Abstract
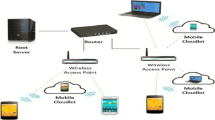
Cloud Computing is the origin for various distributed computing such as mobile cloud computing, mobile edge computing, fog computing, transparent computing etc. The proposed work focuses mainly on mobile cloud computing and mobile edge computing. It discusses various frameworks to execute these computing and pricing models suitable to be incorporated with mentioned computing environments. One such mobile cloud computing framework is scalable key parameter yield of resources (SKYR) framework, which is a cloudlet-based computing framework. In this computing framework, cloudlet is the main computing component which provides the cloud-based services at the local level in the vicinity of the mobile users. This SKYR framework lacks intrinsic pricing module and utility efficiency module. The proposed work facilitates SKYR framework with mentioned modules and hence improves its performance to great extent as shown in the result section. The paper also discusses pricing model which facilitates profit maximization and auction theory for resource providers and users. Latest theoretical profit maximization incentive mechanism (PMIM) pricing model is improved in this proposed work to scalable profit optimized incentive mechanism for resources pricing model. The proposed pricing model addresses the drawbacks of the PMIM. The utility module discusses about the utility efficiency calculation mechanism which helps to analyse the performance of cloudlets and judges the satisfaction level of cloudlets which act as resource provider and mobile users.




































Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Code Availability
Yes.
References
Huerta-Canepa, G., & Lee, D. (2010). A virtual cloud computing provider for mobile devices. In Proceedings of 1st ACM workshop on mobile cloud computing & services: Social networks and beyond (MCS’10) (pp. 1–5).
Fernando, N., Loke, S. W., & Rahayu, J. W. (2012). Mobile cloud computing: A survey. Elsevier Journal of Future Generation Computer System, 29(1), 84–106.
Zhang, T. (2017). Data offloading in mobile edge computing: A coalition and pricing-based approach. Journal of IEEE Access, 6(1), 2760–2767.
Khan, A. U. R., Othman, M., Madani, S. A., & Khan, S. U. (2014). A survey of mobile cloud computing application models. Journal of IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 16(1), 393–413.
Yu, Y. (2016). Mobile edge computing towards 5G: Vision, recent progress, and open challenges. Journal of China Communication, 13(2), 89–99.
Osanaiye, O., Chen, S., Yan, Z., Lu, R., Choo, K. K. R., & Dlodlo, M. (2017). From cloud to fog computing: A review and a conceptual live VM migration framework. Journal of IEEE Access, 5(1), 8284–8300.
Botta, A., Donato, W., Persico, V., & Pescapé, A. (2016). Integration of cloud computing and Internet of things: A survey. Journal of Future Generation Computing System, 56, 684–700.
Aazam, M., & Huh, E. N. (2014). Fog computing and smart gateway-based communication for Cloud of Things. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on future Internet of Things and Cloud (FiCloud) (pp. 464–470).
Yi, S., Li, C., & Li, Q. (2015). A survey of fog computing: concepts, applications and issues. In Proceedings of the ACM workshop on mobile big data (pp. 37–42).
Korrapati, R. (2014). Validated management practices, ser. A.H.W. Sameer series. Diamond Pocket Books, [Online]. Available: https://books.google.com.sg/books?id=z4psBQAAQBAJ
Klemperer, P. (2004). Auctions: Theory and practice, ser. Princeton paperbacks. Princeton University Press, [Online]. Available: https://books.google.com.vn/books?id=-FJjQgAACAAJ
Lucking-Reiley, D. (2000). Vickrey auctions in practice: From nineteenth century philately to twenty-first-century e-commerce. The Journal of Economic Perspectives, 14(3), 183–192.
Sandholm, T. W. (1996). Limitations of the Vickrey auction in computational multiagent systems. In Proceedings of the second international conference on multiagent systems (ICMAS-96) (pp. 299–306).
Klemperer, P. (2002). What really matters in auction design. The Journal of Economic Perspectives, 16(1), 169–189.
Hu, C. (2018). Calculation of the behavior utility of a network system: Conception and principle. Journal of Engineering, 4(1), 78–84.
Gong, Z., Zhang, N., & Chiclana, F. (2018). The optimization ordering model for intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations with utility functions. Journal of Knowledge-Based System, 165(1), 174–184.
Perez, S. (2010). Mobile cloud computing. [Online]. Available: http://exoplanet.eu/catalog.php
Satyanarayanan, M. (1996). Fundamental challenges in mobile computing. In Proceedings of the fifteenth annual ACM symposium on principles of distributed computing, PODC’96, ACM (pp. 1–7).
Siegele, L. (2008). Let it rise: A special report on corporate it. [Online]. Available: http://www.economist.com/node/12411882
Armbrust, M., Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A., Katz, R., Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D., Rabkin, A., & Stoica, I. (2009). Above the clouds: A Berkeley view of cloud computing. Technical Report UCB/EECS-2009-28.
Carolan, J., Gaede, S., Baty, J., Brunette, G., Licht, A., Remmell, J., Tucker, L., & Weise, J. (2009). Introduction to cloud computing architecture. white paper.
Cheng, J., Balan, R.K., & Satyanarayanan, M. (2005). Exploiting rich mobile environments. Technical Report.
Pandey, S., Voorsluys, W., Niu, S., Khandoker, A., & Buyya, R. (2012). An autonomic cloud environment for hosting ecg data analysis services. Journal of Future Generation Computer Systems, 28(1), 147–154.
Kung, H.-Y., Chen, C.-H., & Ku, H.-H. (2012). Designing intelligent disaster prediction models and systems for debris-flow disasters in Taiwan. Journal of Expert Systems with Applications, 39(1), 5838–5856.
Satyanarayanan, M., Bahl, P., & Caceres, R. N. (2009). The case for VM-based cloudlets in mobile computing. Journal of IEEE Pervasive Computing, 8(1), 14–23.
Cuervo, E., Balasubramanian, A., Cho, D.-K., Wolman, A., Saroiu, S., Chandra, R., & Bahl, P. (2010). Maui: Making smartphones last longer with code offload. In Proceedings of the 8th international conference on mobile systems, applications, and services, MobiSys’10, ACM (pp. 49–62).
Coronato, A., & Pietro, G. D. (2008). Mipeg: A middleware infrastructure for pervasive grids. Journal of Future Generation Computer Systems, 24(1), 17–29.
Gupta, A., & Jha, R. K. (2015). A survey of 5G network: Architecture and emerging technologies. Journal of IEEE Access, 3(1), 1206–1232.
Rappaport, T. (1996). Wireless communications: Principles and practice. Prentice-Hall.
Wang, C. X., Haider, F., Gao, X., You, X. H., Yang, Y., Yuan, D., Aggoune, H., Haas, H., Fletcher, S., & Hepsaydir, E. (2014). Cellular architecture and key technologies for 5G wireless communication networks. Journal of IEEE Communication Magazine, 52(2), 122–130.
Silva, P. C., & Walle, B. (2007). Open source software for disaster management. Journal of Communications of the ACM, 50(3), 61–65.
Hu, Y. C., Patel, M., Sabella, D., Sprecher, N., & Young, V. (2015). Mobile edge computing a key technology towards 5G. [Online].Available: https://www.etsi.org/images/files/ETSIWhitePapers/etsi_wp11_mec_a_key_technology_towards_5g.pdf
Patel, M., Hu, Y., Joubert, J., & Ramos, J. R. (2014). European telecommunications standards institute. Mobile Edge Computing Introductory Technical White Paper. [Online]. Available: https://portal.etsi.org/Portals/0/TBpages/MEC/Docs/Mobile-edge_Computing_Introductory_Technical_White_Paper_V1%2018-09-14.pdf
Bronzino, F., Stojadinovic, D., Westphal, C., & Raychaudhuri, D. (2016). Exploiting network awareness to enhance DASH over wireless. In Proceeding of 13th IEEE annual consumer communications & networking conference (CCNC) (pp. 1092–1100).
Zhang, T., Chowdhery, A., & Bahl, P. (2015). The design and implementation of a wireless video surveillance system. In Proceedings 21st annual international conference on mobile computing and networking, ACM (pp. 426–438).
Chen, T. Y., Ravindranath, L., & Deng, S. (2015). Demo: Glimpse—Continuous, real-time object recognition on mobile devices. In Proceedings of 99 international China communications supplement no. 2 conference on embedded networked sensor systems (pp. 1–14).
Kumar, K., Liu, J., & Lu, Y. (2013). A survey of computation offloading for mobile systems. Journal of Mobile Networks and Applications, 18(1), 129–140.
Aazam, M., & Huh, E. N. (2015). Fog computing micro datacenter based dynamic resource estimation and pricing model for IoT. In Proceedings of IEEE 29th international conference on advanced information networking and applications (AINA) (pp. 687–694).
Shi, Y., Ding, G., Wang, H., Roman, H.E., & Lu, S. (2015). The fog computing service for healthcare. In Proceedings of 2nd IEEE international symposium on future information and communication technologies for ubiquitous healthcare (Ubi-HealthTech) (pp. 1–5).
Sarkar, S., Chatterjee, S., & Misra, S. (2015). Assessment of the suitability of fog computing in the context of Internet of Things. Journal of IEEE Transaction of Cloud Computing, 6(1), 46–59.
Lee, K., Kim, D., Ha, D., Rajput, U., & Oh, H. (2015). On security and privacy issues of fog computing supported Internet of Things environment. In Proceedings of 6th IEEE international conference on the network of the future (NOF) (pp. 1–3).
Zhu, X., Chan, D. S., Hu, H., Prabhu, M. S., Ganesan, E., & Bonomi, F. (2015). Improving video performance with edge servers in the fog computing architecture. Journal of Intel Technology, 19(1), 202–224.
Bonomi, F., Milito, R., Natarajan, P., & Zhu, J. (2014). Fog computing: A platform for Internet of Things and analytics. In The proceedings of series studies in computational intelligence, big data and internet of things: a roadmap for smart environments (pp. 169–186).
Dsouza, C., Ahn, G.J., & Taguinod, M. (2014). Policy-driven security management for fog computing: Preliminary framework and a case study. In Proceedings of IEEE 15th international conference on information reuse and integration (IRI) (pp. 16–23).
Roman, R., Lopez, J., & Mambo, M. (2016). Mobile edge computing, Fog et al.: A survey and analysis of security threats and challenges. arXiv preprintarXiv:1602.00484.
Zhang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2006). Transparent computing: A new paradigm for pervasive computing. In Proceedings of international conference on ubiquitous intelligence and computing, Springer (pp. 1–11).
Zhang, Y. (2008). The challenges and opportunities in transparent computing. In Proceedings of IEEE/IFIP EUC (vol. 1, pp. 1–3).
Zhang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2007). 4VP: A novel meta OS approach for streaming programs in ubiquitous computing. In Proceedings of IEEE AINA (pp. 394–403).
Zhang, Y., Guo, K., Ren, J., Zhou, Y., Wang, J., & Chen, J. (2017). Transparent computing: A promising network computing paradigm. Journal of Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 13(1), 64–81.
Fang, Y. (2014). On delivery delay-constrained throughput and end-to-end delay in MANETs. In Proceedings of IEEE HPCC (pp. 456–463).
Wei, L., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2009). Simulation analysis and validation of cache performance in TransCom systems. Journal of Tsinghua University Science and Technology, 49(10), 1700–1703.
Gao, Y., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2012). Performance analysis of virtual disk system for transparent computing. In Proceedings of IEEE UIC/ATC (pp. 470–477).
Liu, H. (2013). Receiving buffer adaptation for high-speed data transfer. Journal of IEEE Transaction Computers, 62(11), 2278–2291.
Xu, Y. (2015). Optimization of transparent computing system based on virtualization. Master’s thesis, Central South University.
Yang, H. (2006). A dynamic load balancing algorithm based on transparent computing. Journal of Computer Engineering, 32(13), 133–135.
Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2014). Leveraging the tail time for saving energy in cellular networks. Journal of IEEE Transaction of Mobile Computing, 13(7), 1536–1549.
Liang, W., Xiong, Y., & Wu, M. (2013). A cross platform computing method and its application for mobile device in transparent computing. In Proceedings of IEEE HPCC (pp. 1838–1845).
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Journal of Information and Control, 8(3), 338–353.
Zadeh, L. A. (2011). A note on Z-numbers. Journal of Information Sciences, 181(14), 2923–2932.
Aliev, R. A., Huseynov, O. H., & Zeinalova, L. M. (2016). The arithmetic of continuous Z-numbers. Journal of Information Science, 373(1), 1339–1351.
Kang, B., Wei, D., Li, Y., & Deng, Y. (2012). A method of converting Z-number to classical fuzzy number. Journal of Information Computer Science, 9(3), 703–709.
Liu, P., Hendiani, S., Bagherpour, M., Ghannadpour, S. F., & Mahmoudi, A. (2019). Utility-numbers theory. Journal of IEEE Access, 7, 56994–57008.
Rawadi, J. M., Artail, H., & Safa, H. (2014). Providing local cloud service to mobile devices with intercloudlet communication. In Proceedings of 17th IEEE Mediterranean electrotechnical conference (pp. 134–138).
Artail, A., Frenn, K., Artail H., & Safa, H. (2015). A framework of mobile cloudlet center based on the use of mobile devices as cloudlets. In Proceedings of 29th IEEE international conference on advanced information networking and applications (pp. 777–784).
Kumar, R., & Yadav, S. K. (2017). Scalable key parameter yield of resources model for performance enhancement in mobile cloud computing. Journal of Wireless Personal Communications, 95(4), 3969–4000.
Luong, N. C., Wang, P., Niyato, D., Yonggang, W., & Han, Z. (2016). Resource management in cloud networking using economic analysis and pricing models: A survey. IEEE Journal of Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 19(2), 954–1001.
Wang, Q., Guo, S., Liu, J., Pan, C., & Yang, L., (2019). Profit maximization incentive mechanism for resource providers in mobile edge computing. In proceedings of IEEE transactions on services computing (pp. 1–12).
Chen, X., Jiao, L., Li, W., & Fu, X. (2016). Efficient multi-user computation offloading for mobile-edge cloud computing. Journal of IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 24(5), 2795–2808.
Zhang, H., Guo, F., Ji, H., & Zhu, C. (2017). Combinational auction-based service provider selection in mobile edge computing networks. Journal of IEEE Access, 5, 13455–13464.
Vickrey, W. (1961). Counter speculation, auctions, and competitive sealed tenders. Journal of Finance, 16(1), 8–37.
Tsai, L., & Liao, W. (2016). Virtualized cloud data center networks: Issues in resource management. Springer briefs in electrical and computer engineering. Springer.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, S.K., Kumar, R. Scalable Profit Optimized Incentive Mechanism for Resources in Cloudlet Based Mobile Edge Computing Framework. Wireless Pers Commun 125, 159–207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09546-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-022-09546-9