Abstract
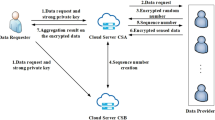
Mobile sensing can be used in many applications. In a mobile sensing system, the time-series data sensed by mobile users can be aggregated by a third-party device, which is called an aggregator. The aggregation statistics are very useful for guiding functions in various applications. Recently proposed privacy-preserving aggregation protocols can deal with untrusted aggregators, which are more common in real world than a trusted aggregator. In addition, some of these works have ideal communication models: uni-direction and one-round communication between the aggregator and each mobile user. This communication model minimizes the communication overhead and latency, making it very popular in real-world applications. However, in these recent works, if an aggregator uses up its aggregation services, the trusted authority needs to update the secret values of all the mobile users. Otherwise, the aggregator can still utilize the sensing system. This updating operation will cause large communication overhead of the sensing system, and will interrupt the system service for a while. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel privacy-preserving aggregation protocol against an untrusted aggregator that the aggregator are not allowed to obtain the detailed sensed data of each mobile user in the sensing system. The protocol is novel because in our protocol, if an aggregator exhausts its aggregation services, no updating is required by each mobile user. And the trusted authority can better charge for the service provided to the aggregator and manage the payment more effectively. Our protocol has been compared with others, and the results show that ours performs better.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Zhao, S., Li, F., Li, H., Lu, R., Ren, S., Bao, H., Lin, J. H., & Han, S. (2020). Smart and practical privacy-preserving data aggregation for fog-based smart grids. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 16, 521–536.
Wz, A., Bo, J. B., Ming, L. B., Rt, B., Qiao, L. A., & Hui, L. A. (2020). Aggregation-based location privacy: An information theoretic approach–sciencedirect. Computers & Security, 97, 101953.
Castelluccia, C., Chan, A. C., Mykletun, E., & Tsudik, G. (2009). Efficient and provably secure aggregation of encrypted data in wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 5(3), 20.
Liu, W. (2022). Privacy-preserving comparison based data aggregation protocols for mobile sensing. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 15(1), 549–558.
Han, S., Lin, J., Zhao, S., Xu, G., Ren, S., He, D., Wang, L., & Shi, L. (2020). Location privacy-preserving distance computation for spatial crowdsourcing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(8), 7550–7563.
Anastasi, G., Conti, M., Di Francesco, M., & Passarella, A. (2009). Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Networks, 7(3), 537–568.
Joye, M., & Libert, B. (2013). A scalable scheme for privacy-preserving aggregation of time-series data. In Financial Cryptography and Data Security (pp. 111–125). Springer
Li, Q., Cao, G., & La Porta, T. (2014). Efficient and privacy-aware data aggregation in mobile sensing. IEEE Transactions on: Dependable and Secure Computing, 11(2), 1–10.
Rastogi, V., & Nath, S. (2010). Differentially private aggregation of distributed time-series with transformation and encryption. In Proceedings of the 2010 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data (pp. 735–746). ACM
Li, F., Luo, B., & Liu, P. (2010). Secure information aggregation for smart grids using homomorphic encryption. In 2010 First IEEE international conference on smart grid communications (SmartGridComm), (pp. 327–332). IEEE
Garcia, F. D., & Jacobs, B. (2011). Privacy-friendly energy-metering via homomorphic encryption. In Security and Trust Management (pp. 226–238). Springer
Rieffel, E., Biehl, J., van Melle, W., & Lee, A. J., (2010) Secured histories: Computing group statistics on encrypted data while preserving individual privacy. arXiv preprint arXiv:1012.2152
Shi, E., Chan, H., Rieffel, E., Chow, R., & Song, D., (2011). Privacy-preserving aggregation of time-series data. In Annual Network & Distributed System Security Symposium
Chan, T. H. H., Shi, E., & Song, D. (2012). Privacy-preserving stream aggregation with fault tolerance. In Financial Cryptography and Data Security (pp. 200–214). Springer
Li, Q., & Cao, G., (2013). Efficient privacy-preserving stream aggregation in mobile sensing with low aggregation error. In Privacy Enhancing Technologies (pp. 60–81). Springer
Han, S., Shuai, Z., Li, Q., Ju, C. H., & Zhou, W. (2016). PPM-HDA: Privacy-preserving and multifunctional health data aggregation with fault tolerance for cloud assisted WBANS. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 11(9), 1940–1955.
Yuan, J., Liu, W., Wang, J., Shi, J., & Miao, L. (2020). An efficient framework for data aggregation in smart agriculture. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 33(10), e6160.
Li, S., Xue, K., Yang, Q., & Hong, P. (2018). PPMA: Privacy-preserving multisubset data aggregation in smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 14(2), 462–471.
Merad-Boudia, O. R., & Senouci, S. M. (2021). An efficient and secure multidimensional data aggregation for fog-computing-based smart grid. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(8), 6143–6153.
Zhang, X., Huang, C., Zhang, Y., & Cao, S. (2022). Enabling verifiable privacy-preserving multi-type data aggregation in smart grids. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 19(6), 4225–4239.
Mohammadali, A., & Haghighi, M. S. (2021). A privacy-preserving homomorphic scheme with multiple dimensions and fault tolerance for metering data aggregation in smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 12(6), 5212–5220.
Fan, H., Liu, Y., & Zeng, Z. (2020). Decentralized privacy-preserving data aggregation scheme for smart grid based on blockchain. Sensors, 20(18), 5282.
Xue, K., Zhu, B., Yang, Q., Wei, D. S. L., & Guizani, M. (2020). An efficient and robust data aggregation scheme without a trusted authority for smart grid. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(3), 1949–1959.
Xia, Z., Zhang, Y., Gu, K., Li, X., & Jia, W. (2022). Secure multi-dimensional and multi-angle electricity data aggregation scheme for fog computing-based smart metering system. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 6(1), 313–328.
Zhang, X., You, L., & Hu, G. (2022). An efficient and robust multidimensional data aggregation scheme for smart grid based on blockchain. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 19(4), 3949–3959.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W. Pyas: Pay for Your Aggregation Service—A Privacy Preserving Aggregation Protocol of Time-series Data. Wireless Pers Commun 132, 757–773 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10637-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10637-4