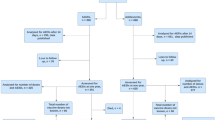
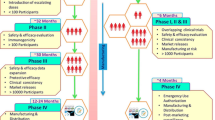
Abstract
The COVID‐19 deadly disease cause momentous distress on physical and mental health on the citizens of various countries. The highly contagious nature of corona virus and its continuous mutating behavior is making the situation even worst. Almost all the countries have tried total lockdown strategies but still, it is spreading very quickly in some of the countries like India, USA, and Brazil. The developed countries like USA, Russia, and China show some ray of hope to the people across the world by bringing vaccination with high efficacy rate for this coronavirus disease. India too brought two vaccines viz; Covishield & Covaxin into its market and exported too. It has been seen that people start experiencing the side effects after getting vaccinated. The fear of side effects from the vaccine among the public is somehow creating problems for the Government to get its countrymen vaccinated quickly. In this chapter, a survey based attempt to analyze the effect of vaccine has been carried out on the population who got vaccinated with first/second dose of these two vaccines. An attempt has been made to create awareness about the side effects of this vaccine. SPSS software is used for the statistical analysis of the obtained data.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [https://www.covid19india.org/] repository.
Code Availability
None.
References
Shereen, M. A., Khan, S., Kazmi, A., Bashir, N., & Siddique, R. (2020). COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. Journal of Advanced Research., 24, 91–98.
Shretta, R., Hupert, N., Osewe, P., & White, L. J. (2021). Vaccinating the world against COVID-19: Getting the delivery right is the greatest challenge. BMJ Global Health, 6, e005273.
Williamson, P. R., Altman, D. G., & Blazeby, J. M. (2012). Developing core outcome sets for clinical trials: Issues to consider. Trials, 13, 132.
Vorsey, M. (2020). Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet, 397(99–111), 14.
Mahase, E. (2020). Covid-19: Oxford vaccine could be 59% effective against asymptomatic infections, analysis shows. The BMJ, 371, m4777.
Prompetchara, E., Ketloy, C., & Palaga, T. (2020). Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: Lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology., 38(1), 1–9.
Liu, Z., Shi, O., Yan, Q., Fang, Q., Zuo, J., & Chen, Y. (2018). Changing Epidemiological Patterns of HIV and AIDS in China in the Post-SARS Era identified by the Nationwide Surveillance System. BMC Infectious Diseases., 18(1), 700.
Polack, F. P. (2020). Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. The New England Journal of Medicine, 383(27), 2603–2615.
Menni, C. (2021). Vaccine side-effects and SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccination in users of the COVID Symptom Study app in the UK: A prospective observational study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 3099(21), 52.
Beatty, A. L., Peyser, N. D., & Butcher, X. E. (2021). Analysis of COVID-19 vaccine type and adverse effects following vaccination. JAMA Network Open., 4(12), 24.
Al, K., Aga, Q. A., Alkhaffaf, W. H., & Hatem, T. H. (2021). Safety of COVID-19 vaccines. Journal of Medical Virology., 93(12), 6588–6594.
Chen, J., Cai, Y., Chen, Y., Williams, A. P., Gao, Y., & Zeng, J. (2021). Nervous and muscular adverse events after covid-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Vaccines., 9(8), 939.
Dhamanti, I., Suwantika, A. A., Adlia, A., Yamini, L. N., & Yakub, F. (2023). Adverse reactions of COVID-19 vaccines: A scoping review of observational studeis. Interational Journal of General Medicine., 16, 609–618.
Wang, H., Paulson, K. R., & Pease, S. A. (2022). Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic analysis of COVID-19- related mortality. Lancet, 399, 1513–1536.
Hogan, A. B., Winskill, P., & Watson, O. J. (2021). Within-country age-based prioritisation, global allocation, and public health impact of a vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A mathematical modelling analysis. Vaccine., 39, 2995–3006.
Huang, C. (2020). Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China. Lancet., 6736(20), 30183–30185.
Jeong, S., Hong, S., & Oh, T. (2022). Analysis of older adults visiting the emergency department with fever as a suspected Covid-19 vaccine-related adverse reaction: A retrospective multicenter study. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy., 28(8), 1159–1164.
Kumar, R., Pandey, A., Geleta, R., Sinwar, D., & Dhaka, V. S. (2021). Study of social and geographical factors affecting the spread of COVID-19 in Ethiopia. Journal of Statistics and Management Systems., 24(1), 99–113.
Rabail, R., Ahmed, W., & Ilyas, M. (2022). The side effects and adverse clinical cases reported after COVID-19 Immunization. Vaccines., 10(4), 1–25.
Kadali, R. A. K., Janagama, R., Peruru, S., & Malayala, S. V. (2021). Side effects of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: A randomized, cross-sectional study with detailed self-reported symptoms from healthcare workers. International Journal of Infectious Diseases., 106, 376–381.
Pormohammad, A., Zarei, M., & Ghorbani, S. (2021). Efficacy and safety of covid-19 vaccines: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Vaccines., 9(5), 467.
Liu, J. Y., Chen, T. J., & Hou, M. C. (2021). Does COVID-19 vaccination cause excess deaths? Journal of the Chinese Medical Association., 84(9), 811–812.
Liu, Y., & Ye, Q. (2022). Safety and efficacy of the common vaccines against COVID-19. Vaccines., 10(4), 513.
Ay, M. O., Erenler, A. K. A. Y. O. O., Kaya, H., Yuskel, M., & Kekec, Z. (2021). A scientometric analysis of COVID-19 vaccine publications. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews., 09(03), 138–147.
Paltiel, A. D., Schwartz, J. L., Zheng, A., & Walensky, R. P. (2021). Clinical outcomes of a COVID-19 vaccine: Implementation over efficacy. Health Affairs., 40(1), 42–52.
Mahase, E. (2020). Covid-19: Pfizer vaccine efficacy was 52% after first dose and 95% after second dose, paper shows. The BMJ, 371, m4826.
Marshall, J. C. (2020). A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 20, e192–e197.
Voysey, M., Clemens, S. A. C., & Madhi, S. A. (2021). Single-dose administration and the influence of the timing of the booster dose on immunogenicity and efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine: A pooled analysis of four randomised trials. Lancet, 397, 881–891.
WHO. (2020). Fair allocation mechanism for COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX facility. Geneva.
You, X. (2021). HIV incidence and sexual behavioural correlates among 4578 men who have sex with men (MSM) in Chengdu, China: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Public Health, 21(802), 1–9.
Funding
No Funding has been received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Juneja, N., Grover, A., Kaur, H. et al. A Survey Based Analysis to Study the Side Effects of Covid-19 Vaccination in Punjab (India). Wireless Pers Commun 132, 1347–1363 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10665-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10665-0