Abstract
Objectives
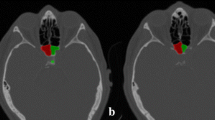
Food flow in the oropharynx changes when the head is rotated. The purpose of this study was to evaluate morphological differences in the upper and lower piriform sinuses in head-on (HO) versus head-rotated (HR) positions.
Methods
Ten healthy adult volunteers with no previous history of dysphagia were subjected to cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) in the HO and HR positions. Binary CBCT images were created at 50% gray scale to examine morphological changes in the lower piriform sinuses.
Results
Upon rotation to the right, the cross-sectional area of the left lower piriform sinus increased significantly (P = 0.037). The depth of the right lower piriform sinus also increased significantly (P = 0.011) upon rotation. The volume of the lower piriform sinuses increased significantly on both sides (right, P = 0.009; left, P = 0.013). The upper piriform sinuses acquired a teardrop shape, with the rotated side narrowed and opposite side enlarged.
Conclusions
These results suggest that changes in food flow during head rotation result mainly from changes in the size and shape of the upper piriform sinuses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achem SR, Devault KR. Dysphagia in aging. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005;39:357–371.
Simons D, Kidd EA, Beighton D. Oral health of elderly occupants in residential homes. Lancet 1999;353:1761.
McMillan AS, Leung KC, Pow EH, Wong MC, Li LS, Allen PF. Oral health-related quality of life of stroke survivors on discharge from hospital after rehabilitation. J Oral Rehabil 2005;32:495–503.
Yoneyama T, Yoshida M, Matsui T, Sasaki H. Oral care and pneumonia. Oral Care Working Group. Lancet 1999;354:515.
Yoneyama T, Yoshida M, Ohrui T, Mukaiyama H, Okamoto H, Hoshiba K, et al. Oral care reduces pneumonia in older patients in nursing homes. J Am Geriatr Soc 2002;50:430–433.
Cotert HS, Aras E. Mastication, deglutition and speech considerations in prosthodontic rehabilitation of a total glossectomy patient. J Oral Rehabil 1999;26:75–79.
Tsuga K, Hayashi R, Sato Y, Akagawa Y. Handy measurement for tongue motion and coordination with laryngeal elevation at swallowing. J Oral Rehabil 2003;30:985–989.
Ekberg O. Posture of the head and pharyngeal swallowing. Acta Radiol Diagn 1986;27:691–696.
Lazzara G, Lazarus C, Logemann JA. Impact of thermal stimulation on the triggering of the swallowing reflex. Dysphagia 1986;1:73–77.
Davis JW, Lazarus C, Logemann J, Hurst PS. Effect of a maxillary glossectomy prosthesis on articulation and swallowing. J Prosthet Dent 1987;57:715–719.
Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin, TX: PRO-ED; 1998. p. 197–201.
Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Kobara M, Vakil NB. The benefit of head rotation on pharyngoesophageal dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1989;70:767–771.
Ohmae Y, Ogura M, Kitahara S, Karaho T, Inouye T. Effects of head rotation on pharyngeal function during normal swallow. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1998;107:344–348.
Sutthiprapaporn P, Tanimoto K, Ohtsuka M, Iida Y, Katsumata A. Positional changes of oropharyngeal structures due to gravity in the upright and supine positions. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2008;37:130–136.
Takehara I, Fujishima I, Ohkuma R, Mizuguchi A, Kojima C, Shibamoto I, et al. The kinesiology of head rotation while swallowing (in Japanese). Sogo Rehabil 2001;29:249–254.
Stoeckli SJ, Huisman TA, Seifert B, Martin-Harris BJ. Interrater reliability of videofluoroscopic swallow evaluation. Dysphagia 2003;18:53–57.
Silverman PM, Korobkin M. High-resolution computed tomography of the normal larynx. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1983;140:875–879.
Tsukamoto Y. CT study of closure of the hemipharynx with head rotation in a case of lateral medullary syndrome. Dysphagia 2000;15:17–18.
Takehara I, Chu J. Pharynx and oesophagus evaluation during the swallow using helical computerized tomography. Disabil Rehabil 2004;26:733–738.
Baba R, Ueda K, Kuba A, Kohda E, Shiraga N, Sanmiya T. Development of a subject-standing-type cone-beam computed tomography for chest and orthopedic imaging. Front Med Biol Eng 2001;11:177–189.
Endo M, Tsunoo T, Nakamori N, Yoshida K. Effect of scattered radiation on image noise in cone beam CT. Med Phys 2001;28:469–474.
Yamamoto K, Ueno K, Seo K, Shinohara D. Development of dento-maxillofacial cone beam X-ray computed tomography system. Orthod Craniofac Res 2003;6Suppl 1:1.
Araki K, Maki K, Seki K, Sakamaki K, Harata Y, Sakaino R, et al. Characteristics of a newly developed dentomaxillofacial X-ray cone beam CT scanner (CB MercuRay): system configuration and physical properties. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2004;33:51–59, 60–2.
Standrind S. Gray’s anatomy. 39th ed. London: Elsevier; 2005. p. 625.
Yamashina A, Tanimoto K, Sutthiprapaporn P, Hayakawa Y. The reliability of computed tomography (CT) values and dimensional measurements of the oropharyngeal region using cone beam CT: comparison with multidetector CT. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2008;37:245–251.
Kemerink GJ, Lamers RJ, Pellis BJ, Kruize HH, van Engelshoven JM. On segmentation of lung parenchyma in quantitative computed tomography of the lung. Med Phys 1998;25:2432–2439.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashina, A., Tanimoto, K., Ohtsuka, M. et al. A morphological comparison of the piriform sinuses in head-on and head-rotated views of seated subjects using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol 24, 64–70 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-008-0077-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-008-0077-3