GEN RES) project. Acta Hort 1052:67–74
Balta MF, Yarılgaç T, Aşkın MA, Kuçuk M, Balta F, Özrenk K (2006) Determination of fatty acid compositions, oil contents and some quality traits of hazelnut genetic resources grown in eastern Anatolia of Turkey. J Food Compos Anal 19:681–686
Bassil NV, Botta R, Mehlenbacher SA (2005) Additional microsatellite markers of the European hazelnut. Acta Hortic 686:105
Bassil N, Boccacci P, Botta R, Postman J, Mehlenbacher SA (2013) Nuclear and chloroplast microsatellite markers to assess genetic diversity and evolution in hazelnut species, hybrids and cultivars. Gen Res Crop Evol 60:543–568
Beltramo C, Valentini N, Portis E, Torello D, Boccacci P, Angelica M, Botta R (2016) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis in European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.). Mol Breed 36:27
Boccacci P, Botta R (2009) Investigating the origin of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars using chloroplast microsatellites. Gen Res Crop Evol 56:851–859
Boccacci P, Botta R (2010) Microsatellite variability and genetic structure in hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars from different growing regions. Sci Hortic 124:128–133
Boccacci P, Akkak A, Bassil NV, Mehlenbacher SA, Botta R (2005) Characterization and evaluation of microsatellite loci in European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) and their transferability to other Corylus species. Mol Ecol Notes 5:934–937
Boccacci P, Akkak A, Botta R (2006) DNA typing and genetic relationship among European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars using microsatellite markers. Genome 49:598–611
Boccacci P, Botta R, Rovira M (2008) Genetic diversity of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) germplasm in northeastern Spain. Hort Sci 43:667–672
Boccacci P, Aramini M, Valentini N, Bacchetta L, Rovira M, Drogoudi P, Silva AP, Solar A, Calizzano F, Erdogan V, Cristoferi V, Ciarmiello LF, Contessa C, Ferreira JJ, Marra FP, Botta R (2013) Molecular and morphological diversity of on-farm hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) landraces from southern Europe and their role in the origin and diffusion of cultivated germplasm. Tree Genet Genomes 9:1465–1480
Boccacci P, Beltramo C, Prando MS, Lembo A, Sartor C, Mehlenbacher SA, Botta R, Marinoni DT (2015) In silico mining, characterization and cross-species transferability of EST-SSR markers for European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.). Mol Breed 35:1–14
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Campa A, Trabanco N, Pérez-Vega E, Rovira M, Ferreira JJ (2011) Genetic relationship between cultivated and wild hazelnuts (Corylus avellana L.) collected in northern Spain. Plant Breed 130:360–366
Celik I, Camci H, Kose A, Kosar FC, Doganlar S, Frary A (2016) Molecular genetic diversity and association mapping of morphine content and agronomic traits in Turkish opium poppy (Papaver somniferum) germplasm. Mol Breed 36(4):1–13
Cristofori V, Ferramondo S, Bertazza G, Bignami C (2008) Nut and kernel traits and chemical composition of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars. J Sci Food Agric 88:1091–1098
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Earl DA, von Holdt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Ferrari M, Gori M, Monnanni R, Buiatti M, Scarascia Mugnozza GT, De Pace C (2004) DNA fingerprinting of Corylus avellana L. accessions revealed by AFLP molecular markers. Acta Hortic 686:125–134
Ferreira JJ, Garcia-Gonzalez C, Tous J, Rovira M (2010) Genetic diversity revealed by morphological traits and ISSR markers in hazelnut germplasm from northern Spain. Plant Breed 129:435–441
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, FAOSTAT (2013) http://www.fao.org/corp/statistics/en. Accessed 07.07.2014
Fulton TM, Chunwongse J, Tanksley SD (1995) Microprep protocol for extraction of DNA from tomato and other herbaceous plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 13:207–207
Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Di Bernanrdo G, De Masi L, Galano G, Cascino A (1999) Identification of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars by RAPD analysis. Plant Cell Rep 18:652–655
Gao H, Williamson S, Bustamante CD (2007) A Markov chain Monte Carlo approach for joint inference of population structure and inbreeding rates from multilocus genotype data. Genetics 176:1635–1651
Gökirmak T, Mehlenbacher SA, Bassil NV (2009) Characterization of European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars using SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56:147–172
Gómez G, Álvarez MF, Mosquera T (2011) Association mapping, a method to detect quantitative trait loci: statistical bases. Agronomía Colombiana 29:367–376
Gurcan K, Mehlenbacher SA (2010) Development of microsatellite marker loci for European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) from ISSR fragments. Mol Breed 26:551–559
Gurcan K, Mehlenbacher SA, Botta R, Boccacci P (2010a) Development, characterization, segregation, and mapping of microsatellite markers for European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) from enriched genomic libraries and usefulness in genetic diversity studies. Tree Genet Genomes 6:513–531
Gurcan K, Mehlenbacher SA, Erdogan V (2010b) Genetic diversity in hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars from Black Sea countries assessed using SSR markers. Plant Breed 129:422–434
Kafkas S, Doğan Y, Sabır A, Turan A, Seker H (2009) Genetic characterization of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cultivars from Turkey using molecular markers. Hortscience 44:1557–1561
Khan MA, Korban SS (2012) Association mapping in forest trees and fruit crops. J Exp Bot 63:4045–4060
Leinemann L, Steiner W, Hosius B, Kuchma O, Arenhövel W, Fussi B, Finkeldey R (2013) Genetic variation of chloroplast and nuclear markers in natural populations of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) in Germany. Plant Syst Evol 299:369–378
Martins S, Simões F, Mendonça D, Matos J, Silva AP, Carnide V (2013) Chloroplast SSR genetic diversity indicates a refuge for Corylus avellana in northern Portugal. Gen Res Crop Evol 60:1289–1295
Martins S, Simões F, Matos J, Silva AP, Carnide V (2014) Genetic relationship among wild, landraces and cultivars of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) from Portugal revealed through ISSR and AFLP markers. Plant Syst Evol 300:1035–1046
Martins S, Simões F, Mendonça D, Matos J, Silva AP, Carnide V (2015) Western European wild and landraces hazelnuts evaluated by SSR markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1–9
Mehlenbacher SA, Brown RN, Nouhra ER, Gokirmak T, Bassil NV, Kubisiak TL (2006) A genetic linkage map for hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) based on RAPD and SSR markers. Genome 49:122–133
Miaja ML, Vallania R, Me C, Akkak O, Nassi O, Lepori G (2001) Varietal characterization in hazelnut by RAPD markers. Acta Hortic 556:247–250
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 70:3321–3323
Norusis MJ (2010) PASW statistics 18 advanced statistical procedures. Prentice Hall Press, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Ozdemir F, Akinci I (2004) Physical and nutritional properties of four major commercial Turkish hazelnut varieties. J Food Eng 63:341–347
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin software. Available: http://darwin.cirad.fr/darwin
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Rosenberg NA, Donnelly P (2000) Association mapping in structured populations. Am J Hum Genet 67:170–181
Roldàn-Ruiz I, Dendauw J, Van Bockstaele E, Depicker A, De Loose M (2000) AFLP markers reveal high polymorphic rates in ryegrasses (Lolium spp.). Mol Breed 6:125–134
Romero A, Tous J, Durfort M, Rius M (2003) Histology of hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) kernel affected by brown spots in kernel cavity physiopathy. Span J Agr Res 1:47–53
Slatnar A, Mikulic-Petkovsek M, Stampar F, VebericR SA (2014) HPLC-MS identification and quantification of phenolic compounds in hazelnut kernels, oil and bagasse pellets. Food Res Int 64:783–789
Solar A, Stampar F (2009) Performance of hazelnut cultivars from Oregon in northeastern Slovenia. HortTechnology 19:653–659
Solar A, Stampar F (2011) Characterisation of selected hazelnut cultivars: phenology, growing and yielding capacity, market quality and nutraceutical value. J Sci Food Agr 91:1205–1212
Stich B, Melchinger AE, Frisch M, Maurer HP, Heckenberger M, Reif JC (2005) Linkage disequilibrium in European elite maize germplasm investigated with SSRs. Theor Appl Genet 111:723–730
Storey JD (2002) A direct approach to false discovery rates. J R Stat Soc Ser B 64:479–498
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) R: statistical significance for genome-wide experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:9440–9445
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Teviotdale BL, Michailides TJ, Pscheidt JW (2002) Compendium of nut crop diseases in temperate zones. APS Press, St. Paul, MN
United Nations (2010) Unece Standard DDP-04. https://www.nutfruit.org/wp-continguts/exportacions_mycored/standard-11_4597.pdf. Accessed 07.07.2014
Vos F, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new concept for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Xu YX, Hanna MA (2010) Evaluation of Nebraska hybrid hazelnuts: nut/kernel characteristics, kernel proximate composition, and oil and protein properties. Ind Crop Prod 31:84–91
Zhu C, Gore M, Buckler ES, Yu J (2008) Status and prospects of association mapping in plants. The Plant Genome 1:5–20
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK, project no: 212T201). It was carried out in the frame of The Bilateral Scientific and Technological Cooperation between the Republic of Slovenia and Turkey, BI-TR/13-15-003. We thank Amy Frary for review of the manuscript.
Author contribution statement
SCO and SEO performed laboratory experiments and drafted manuscript; SCO analyzed the genetic diversity data; IC analyzed the association mapping data; FS, RV, and AS performed all morphological characterization; AF helped design the study and write the manuscript; SD designed the study and received funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data archiving
Data will be available at http://plantmolgen.iyte.edu.tr/data/ upon publication.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Troggio
SC. Ozturk and SE Ozturk contributed equally to this paper
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, S.C., Ozturk, S.E., Celik, I. et al. Molecular genetic diversity and association mapping of nut and kernel traits in Slovenian hazelnut (Corylus avellana) germplasm. Tree Genetics & Genomes 13, 16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1098-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1098-4