Abstract
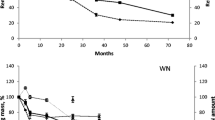
The effects of simulated N deposition on changes in mass, C, N and P of decomposing pine (Pinus massoniana) needles in a disturbed and a rehabilitated forest in tropical China were studied during a 24-month period. The objective of the study was to test the hypothesis that litter decomposition in a disturbed forest is more sensitive to N deposition rate than litter decomposition in a rehabilitated forest due to the relatively low nutrient status in the former as a result of constant human disturbance (harvesting understory and litter). The litterbag method and N treatments (control, no N addition; low-N, 5 g N m−2 year−1; medium-N, 10 g N m−2 year−1) were employed to evaluate decomposition. The results revealed that N addition increased (positive effect) mass loss rate and C release rate but suppressed (negative effect) the release rate of N and P from decomposing needles in both disturbed and rehabilitated forests. The enhanced needle decomposition rate by N addition was significantly related to the reduction in the C/N ratio in decomposing needles. However, N availability is not the sole factor limiting needle decomposition in both disturbed and rehabilitated forests. The positive effect was more sensitive to the N addition rate in the rehabilitated forest than in the disturbed forest, however the reverse was true for the negative effect. These results suggest that nutrient status could be one of the important factors in controlling the response of litter decomposition and its nutrient release to elevated N deposition in reforested ecosystems in the study region.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Logtestijn R, van Staalduinen M, van Toet S (1995) Nitrogen supply effects on productivity and potential leaf litter decay of Carex species from peatlands differing in nutrient limitation. Oecologia 104:447–453
Ågren GK, Bosatta E, Magill AH (2001) Combining theory and experiment to understand effects of inorganic nitrogen on litter decomposition. Oecologia 128:94–98
Anderson JM, Ingram JSI (1989) Tropical soil biology and fertility: a handbook of methods. CAB International, Wallingford
Anderson JM, Proctor J, Vallack HW (1983) Ecological studies in four contrasting lowland rain forests in Gunung-Mulu National Park Sarawak. 3. Decomposition processes and nutrient losses from leaf litter. J Ecol 71:503–527
Baxter JW, Pickett STA, Dighton J, Carreiro MM (2002) Nitrogen and phosphorus availability in oak forest stands exposed to contrasting anthropogenic impacts. Soil Biol Biochem 34:623–633
Berg B (1986) Nutrient release from litter and humus in coniferous soil – a mini review. Scand J For Res 1:359–369
Berg B, Matzner E (1997) Effect of N deposition on decomposition of plant litter and soil organic matter in forest systems. Environ Rev 5:1–25
Berg MP, Kniese JP, Zoomer R, Verhoef HA (1998) Long-term decomposition of successive organic strata in a nitrogen saturated Scots pine forest soil. For Ecol Manage 107:159–172
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2: chemical and microbial properties. Agronomy Monograph 9. Agronomy Society of America, Madison, pp 595–624
Brown S, Lenart MT, Mo JM, Kong GH (1995) Structure and organic matter dynamics of a human-impacted pine forest in a MAB reserve of subtropical China. Biotropica 27:276–289
Conn CE, Day FP (1996) Response of root and cotton strip decay to nitrogen amendment along a barrier island dune chronosequence. Can J Bot 74:276–284
Fang YT, Zhu WX, Mo JM, Zhou GY, Gundersen P (2006) Dynamics of soil inorganic nitrogen and their responses to nitrogen additions in three subtropical forests, South China. J Environ Sci 18:752–759
He S, Yu Z (1984) The studies on the reconstruction of vegetation in tropical coastal eroded land in Guangdong (in Chinese with English abstract). In: Tropical and subtropical forest ecosystem, vol 2. Science Press, Beijing, pp 87–90
Holdridge LR (1967) Life zone ecology. Tropical Science Center, Costa Rica
Huang ZF, Fan ZG (1982) The climate of Ding Hu Shan (in Chinese with English abstract). In: Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem, vol 1. Science Press, Beijing, pp 11–23
Huang ZL, Ding MM, Zhang ZP, Yi WM (1994) The hydrological processes and nitrogen dynamics in a monsoon evergreen broad-leafed forest of Dinghu shan (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Phytoecol Sinica 18:194–199
Koopmans CJ, Tietema A, Verstraten JM (1998) Effects of reduced N deposition on litter decomposition and N cycling in two N saturated forests in the Netherlands. Soil Biol Biochem 30:141–151
Kuperman RG (1999) Litter decomposition and nutrient dynamics in oak-hickory forests along a historic gradient of nitrogen and sulfur deposition. Soil Biol Biochem 31:237–244
Liu GH, Fu BJ, Chen LD, Guo XD (2000) Characteristics and distributions of degraded ecological types in China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Ecol Sinica 20:13–19
Magill AH, Aber JD (1998) Long-term effects of experimental nitrogen addition on foliar litter decay and humus formation in forest ecosystems. Plant Soil 203:301–311
McGroddy ME, Silver WL, Cosme de Oliveira R Jr (2004) The effect of phosphorus availability on decomposition dynamics in a seasonal lowland Amazonian forest. Ecosystems 7:172–179
Micks P, Down MR, Magill AH, Nadelhoffer KJ, Aber JD (2004) Decomposition litter as a sink for 15N-enriched additions to an oak forest and a red pine plantation. For Ecol Manage 196:71–87
Mo JM, Brown S, Lenart M, Kong GH (1995) Nutrient dynamics of a human-impacted pine forest in a MAB Reserve of subtropical China. Biotropica 27:290–304
Mo JM, Brown S, Peng SL, Kong GH (2003) Nitrogen availability in disturbed, rehabilitated and mature forests of tropical China. For Ecol Manage 175:573–583
Mo JM, Peng SL, Brown S, Kong GH, Fang YT (2004) Nutrient dynamics in response to harvesting practices in a pine forest of subtropical China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Phytoecol Sinica 28:810–822
Mo JM, Fang YT, Xu GL, Li DJ, Xue JH (2005) The short-term responses of soil CO2 emission and CH4 uptake to simulated N deposition in nursery and forests of Dinghushan in subtropical China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Ecol Sinica 25:682–690
Mo JM, Brown S, Xue JH, Fang YT, Li ZA (2006) Response of litter decomposition to simulated N deposition in disturbed, rehabilitated and mature forests in subtropical China. Plant Soil 282:135–151
Molina JAE, Clapp CE, Shaffer MJ, Chichester FW, Larson WE (1983) A model of nitrogen and carbon transformations in soil: description, calibation and behaviour. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47:85–91
Olson JS (1963) Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44:322–331
Ostertag R, Hobbie SE (1999) Early stages of root and leaf decomposition in Hawaiian forests: effects of nutrient availability. Oecologia 121:564–573
Prescott CE (1996) Influence of forest floor type on rates of litter decomposition in microcosms. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1436–1443
Prescott CE, Kabzems R, Zabek LM (1999) Effects of fertilization on decomposition rate of Populus tremuloides foliar litter in a boreal forest. Can J For Res 29:393–397
Sayer E (2006) Using experimental manipulation to assess the roles of leaf litter in the functioning of forest ecosystems. Biol Rev 81:1–31
Staaf H, Berg B (1981) Accumulation and release of plant nutrients in decomposing Scots pine needle litter: long-term decomposition in a Scots pine forest II. Can J Bot 60:1561–1568
Sundarapandian SM, Swamy PS (1999) Litter production and leaf-litter decomposition of selected tree species in tropical forests at Kodayar in the Western Ghats, India. For Ecol Manage 123:231–244
Vestgarden LS (2001) Carbon and nitrogen turnover in the early stage of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) needle litter decomposition: effects of internal and external nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 33:465–474
Vitousek PM (1998) Foliar and litter nutrients, nutrient resorption, and decomposition in Hawaiian Metrosideros polymorpha. Ecosystems 1:401–407
Wang Z, He D, Song S, Chen S, Chen D, Tu M (1982) The vegetation of Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve (in Chinese with English abstract). In: Tropical and subtropical forest ecosystem, vol 1. Science Press, Beijing, pp 77–141
Xu GL, Mo JM, Zhou GY (2005) Early responses of soil fauna in three typical forests of south subtropical China to simulated N deposition addition (in Chinese with English abstract). Chin J Appl Ecol 16:1235–1240
Xuluc-Tolosa FJ, Vester HFM, Ramirez-Marcial N, Castellanos-Albores J, Lawrence D (2003) Leaf litter decomposition of tree species in three successional phases of tropical dry secondary forest in Campeche, Mexico. For Ecol Manage 174:401–412
Yi WM, Yi ZZ, Ding MM, Zhou LX (2002) Soil microbial biomass and its carbon dynamic in the main forest vegetations in Dinghushan Area (in Chinese with English abstract). Tropical and subtropical forest ecosystem, vol 9. Science Press, Beijing, pp 180–185
Zhang B, Zhuo M (1989) The storage capacity of soil moisture under different forest types in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve (in Chinese with English abstract). Tropical and subtropical forest ecosystem, vol 5. Science press, Beijing, pp 1–6
Zhang DQ, Ye WH, Yu QF, Kong GH, Zhang YC (2000) The litter-fall of representative forests of successional series in Dinghushan (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Ecol Sinica 20:938–944
Zheng X, Fu C, Xu X, Xiaodong Y, Huang Y, Chen G, Han S, Hu F (2002) The Asian nitrogen cycle case study. Ambio 31:79–87
Zhou GY, Yan JH (2001) The influence of region atmospheric precipitation characteristics and its element inputs on the existence and development of Dinghushan forest ecosystems (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Ecol Sinica 21:2002–2012
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30670392) and Key Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences Knowledge Innovation Program (KSCX2-SW-133). We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, J., Brown, S., Xue, J. et al. Response of nutrient dynamics of decomposing pine (Pinus massoniana) needles to simulated N deposition in a disturbed and a rehabilitated forest in tropical China. Ecol Res 22, 649–658 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-006-0317-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-006-0317-0