Abstract
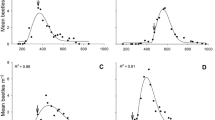
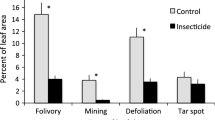
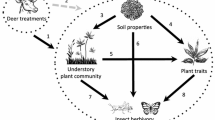
Wild ungulates are key determinants in shaping boreal plant communities, and may also affect ecosystem function through inducing the plant defence systems of key plant species. We examined whether winter browsing by deer could increase the resistance of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus). We used three indicators of induced bilberry defence: reduced growth (a), reduced reproduction (b) and decreased insect herbivory (c) in focal plants. In a field experiment, using a randomised block design, we exposed half of plants twice in winter to exogenously applied methyl jasmonate (MeJA) and crossed this factor with randomly selecting browsed and unbrowsed plants. We predicted that MeJA-plants would have significant lower growth, reproduction and insect herbivory than Control plants. We also expected that Browsed plants would experience similar negative effects and that there would be an interaction between MeJa and Browsed indicating a possible additive effect. Growth, flowering and insect herbivory were significantly lower in MeJA than in Control, as expected. We did not find the same reduction for Browsed and no significant interaction between factors. The combined treatment, unexpectedly, flowered more and showed higher levels of insect herbivory than MeJA. Our study showed that defence responses of bilberry may be induced by exogenously-applied MeJA in winter. Our study could not confirm whether winter browsing by deer can induce the same defence responses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarssen LW, Irwin DL (1991) What selection: herbivory or competition? Oikos 60:261–262. doi:10.2307/3544874
Agrawal AA (2011) Current trends in the evolutionary ecology of plant defence. Func Ecol 25:420–432. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2435.2010.01796.x
Baldwin IT (1996) Methyl jasmonate-induced nicotine production in Nicotiana attenuata: inducing defenses in the field without wounding. Entomol Exp Appl 80:213–220
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48. doi:10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bryant JP (2003) Winter browsing on Alaska feltleaf willow twigs improves leaf nutritional value for snowshoe hares in summer. Oikos 102:25–32
Cipollini DF, Sipe ML (2001) Jasmonic acid treatment and mammalian herbivory differentially affect chemical defenses and growth of wild mustard (Brassica kaber). Chemoecology 11:137–143. doi:10.1007/s00049-001-8319-4
Côte SD, Rooney TP, Tremblay J-P, Dussault C, Waller DM (2004) Ecological impacts of deer overabundance. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 35:113–147
Crawley M (2013) The R book, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Dahlgren J, Oksanen L, Sjödin M, Olofsson J (2007) Interactions between gray-sided voles (Clethrionomys rufucanus) and bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus), their main winter food plant. Oecologia 152:525–532
Danell K, Huss-Danell K, Bergstrom R (1985) Interactions between browsing moose and two species of birch in Sweden. Ecology 66:1867–1878. doi:10.2307/2937382
den Herder M, Bergstrom R, Niemela P, Danell K, Lindgren M (2009) Effects of natural winter browsing and simulated summer browsing by moose on growth and shoot biomass of birch and its associated invertebrate fauna. Ann Zool Fenn 46:63–74
Eriksson O, Fröborg H (1996) “Windows of opportunity” for recruitment in long-lived clonal plants: experimental studies of seedling establishment in Vaccinium shrubs. Can J Bot 74:1369–1374
Flower-Ellis JGK (1971) Age structure and dynamics in stands of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.). PhD, Royal College of Forestry
Fornara DA, Du Toit JT (2008) Browsing-induced effects on leaf litter quality and decomposition in a southern African savanna. Ecosystems 11:238–249. doi:10.1007/s10021-007-9119-7
Hegland SJ, Rydgren K (2016) Eaten but not always beaten: winners and losers along a red deer herbivory gradient in boreal forest. J Veg Sci 27:111–122. doi:10.1111/jvs.12339
Hegland SJ, Rydgren K, Seldal T (2005) The response of Vaccinium myrtillus to variations in grazing intensity in a Scandinavian pine forest on the island of Svanøy. Can J Bot 83:1638–1644
Hegland SJ, Jongejans E, Rydgren K (2010) Investigating the interaction between ungulate grazing and resource effects on Vaccinium myrtillus populations with integral projection models. Oecologia 163:695–706. doi:10.1007/s00442-010-1616-2
Hegland SJ, Lilleeng MS, Moe SR (2013) Old-growth forest floor richness increases with red deer herbivory intensity. For Ecol Manag 310:267–274. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2013.08.031
Hidding B, Tremblay J-P, Côté SD (2013) A large herbivore triggers alternative successional trajectories in the boreal forest. Ecology 94:2852–2860. doi:10.1890/12-2015.1
Hjältén J, Danell K, Ericson L (2004) Hare and vole browsing preferences during winter. Acta Theriol 49:53–62
Hjeljord O, Hövik N, Pedersen HB (1990) Choice of feeding sites by moose during summer, the influence of forest structure and plant phenology. Ecography 13:281–292. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.1990.tb00620.x
Howe GA, Jander G (2008) Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Ann Rev Plant Biol 59:41–66. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092825
Jacquemart AL (1993) Floral visitors of Vaccinium species in the high Ardennes, Belgium. Flora 188:263–273
Jacquemart AL (1997) Pollen limitation in three sympatric species of Vaccinium (Ericaceae) in the upper Ardennes, Belgium. Plant Syst Evol 207:159–172
Jacquemart AL, Thompson JD (1996) Floral and pollination biology of three sympatric Vaccinium (Ericaceae) species in the upper Ardennes, Belgium. Can J Bot 74:210–221
Karban R, Yang LH, Edwards KF (2014) Volatile communication between plants that affects herbivory: a meta-analysis. Ecol Lett 17:44–52. doi:10.1111/ele.12205
Kuijper DPJ, Cromsigt J, Jedrzejewska B, Miscicki S, Churski M, Jedrzejewski W, Kweczlich I (2010) Bottom-up versus top-down control of tree regeneration in the Bialowieza Primeval Forest, Poland. J Ecol 98:888–899. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2010.01656.x
Kuusipalo J (1988) Factors affecting the fruiting of bilberries: an anlysis of categorical data set. Vegetatio 76:71–77
Lindgren A, Klint J, Moen J (2007) Defense mechanisms against grazing: a study of trypsin inhibitor responses to simulated grazing in the sedge Carex bigelowii. Oikos 116:1540–1546. doi:10.1111/j.2007.0030-1299.15481.x
Mathisen KM, Buhtz F, Danell K, Bergström R, Skarpe C, Suominen O, Persson IL (2010) Moose density and habitat productivity affects reproduction, growth and species composition in field layer vegetation. J Veg Sci 21:705–716. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2010.01180.x
Meisingset EL, Loe LE, Brekkum Ø, Mysterud A (2014) Targeting mitigation efforts: The role of speed limit and road edge clearance for deer–vehicle collisions. J Wildl Manag 78:679–688. doi:10.1002/jwmg.712
Melis C, Buset A, Aarrestad PA, Hanssen O, Meisingset EL, Andersen R, Moksnes A, Roskaft E (2006) Impact of red deer Cervus elaphus grazing on bilberry Vaccinium myrtillus and composition of ground beetle (Coleoptera, Carabidae) assemblage. Biodivers Conserv 15:2049–2059
Milner JM, Bonenfant C, Mysterud A, Gaillard JM, Csanyi S, Stenseth NC (2006) Temporal and spatial development of red deer harvesting in Europe: biological and cultural factors. J Appl Ecol 43:721–734
Moen A (1999) National atlas of Norway: Vegetation. National Atlas of Norway. Norwegian Mapping Authority, Hønefoss
Nykänen H, Koricheva J (2004) Damage-induced changes in woody plants and their effects on insect herbivore performance: a meta-analysis. Oikos 104:247–268. doi:10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.12768.x
Pato J, Obeso JR (2013a) Effects of clipping and N fertilization on insect herbivory and infestation by pathogenic fungi on bilberry. Basic Appl Ecol 14:347–356. doi:10.1016/j.baae.2013.02.005
Pato J, Obeso JR (2013b) Simulated ungulate herbivory affects differently two herbivorous arthropod guilds in bilberry. Arthropod Plant Interact 7:555–565. doi:10.1007/s11829-013-9269-9
Pieterse CMJ, Van der Does D, Zamioudis C, Leon-Reyes A, Van Wees SCM (2012) Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Ann Rev Cell Develop Biol 28:489–521. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154055
Price PW (1991) The plant vigor hypothesis and herbivore attack. Oikos :244–251
Rodriguez-Saona C, Polashock J, Malo E (2013) Jasmonate-mediated induced volatiles in the American cranberry, Vaccinium macrocarpon: from gene expression to organismal interactions. Front Plant Sci 4:1–17. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00115
Rydgren K, Hestmark G, Økland RH (1998) Revegetation following experimental disturbance in a boreal old-growth Picea abies forest. J Veg Sci 9:763–776
Saetnan ER, Batzli GO (2009) Effects of simulated herbivory on defensive compounds in forage plants of Norwegian alpine rangelands. J Chem Ecol 35:469–475. doi:10.1007/s10886-009-9616-6
Sampedro L, Moreira X, Zas R (2011) Costs of constitutive and herbivore-induced chemical defences in pine trees emerge only under low nutrient availability. J Ecol 99:818–827. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2011.01814.x
Schimmel J, Granström A (1996) Fire severity and vegetation response in the boreal Swedish forest. Ecology 77:1436–1450
Selås V (1997) Cyclic population fluctuations of herbivores as an effect of cyclic seed cropping of plants: the mast depression hypothesis. Oikos 80:257–268
Selås V (2000) Population dynamics of capercaillie Tetrao urogallus in relation to bilberry Vaccinium myrtillus production in southern Norway. Wildl Biol 6:1–11
Selås V (2001) Autumn population size of capercaillie Tetrao urogallus in relation to bilberry Vaccinium myrtillus production and weather: an analysis of Norwegian game reports. Wildl Biol 7:17–25
Selås V (2006) Explaining bank vole cycles in southern Norway 1980–2004 from bilberry reports 1932–1977 and climate. Oecologia 147:625–631
Selås V, Kobro S, Sonerud GA (2013) Population fluctuations of moths and small rodents in relation to plant reproduction indices in southern Norway. Ecosphere 4:11. doi:10.1890/es13-00228.1
Seldal T, Andersen KJ, Högstedt G (1994a) Grazing-induced proteinase-inhibitors: a possible cause for lemming population cycles. Oikos 70:3–11
Seldal T, Dybwad E, Andersen KJ, Högstedt G (1994b) Wound-induced proteinase-inhibitors in grey alder (Alnus incana)—a defense mechanism against attacking insects. Oikos 71:239–245
Solberg EJ et al (2012) Hjortevilt 1991–2011: Oppsummeringsrapport fra Overvåkingsprogrammet for hjortevilt. NINA, Trondheim
Speed JDM, Meisingset EL, Austrheim G, Hester A, Mysterud A, Tremblay J-P, Solberg EJ (2013) Low intensities of red deer browsing constrain rowan growth in mature boreal forest of western Norway. Ecoscience 20:311–318
Statistics-Norway (2014) Increase in deer hunters’ yield. http://www.ssb.no/hjortejakt/. Statistics Norway. http://www.ssb.no/english/subjects/10/04/10/hjortejakt_en/. Accessed 4 April 2014
Strengbom J, Olofsson J, Witzell J, Dahlgren J (2003) Effects of repeated damage and fertilization on palatability of Vaccinium myrtillus to grey sided voles, Clethrionomys rufocanus. Oikos 103:133–141
Tolvanen A, Laine K, Pakonen T, Havas P (1994) Responses to harvesting intensity in a clonal dwarf shrub, the bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.). Vegetatio 110:163–169
van Kleunen M, Ramponi G, Schmid B (2004) Effects of herbivory simulated by clipping and jasmonic acid on Solidago canadensis. Basic Appl Ecol 5:173–181. doi:10.1078/1439-1791-00225
Wegge P, Olstad T, Gregersen H, Hjeljord O, Sivkov AV (2005) Capercaillie broods in pristine boreal forest in Northwestern Russia: the importance of insects and cover in habitat selection. Can J Zool 83:1547–1555
Welch CA, Keay J, Kendall KC, Robbins CT (1997) Constraints on frugivory by bears. Ecology 78:1105–1119
White TCR (1978) The importance of a relative shortage of food in animal ecology. Oecologia 33:71–86
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the landowner Kaupanger Hovedgård for allowing us to use their forest roads and property for research, Alison Coulthard for linguistic review, and the Research Council of Norway (Miljø 2015 programme, project number 204403/E40) and the Norwegian Environment Agency for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hegland, S.J., Seldal, T., Lilleeng, M.S. et al. Can browsing by deer in winter induce defence responses in bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus)?. Ecol Res 31, 441–448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-016-1351-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-016-1351-1