Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to clarify which panoramic radiographic features can predict the development of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ).
Methods
Participants included 24 patients treated with bisphosphonates (BP) for osteoporosis who developed osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ+ group). Controls included 179 patients treated with BP who did not have osteonecrosis (ONJ− group) and 200 patients with no history of BP administration (unmedicated group). The mandibular cortical width, mandibular cortical index (MCI), sclerosis of trabecular bone, and thickening of the lamina dura were evaluated on panoramic radiographs.
Results
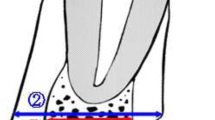
The mandibular cortical width was significantly smaller in the ONJ– group than in the other groups. Class II MCI (semilunar defects of endosteal margin) was frequently noted on the affected and contralateral sides in the ONJ+ group but not in the ONJ− or unmedicated groups. Sclerosis of the trabecular bone was significantly more frequently observed on the affected side in the ONJ+ group than in the other groups. Thickening of the lamina dura was observed significantly more frequently in the BP-treated groups than in the unmedicated group.
Conclusions
Class II MCI may be an indicator to predict the development of BRONJ. Sclerosis of trabecular bone was a characteristic imaging feature of BRONJ. Thickening of the lamina dura may be an imaging feature caused by BP administration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marx RE. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: a growing epidemic. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61:1115–7.
Phal PM, Myall RW, Assael LA, Weissman JL. Imaging findings of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaws. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:1139–45.
Guo Y, Wang D, Wang Y, Peng X, Guo C. Imaging features of medicine-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: comparison between panoramic radiography and computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2016;122:e69–76.
Farias DS, Zen Filho EV, de Oliveira TF, Tinôco-Araújo JE, Sampieri MB, Antunes HS, et al. Clinical and image findings in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24:1248–51.
Krishnan A, Arslanoglu A, Yildirm N, Silbergleit R, Aygun N. Imaging findings of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw with emphasis on early magnetic resonance imaging findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2009;33:298–304.
Mücke T, Deppe H, Hein J, Wolff KD, Mitchell DA, Kesting MR, et al. Prevention of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in patients with prostate cancer treated with zoledronic acid—a prospective study over 6 years. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016;44:1689–93.
Paek SJ, Park WJ, Shin HS, Choi MG, Kwon KH, Choi EJ. Diseases having an influence on inhibition of angiogenesis as risk factors of osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;42:271–7.
Otto S, Tröltzsch M, Jambrovic V, Panya S, Probst F, Ristow O, et al. Tooth extraction in patients receiving oral or intravenous bisphosphonate administration: a trigger for BRONJ development? J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43:847–54.
Huang YF, Chang CT, Muo CH, Tsai CH, Shen YF, Wu CZ. Impact of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw on osteoporotic patients after dental extraction: a population-based cohort study. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0120756.
Reiss S, Sultan D. Risk factors in the development of oral bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis. N Y State Dent J. 2015;81:30–3.
Polymeri AA, Kodovazenitis GJ, Polymeris AD, Komboli M. Bisphosphonates: clinical applications and adverse events in dentistry. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2015;13:289–99.
Mücke T, Krestan CR, Mitchell DA, Kirschke JS, Wutzl A. Bisphosphonate and medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: a review. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2016;20:305–14.
Kim HY, Kim JW, Kim SJ, Lee SH, Lee HS. Uncertainty of current algorithm for bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in population-based studies: a systematic review. J Bone Miner Res. 2016 (in press).
Taniguchi T, Ariji Y, Nozawa M, Naitoh M, Kuroiwa Y, Kurita K, et al. Computed tomographic assessment of early changes of the mandible in bisphosphonate-treated patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2016;122:362–72.
Klingelhöffer C, Klingelhöffer M, Müller S, Ettl T, Wahlmann U. Can dental panoramic radiographic findings serve as indicators for the development of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw? Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2016;45:20160065.
Torres SR, Chen CS, Leroux BG, Lee PP, Hollender LG, Lloid M, et al. Mandibular inferior cortical bone thickness on panoramic radiographs in patients using bisphosphonates. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2015;119:584–92.
Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Fantasia J, Goodday R, Aghaloo T, Mehrotra B, et al. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw–2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72:1938–56.
Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Assael LA, Landesberg R, Marx RE, Mehrotra B. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws–2009 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67:2–12.
Muramatsu C, Matsumoto T, Hayashi T, Hara T, Katsumata A, Zhou X, et al. Automated measurement of mandibular cortical width on dental panoramic radiographs. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2013;8:877–85.
Muramatsu C, Horiba K, Hayashi T, Fukui T, Hara T, Katsumata A, et al. Quantitative assessment of mandibular cortical erosion on dental panoramic radiographs for screening osteoporosis. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2016;11:2021–32.
Katsumata A, Fujita H, Taguchi A, Ariji Y, Ariji E. Computer analysis of mandibular cortex morphology for screening of osteoporosis. J Jpn Stomatol Soc. 2016;65:256–63 (in Japanese).
Taguchi A, Suei Y, Sanada M, Ohtsuka M, Nakamoto T, Sumida H, et al. Validation of dental panoramic radiography measures for identifying postmenopausal women with spinal osteoporosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183:1755–60.
Taguchi A, Suei Y, Ohtsuka M, Otani K, Tanimoto K, Ohtaki M. Usefulness of panoramic radiography in the diagnosis of postmenopausal osteoporosis in women. Width and morphology of inferior cortex of the mandible. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1996;25:263–7.
Taguchi A, Tanimoto K, Suei Y, Wada T. Tooth loss and mandibular osteopenia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995;79:127–32.
Taguchi A, Suei Y, Sanada M, Higashi Y, Ohtsuka M, Nakamoto T, et al. Detection of vascular disease risk in women by panoramic radiography. J Dent Res. 2003;82:838–43.
Klemetti E, Kolmakov S, Kröger H. Pantomography in assessment of the osteoporosis risk group. Scand J Dent Res. 1994;102:68–72.
Leite AF, dos Santos Ogata F, de Melo NS, de Souza Figueiredo PT. Imaging findings of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: a critical review of the quantitative studies. Int J Dent. 2014;2014:784348.
Ariji Y, Katsumata A, Kubo R, Taguchi A, Fujita H, Ariji E. Factors affecting observer agreement in morphological evaluation of mandibular cortical bone on panoramic radiographs. Oral Radiol. 2017;33:117–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors received no funding for this study.
Conflict of interest
Ryota Kubo, Yoshiko Ariji, Tohru Taniguchi, Michihito Nozawa, Akitoshi Katsuma, and Eiichiro Ariji declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human rights statements
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Animal rights statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors. Panoramic radiographic features predict the development of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubo, R., Ariji, Y., Taniguchi, T. et al. Panoramic radiographic features that predict the development of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Oral Radiol 34, 151–160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-017-0293-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-017-0293-9