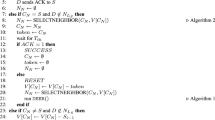Abstract
In these days, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) shows a huge impact on all appliances but one of the huge challenges in WSN is management of energy because the nodes in the network run with battery power. As the replacement of energy drained nodes is difficult, and frequent failure of links may occur and it incurs huge data loss. To avoid this issue the we proposed a Hybrid Krill Herd and Spider Monkey with Grid-Based Data Dissemination (HKHSM-GBDD) protocol with the Shortest Energy Resourceful Routing (SERR) mechanism to develop an efficient and better wireless communication channel. The presented HKHSM framework is utilized to classify malicious and energy drained nodes in earlier stage and to detect the link failure. Furthermore, the SERR mechanism is processed to recover the link and route maintenance. This novel proposed protocol has improved packet delivery ratio and energy consumption. It also enhances energy state of sensor nodes by mounting its lifetime and rerouting. Finally, the competence of the proposed mechanism is compared with existing works and it shows significant improvement over existing algorithms for the considered parameters.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farsi, M., et al. (2019). Deployment techniques in wireless sensor networks, coverage and connectivity: A survey. IEEE Access, 7, 28940–28954.
Deepa, J., & Sutha, J. (2019). A new energy based power aware routing method for MANETs. Cluster Computing, 22(6), 13317–13324.
El-Sayed, W. M., El-Bakry, H. M., & El-Sayed, S. M. (2019). Integrated data reduction model in wireless sensor networks. Applied Computing and Informatics, 3(1), 23–32.
Chauhdary, S., et al. (2019). A twofold sink-based data collection in wireless sensor network for sustainable cities. Sustainable cities and society, 45, 1–7.
Julme, B., & Patil, P. (2019). A review on clustering algorithms in wireless sensor networks for optimal energy utilization. Intelligent communication technologies and virtual mobile networks. Cham: Springer.
Guravaiah, K., & LeelaVelusamy, R. (2019). Prototype of home monitoring device using Internet of Things and river formation dynamics-based multi-hop routing protocol (RFDHM). IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 65(3), 329–338.
Ullah, Z., et al. (2019). DSCB: Dual sink approach using clustering in body area network. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 12(2), 357–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-017-0587-z.
Pramanik, P. K. D., Nayyar, A., & Pareek, G. (2019). WBAN: Driving e-healthcare beyond telemedicine to remote health monitoring: Architecture and protocols. Telemedicine Technologies, 7(1), 89–119.
Tan, Q., et al. (2019). Interference-aware lifetime maximization with joint routing and charging in wireless sensor networks. CCF Transactions on Networking, 2(3), 188–206.
Arjunan, S., & Pothula, S. (2019). A survey on unequal clustering protocols in wireless sensor networks. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 31(3), 304–317.
Dey, I., et al. (2019). Virtual MIMO wireless sensor networks: Propagation measurements and fusion performance. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 67(8), 5555–5568.
Fahmy, H. M. A. (2020). Energy harvesting projects for WSNs. Wireless Sensor Networks. (pp. 489–609) Cham: Springer.
Aslam, N., Xia, K., & Hadi, M. U. (2019). Optimal wireless charging inclusive of intellectual routing based on SARSA learning in renewable wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 19(18), 8340–8351.
Merlin, R. T., & Ravi, R. (2019). Novel trust based energy aware routing mechanism for mitigation of black hole attacks in MANET. Wireless Personal Communications, 104(4), 1599–1636.
Alfouzan, F. A., et al. (2019). An energy-conserving collision-free MAC protocol for underwater sensor networks. IEEE Access, 7, 27155–27171.
Ramya, K. M., & Hanumanthappa S. N. (2019). Cluster head enhance selection using type-II fuzzy logic for multi-hop wireless sensor network. In International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things. Springer, Cham.
Guleria, K., & Verma, A. K. (2019). Comprehensive review for energy efficient hierarchical routing protocols on wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 25(3), 1159–1183.
Bengheni, A., Didi, F., & Bambrik, I. (2019). EEM-EHWSN: Enhanced energy management scheme in energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 25(6), 3029–3046.
Alarifi, A., & Tolba, A. (2019). Optimizing the network energy of cloud assisted internet of things by using the adaptive neural learning approach in wireless sensor networks. Computers in Industry, 106, 133–141.
Kassan, S., Gaber, J. & Lorenz, P. (2020). Autonomous energy management system achieving piezoelectric energy harvesting in wireless sensors. Mobile Network Applications, 25, 794–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01303-w.
Abella, C. S., et al. (2019). Autonomous energy-efficient wireless sensor network platform for home/office automation. IEEE Sensors Journal, 19(9), 3501–3512.
Sharma, H., Haque, A., & Jaffery, Z. A. (2019). Maximization of wireless sensor network lifetime using solar energy harvesting for smart agriculture monitoring. Ad Hoc Networks, 94, 101966.
Kanthimathi, M., Amutha, R., & Kumar, K. S. (2018). Energy efficient differential cooperative MIMO algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 103(4), 2715–2728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5957-1
Behzad, M., et al. (2019). Performance optimization in IoT-based next-generation wireless sensor networks. Transactions on Computational Collective Intelligence XXXIII. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, (pp. 1–31).
Srivastava, V., Tripathi, S., & Singh, K. (2020). Energy efficient optimized rate based congestion control routing in wireless sensor network. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 11(3), 1325–1338.
Renold, A. P., & Balaji Ganesh, A. (2019). Energy efficient secure data collection with path-constrained mobile sink in duty-cycled unattended wireless sensor network. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 55, 1–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocherla, R., Vatambeti, R. An Efficient Routing Strategy for Energy Management in Wireless Sensor Network Using Hybrid Routing Protocols. Wireless Pers Commun 124, 49–73 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09318-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09318-x