Abstract
Purposes
Head rotation is widely used as a postural technique for dysphagic patients. In this study, we evaluated the effects of head rotation on pharyngeal swallowing in healthy subjects.
Methods
A videofluoroscopic swallow study (VFSS) of pharyngeal swallowing was performed on subjects with the head in neutral (upright and full-faced) and rotated positions. Seventeen volunteers were given samples of liquid barium and custard pudding mixed with barium to swallow.
Results
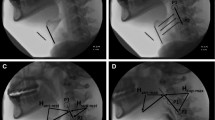
VFSS findings revealed that the head-rotated swallow causes the bolus to lateralize away from the direction of head rotation. Satisfactory lateralization of the food or liquid bolus during a head-rotated swallow was observed in approximately 80% of cases with liquid barium and in 60% of those with material of pudding consistency. A spillage of bolus into the pharynx before swallow initiation occurred in only approximately 15% of cases when a subject rotated his/her head.
Conclusion
In this study, the effects of head rotation on pharyngeal swallowing in healthy subjects were evaluated. Results from this study suggest that the efficacy of head rotation is affected by the consistency of food and liquid materials.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Kobara M, Vakil NB. The benefit of head rotation on pharyngoesophageal dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989;70:767–71.
Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of postural change on aspiration in head and neck surgical patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994;110(2):222–7.
Ohmae Y, Ogura M, Kitahara S, Karaho T, Inouye T. Effects of head rotation on pharyngeal function during normal swallow. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1998;107(4):344–8.
Takasaki K, Umeki H, Enatsu K, Tanaka F, Sakihama N, Kumagami H, Takahashi H. Investigation of pharyngeal swallowing function using high-resolution manometry. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:1729–32.
Takasaki K, Umeki H, Kumagami H, Takahashi H. Influence of head rotation on upper esophageal sphincter pressure evaluated by high-resolution manometry system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;142(2):214–7.
Leder SB, Karas DE. Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in the pediatric population. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(7):1132–6.
Yamashina A, Tanimoto K, Ohtsuka M, Nagasaki T, Sutthiprapaporn P, Iida Y, Katsumata A. A morphological comparison of the piriform sinuses in head-on and head-rotated views of seated subjects using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiology. 2008;24:64–70.
Takehara I, Chu J. Pharynx and oesophagus evaluation during the swallow using helical computerized tomography. Disabil Rehabil. 2004;26:733–8.
Gilbert RJ, Daftary S, Campbell TA, Weisskoff RM. Patterns of lingual tissue deformation associated with bolus containment and propulsion during deglutition as determined by echo-planar MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1998;8(3):554–60.
Sutthiprapaporn P, Tanimoto K, Ohtsuka M, Nagasaki T, Iida Y, Katsumata A. Positional changes of oropharyngeal structures to gravity in the upright and supine positions. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008;37:130–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iida, Y., Katsumata, A. & Fujishita, M. Effect of head rotation on the pathway of a food bolus through the pharynx as evaluated by a videofluoroscopic swallow study. Oral Radiol 27, 17–21 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-010-0054-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-010-0054-5