Abstract
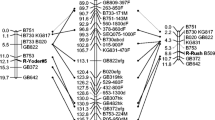
Eastern filbert blight (EFB), caused by the pyrenomycete Anisogramma anomala (Peck) E. Müller, is a major disease problem and production constraint in orchards of European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) in Oregon’s Willamette Valley. Host genetic resistance is viewed as the most economical means of controlling this disease. A dominant resistance gene from “Gasaway” has been used extensively in the hazelnut breeding program at Oregon State University, but concern about the durability of a single resistance gene stimulated a search for new sources of resistance. “Ratoli,” a minor cultivar from Spain, showed no signs or symptoms of the fungus following a series of inoculations. The objective of this study was to study segregation for disease response in two progenies from crosses of Ratoli with susceptible selections and identify linked DNA markers. About half of the seedlings were resistant, suggesting control by a dominant allele at a single locus. A total of 900 random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers and 64 amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) primer combinations were screened. Four RAPD markers and two ALFP markers were identified and a linkage map constructed. On this map, disease resistance was flanked by AFLP marker C4-255 and RAPD marker G17-800 at distances of 0.4 cM and 2.8 cM, respectively. Based on co-segregation with SSR markers, Ratoli resistance was assigned to linkage group 7 while Gasaway resistance is on linkage group 6. Ratoli provides a novel source of EFB resistance, and robust RAPD marker G17-800 is useful for marker-assisted selection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassil NV, Botta R, Mehlenbacher SA (2005a) Microsatellite markers in hazelnut: isolation, characterization and cross-species amplification. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 130:543–549
Bassil NV, Botta R, Mehlenbacher SA (2005b) Additional microsatellite markers of the European hazelnut. Acta Hort 686:105–110
Boccacci P, Akkak A, Bassil NV, Mehlenbacher SA, Botta R (2005) Characterization and evaluation of microsatellite loci in European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) and their transferability to other Corylus species. Mol Ecol Notes 5:934–937
Cameron HR (1976) Eastern filbert blight established in the Pacific Northwest. Plant Dis Rep 60:737–740
Chen H, Mehlenbacher SA, Smith DC (2005) AFLP markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance from OSU 408.040 hazelnut. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 130:412–417
Chen H, Mehlenbacher SA, Smith DC (2007) Hazelnut accessions provide new sources of resistance to eastern filbert blight. HortScience 42:466–469
Coyne CJ, Mehlenbacher SA, Hampton RO, Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB (1996) Use of ELISA to rapidly screen hazelnut for resistance to eastern filbert blight. Plant Dis 80:1327–1330
Davison AR, Davidson RM Jr (1973) Apioporthe and Monochaetia cankers reported in western Washington. Plant Dis Rep 57:522–523
Devos KM, Gale MD (1992) The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84:567–572
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2007) Production yearbook. http://faostat.fao.org/. Accessed 1 Dec 2009
Gökirmak T, Mehlenbacher SA, Bassil NA (2009) Characterization of European hazelnut (Corylus avellana) cultivars using SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56:147–172
Gürcan K (2009) Simple sequence repeat marker development and use in European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.). PhD Dissertation. Department of Horticulture, Oregon State University, Corvallis, Oregon
Gürcan K, Mehlenbacher SA (2010) Development of microsatellite marker loci for European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) from ISSR fragments. Mol Breeding doi:10.1007/s11032-010-9464-7
Gürcan K, Mehlenbacher SA, Botta R, Boccacci P (2010) Development, characterization, segregation, and mapping of microsatellite for European hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) from enriched genomic libraries and usefulness in genetic diversity studies. Tree Genetics & Genomes 6:513–531. doi:10.1007/s11295-010-0269-y
Hazelnut Marketing Board (2004) A filbert or hazelnut? Food safety information http://oregonhazelnuts.org/. Accessed 12 Mar 2007
Johnson KB, Mehlenbacher SA, Stone JK, Pscheidt JW (1996) Eastern filbert blight of European hazelnut—it’s becoming a manageable disease. Plant Dis 80:1308–1316
Lunde CF, Mehlenbacher SA, Smith DC (2000) Survey of hazelnut cultivars for response to eastern filbert blight inoculation. HortScience 35:729–731
Mehlenbacher SA (1994) Genetic improvement of hazelnut. Acta Hort 351:23–28
Mehlenbacher SA, Thompson MM, Cameron HR (1991) Occurrence and inheritance of resistance to eastern filbert blight in ‘Gasaway’ hazelnut. HortScience 26:410–411
Mehlenbacher SA, Brown RN, Davis JW, Chen H, Bassil NV, Smith DC (2004) RAPD markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance in Corylus avellana. Theor Appl Genet 108:651–656
Mehlenbacher SA, Brown RN, Nouhra EN, Gökirmak T, Bassil NV, Kubisiak TL (2006) A genetic linkage map for hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) based on RAPD and SSR markers. Genome 49:122–133
Meunier JR, Grimont PAD (1993) Factors affecting reproducibility of random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting. Res Microbiol 144:373–379
Mohan MS, Nair A, Bhaqwat TG, Krishna M, Yano CR, Bhatia T, Sasaki (1997) Genome mapping, molecular markers and marker-assisted selection in crop plants. Mol Breed 3:87–103
Molnar TJ (2006) Genetic resistance to eastern filbert blight in hazelnut (Corylus). PhD Dissertation. Department of Plant Biology. Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey. New Brunswick, NJ
Molnar TJ, Baxer SN, Goffreda JC (2005) Accelerated screening of hazelnut seedlings for resistance to eastern filbert blight. HortScience 40:1667–1669
Orita M, Suzuki Y, Sekiya Y, Hayashi K (1989a) Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5:874–879
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Sekiya T (1989b) Detection of polymorphism of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single strand conformation polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2766–2770
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Theiling KM, Griesbach JA (1992) Distribution and characteristics of the eastern filbert blight epidemic in western Oregon. Plant Dis 76:1179–1182
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Mehlenbacher SA, Pscheidt JW (1993) Susceptibility of European hazelnut clones to eastern filbert blight. Plant Dis 77:261–266
Pinkerton JN, Stone JK, Nelson SJ, Johnson KB (1995) Infection of European hazelnut by Anisogramma anomala: ascospore adhesion, mode of penetration of immature shoots, and host response. Phytopathology 88:1260–1268
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Stone JK, Ivors KL (1998a) Factors affecting the release of ascospores of Anisogramma anomala. Phytopathology 88:122–128
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Stone JK, Ivors KL (1998b) Maturation and seasonal discharge pattern of ascospores of Anisogramma anomala. Phytopathology 88:1165–1173
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Aylor DE, Stone JK (2001) Spatial and temporal increase of eastern filbert blight in European hazelnut orchards in the Pacific Northwest. Phytopathology 91:1214–1223
Pscheidt JW (2006) Potential EFB control programs. Proc Nut Grow Soc Or Wash B C 91:72–78
Staub J, Serquen F (1996) Genetic markers, map construction, and their application in plant breeding. HortScience 31:729–741
Stone JK, Johnson KB, Pinkerton JN, Pscheidt JW (1992) Natural infection period and susceptibility of vegetative seedlings of European hazelnut to Anisogramma anomala. Plant Dis 76:348–352
Tasias Valls J (1975) El avellano en la provincia de Tarragona. Excma. Diputacion Provincial de Tarragona, Fundacion Servicio Agropecuario Provincial. Tarragona, Spain (in Spanish)
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2006) JoinMap 4.0. Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Kyazama B.V., Wageningen, Netherlands
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kulper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Williams J, Kubelik A, Livak K, Rafalski J, Tingey S (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Yi G, Lee SK, Hong YK, Cho TYC, Nam MH, Kim SC, Han SS, Wang GL, Hahn TR, Ronald PC, Jeon JS (2004) Use of Pi5(t) markers in marker-assisted selection to screen for cultivars with resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Theor Appl Genet 109:978–985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Grattapaglia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sathuvalli, V.R., Chen, H., Mehlenbacher, S.A. et al. DNA markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance in “Ratoli” hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.). Tree Genetics & Genomes 7, 337–345 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0335-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0335-5