Abstract
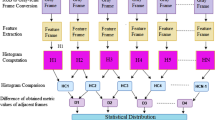
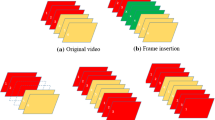
It is a generic belief that digital video can be proffered as visual evidence in areas like politics, criminal litigation, journalism and military intelligence services. Multicamera smartphones with megapixels of resolution are a common hand-held device used by everyone. This has made the task of video recording very easy. At the same time a variety of applications available on smart phones have made this indispensable source of information vulnerable to deliberate manipulations. Hence, content authentication of video evidence becomes essential. Copy-move forgery or Copy-paste forgery is consequential forgery done by forgers for changing the basic understanding of the scene. Removal or addition of frames in a video clip can also be managed by advanced apps on smartphones. In case of surveillance, the video camera and the background are stable which makes forgery easy and imperceptible. Therefore, accurate Video forgery detection is crucial. This paper proposes an efficient method—VFDHSOG based on Histograms of the second order gradient to locate ‘suspicious’ frames and then localize the CMF within the frame. A ‘suspicious’ frame is located by computing correlation coefficients of the HSOG feature after obtaining a binary image of a frame. Performance evaluation is done using the benchmark datasets Surrey university library for forensic analysis (SULFA), the Video tampering dataset (VTD) and SYSU-OBJFORGED dataset. SULFA has video files of different quality like q10, q20 etc., which represents high compression. The VTD dataset provides both, i.e. inter and intra frame forgery. The SYSU dataset covers different attacks like scaling and rotation. An overall accuracy of 92.26% is achieved with the capability to identify attacks like scale up/down and rotation.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le, T.T., Almansa, A., Gousseau, Y., Masnou. S. (2017). Motion-consistent video inpainting. In 2017 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE p 2094–2098.
Wang, T. C., Liu, M. Y., Zhu, J. Y., Liu, G., Tao, A., Kautz, J., Catanzaro, B. (2018). Video-to-video synthesis. arXiv preprint.
Bansal, A., Ma, S., Ramanan, D., Sheikh, Y. (2018). Recycle-gan: unsupervised video retargeting. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) p. 119–135.
Liu, M. Y., Breuel, T., Kautz, J. (2017). Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks. arXiv preprint.
Dong, H., Neekhara, P., Wu, C., Guo, Y. (2017). Unsupervised image-to-image translation with generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint.
Suwajanakorn, S., Seitz, S. M., & Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. (2017). Synthesizing obama: Learning lip sync from audio. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG), 36(4), 1–13.
Fridrich, A. J., Soukal, B. D., Lukáš, A. J. (2003). Detection of copy-move forgery in digital images. In in Proceedings of Digital Forensic Research Workshop.
Fridrich, J. (1999). Methods for tamper detection in digital images. In Multimedia and Security, Workshop at ACM Multimedia, p. 29–34.
Luo, W., Qu, Z., Pan, F., & Huang, J. (2007). A survey of passive technology for digital image forensics. Frontiers of Computer Science in China, 1(2), 166–179.
Rey, C., & Dugelay, J. L. (2002). A survey of watermarking algorithms for image authentication. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2002(6), 1–9.
Shivakumar, B. L., Baboo, S. S. (2011). Detection of region duplication forgery in digital images using SURF. International Journal of Computer Science Issues (IJCSI), 8(4), 199.
Lu, C. S., & Liao, H. Y. (2003). Structural digital signature for image authentication: an incidental distortion resistant scheme. IEEE transactions on multimedia, 5(2), 161–173.
Tolosana, R., Vera-Rodriguez, R., Fierrez, J., & Ortega-Garcia, J. (2015, March). Feature-based dynamic signature verification under forensic scenarios. In 3rd International Workshop on Biometrics and Forensics (IWBF 2015) IEEE, p 1-6.
Pawar, A. B., Sheikh, H. I., & Dhawade, N. A. (2016). Data encryption and security using video watermarking. International Journal of Engineering Science, 4(4), 3238.
Khan, E. S., & Kulkarni, E. A. (1801). An efficient method for detection of copy-move forgery using discrete wavelet transform. International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering, 2(5), 2010.
Feng, C., Xu, Z., Zhang, W., & Xu, Y. (2014). Automatic location of frame deletion point for digital video forensics. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM workshop on Information hiding and multimedia security, p. 171–179.
Bestagini, P., Milani, S., Tagliasacchi, M., & Tubaro, S. (2013). Local tampering detection in video sequences. In 2013 IEEE 15th international workshop on multimedia signal processing (MMSP), IEEE. p. 488–493.
Milani, S., Fontani, M., Bestagini, P., Barni, M., Piva, A., Tagliasacchi, M., & Tubaro, S. (2012). An overview on video forensics. APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing, 1.
Zhang, Z., Hou, J., Ma, Q., Li, Z. (2015). Efficient video frame insertion and deletion detection based on inconsistency of correlations between local binary pattern coded frames. Security and Communication networks, 8(2), 311–320.
Chao, J., Jiang, X., Sun, T. (2012). A novel video inter-frame forgery model detection scheme based on optical flow consistency. In International Workshop on Digital Watermarking (pp. 267–281). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Yang, J., Huang, T., Su, L. (2016). Using similarity analysis to detect frame duplication forgery in videos. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 75(4), 1793–1811.
Jiang, X., Wang, W., Sun, T., Shi, Y. Q., Wang, S. (2013). Detection of double compression in MPEG-4 videos based on Markov statistics. IEEE Signal processing letters, 20(5), 447–450.
Wang, W., & Farid, H. (2006, September). Exposing digital forgeries in video by detecting double MPEG compression. In Proceedings of the 8th workshop on Multimedia and security, p. 37–47.
Sekhar, R., & Shaji, R. S. (2014). A methodological review on copy-move forgery detection for image forensics. International Journal of Digital Crime and Forensics (IJDCF), 6(4), 34–49.
Zhao, J., & Guo, J. (2013). Passive forensics for copy-move image forgery using a method based on DCT and SVD. Forensic science international, 233(1–3), 158–166.
Lin, C., Chen, C., & Chang, Y. (2015). An Efficiency Enhanced Cluster Expanding Block Algorithm for Copy-Move Forgery Detection. International Conference on Intelligent Networking and Collaborative Systems, 2015, 228–231. https://doi.org/10.1109/INCoS.2015.90
Chauhan, D., Kasat, D., Jain, S., Thakare, V. (2016). Survey on keypoint based copy-move forgery detection methods on image. Procedia Computer Science, 85, 206–212.
Teerakanok, S., Uehara, T. (2019). Copy-move forgery detection: a state-of-the-art technical review and analysis. IEEE Access, 7, 40550–40568.
Huang, D., Zhu, C., Wang, Y., Chen, L. (2014). HSOG: A novel local image descriptor based on histograms of the second-order gradients. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 23(11), 4680–4695.
Wang, W., Farid, H. (2007). Exposing digital forgeries in video by detecting duplication. In Proceedings of the 9th workshop on Multimedia & security, p. 35–42.
Wang, Q., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., Ma, Q. (2014). Video inter-frame forgery identification based on consistency of correlation coefficients of gray values. Journal of Computer and Communications, 2(04), 51.
Liu, Y., Huang, T. (2017). Exposing video inter-frame forgery by Zernike opponent chromaticity moments and coarseness analysis. Multimedia Systems, 23(2), 223–238.
Liao, S. Y., Huang, T. Q. (2013). Video copy-move forgery detection and localization based on Tamura texture features. In 2013 6th international congress on image and signal processing (CISP) (Vol. 2, pp. 864–868). IEEE.
Lin, G. S., Chang, J. F. (2012). Detection of frame duplication forgery in videos based on spatial and temporal analysis. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 26(07), 1250017.
Hsu, C. C., Hung, T. Y., Lin, C. W., Hsu, C. T. (2008). Video forgery detection using correlation of noise residue. In 2008 IEEE 10th workshop on multimedia signal processing (pp. 170–174). IEEE.
Kobayashi, M., Okabe, T., & Sato, Y. (2010). Detecting forgery from static-scene video based on inconsistency in noise level functions. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 5(4), 883–892.
Pun, C. M., Yuan, X. C., & Bi, X. L. (2015). Image forgery detection using adaptive oversegmentation and feature point matching. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 10(8), 1705–1716.
Li, J., Li, X., Yang, B., & Sun, X. (2014). Segmentation-based image copy-move forgery detection scheme. IEEE transactions on information forensics and security, 10(3), 507–518.
Birajdar, G. K., & Mankar, V. H. (2013). Digital image forgery detection using passive techniques: A survey. Digital investigation, 10(3), 226–245.
Asghar, K., Habib, Z., & Hussain, M. (2017). Copy-move and splicing image forgery detection and localization techniques: A review. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences, 49(3), 281–307.
Soni, B., Das, P. K., & Thounaojam, D. M. (2018). CMFD: A detailed review of block based and key feature based techniques in image copy-move forgery detection. IET Image Processing, 12(2), 167–178.
Abd Warif, N. B., Wahab, A. W. A., Idris, M. Y. I., Ramli, R., Salleh, R., Shamshirband, S., & Choo, K. K. R. (2016). Copy-move forgery detection: survey, challenges and future directions. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 75, 259–278.
Bayram, S., Sencar, H. T., & Memon, N. (2009, April). An efficient and robust method for detecting copy-move forgery. In 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, IEEE, p. 1053–1056.
Cozzolino, D., Poggi, G., & Verdoliva, L. (2015). Efficient dense-field copy–move forgery detection. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 10(11), 2284–2297.
Ryu, S. J., Lee, M. J., & Lee, H. K. (2010). Detection of copy-rotate-move forgery using Zernike moments. In International workshop on information hiding (pp. 51–65). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Mahdian, B., & Saic, S. (2007). Detection of copy–move forgery using a method based on blur moment invariants. Forensic science international, 171(2–3), 180–189.
Huang, D. Y., Huang, C. N., Hu, W. C., & Chou, C. H. (2017). Robustness of copy-move forgery detection under high JPEG compression artifacts. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 76(1), 1509–1530.
Costanzo, A., Amerini, I., Caldelli, R., & Barni, M. (2014). Forensic analysis of SIFT keypoint removal and injection. IEEE transactions on information forensics and security, 9(9), 1450–1464.
Yang, B., Sun, X., Guo, H., Xia, Z., & Chen, X. (2018). A copy-move forgery detection method based on CMFD-SIFT. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 77(1), 837–855.
Manu, V. T., Mehtre, B. M. (2016). Detection of copy-move forgery in images using segmentation and SURF. In Advances in signal processing and intelligent recognition systems (pp. 645–654). Springer, Cham.
Silva, E., Carvalho, T., Ferreira, A., & Rocha, A. (2015). Going deeper into copy-move forgery detection: exploring image telltales via multi-scale analysis and voting processes. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 29, 16–32.
Ardizzone, E., Bruno, A., & Mazzola, G. (2015). Copy–move forgery detection by matching triangles of keypoints. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 10(10), 2084–2094.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International journal of computer vision, 60(2), 91–110.
Lee, J. C., Chang, C. P., & Chen, W. K. (2015). Detection of copy–move image forgery using histogram of orientated gradients. Information Sciences, 321, 250–262.
Tralic, D., Zupancic, I., Grgic, S., & Grgic, M. (2013). CoMoFoD—New database for copy-move forgery detection. In Proceedings ELMAR-2013 (pp. 49–54). IEEE.
Lee, J. C. (2015). Copy-move image forgery detection based on Gabor magnitude. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 31, 320–334.
Chao, (2013). Research on digital video inter-frame forgery passive detection algorithm based on visual content, M.S. thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ., Shanghai, China.
Kingra, S., Aggarwal, N., & Singh, R. D. (2017). Inter-frame forgery detection in H. 264 videos using motion and brightness gradients. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 76(24), 25767–25786.
Aghamaleki, J. A., & Behrad, A. (2016). Inter-frame video forgery detection and localization using intrinsic effects of double compression on quantization errors of video coding. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 47, 289–302.
Subramanyam, A. V., & Emmanuel, S. (2012). Video forgery detection using HOG features and compression properties. In 2012 IEEE 14th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP) (pp. 89–94). IEEE.
Khalid, M., Yousaf, M. M., Murtaza, K., & Sarwar, S. M. (2018). Image de-fencing using histograms of oriented gradients. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 12(6), 1173–1180.
Iqbal, N., Missen, M. M. S., Salamat, N., & Prasath, V. S. (2019). On Video Based Human Abnormal Activity Detection with Histogram of Oriented Gradients. In Handbook of Multimedia Information Security: Techniques and Applications (pp. 431–448). Cham: Springer.
Surasak, T., Takahiro, I., Cheng, C. H., Wang, C. E., & Sheng, P. Y. (2018). Histogram of oriented gradients for human detection in video. In 2018 5th International Conference on Business and Industrial Research (ICBIR) (pp. 172–176). IEEE.
Maurya, A., & Tarar, S. (2016). Spoofed Video Detection Using Histogram of Oriented Gradients. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Computer Vision and the Internet (pp. 1–7).
Arora, P., Chaudhary, G., & Srivastava, S. (2019). Exploiting Oriented Gradient Histogram for Dorsal Vein Recognition. In 2019 Twelfth International Conference on Contemporary Computing (IC3) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Yang, X., Zhang, C., & Tian, Y. (2012). Recognizing actions using depth motion maps-based histograms of oriented gradients. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 1057–1060).
Hubel, D. H., & Wiesel, T. N. (1979). Brain mechanisms of vision. Scientific American, 241(3), 150–163.
Morgan, M. J. (2011). Features and the ‘primal sketch.’ Vision research, 51(7), 738–753.
Wallis, S. A., & Georgeson, M. A. (2012). Mach bands and multiscale models of spatial vision: The role of first, second, and third derivative operators in encoding bars and edges. Journal of vision, 12(13), 18–18.
Muhammad, G., Al-Hammadi, M. H., Hussain, M., & Bebis, G. (2014). Image forgery detection using steerable pyramid transform and local binary pattern. Machine Vision and Applications, 25(4), 985–995.
Brown, M., Hua, G., & Winder, S. (2010). Discriminative learning of local image descriptors. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 33(1), 43–57.
Singh, R. D., & Aggarwal, N. (2017). Detection and localization of copy-paste forgeries in digital videos. Forensic science international, 281, 75–91.
Fadl, S., Han, Q., & Qiong, L. (2020). Exposing video inter-frame forgery via histogram of oriented gradients and motion energy image. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 31(4), 1365–1384.
Wang, H., & Wang, H. (2018). Perceptual hashing-based image copy-move forgery detection. Security and Communication Networks.
Al-Sanjary, O. I., Ahmed, A. A., & Sulong, G. (2016). Development of a video tampering dataset for forensic investigation. Forensic science international, 266, 565–572.
Singh, V. K., Chakraborty, P., & Tripathi, R. C. (2017). Detection and Localization of Duplicated Frames in Doctored Video. In International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications (pp. 661–669). Cham: Springer.
Su, L., & Li, C. (2018). A novel passive forgery detection algorithm for video region duplication. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 29(3), 1173–1190.
Wang, J., Liu, G., Zhang, Z., Dai, Y., & Wang, Z. (2009). Fast and robust forensics for image region-duplication forgery. Acta Automatica Sinica, 35(12), 1488–1495.
Zhang, J., Chen, G., & Jia, Z. (2017). An image stitching algorithm based on histogram matching and SIFT algorithm. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 31(04), 1754006.
Qadir, G., Yahaya, S., & Ho, A. T. (2012). Surrey university library for forensic analysis (SULFA) of video content.
Bakas, J., Naskar, R., & Dixit, R. (2019). Detection and localization of inter-frame video forgeries based on inconsistency in correlation distribution between Haralick coded frames. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 78(4), 4905–4935.
Zhao, D. N., Wang, R. K., & Lu, Z. M. (2018). Inter-frame passive-blind forgery detection for video shot based on similarity analysis. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 77(19), 25389–25408.
Ardizzone, E., & Mazzola, G. (2015). A tool to support the creation of datasets of tampered videos. In International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing (pp. 665–675). Cham: Springer.
Li, Y., & Zhou, J. (2018). Fast and effective image copy-move forgery detection via hierarchical feature point matching. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 14(5), 1307–1322.
Zhong, J., Gan, Y., Young, J., & Lin, P. (2017). Copy move forgery image detection via discrete Radon and polar complex exponential transform-based moment invariant features. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 31(02), 1754005.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Manuscript title: “VFDHSOG: Copy-Move Video Forgery Detection using Histogram of Second Order Gradients All persons who meet authorship criteria are listed as authors, and all authors certify that they have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content, including participation in the concept, design, analysis, writing, or revision of the manuscript. Furthermore, each author certifies that this material or similar material has not been and will not be submitted to or published in any other publication before its appearance in the Wireless Personal Communication. Authorship contributions Category 1 Conception and design of study: Mrs. Punam S. Raskar Acquisition of data: Mrs. Punam S. Raskar Analysis and/or interpretation of data: Mrs.Punam S. Raskar, Dr. Sanjeevani K. Shah Category 2 Drafting the manuscript: Mrs. Punam S. Raskar Revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content: Mrs.Punam S. Raskar, Dr. Sanjeevani K. Shah Category 3 Approval of the version of the manuscript to be published (the names of all authors must be listed): Mrs.Punam S. Raskar, Dr. Sanjeevani K. Shah.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interet. We do confirm that, this work is original and has not been published elsewhere, nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere. Also, all authors of this research article have approved the manuscript for submission.
Code availability
Stepwise Algorithm is provided in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raskar, P.S., Shah, S.K. VFDHSOG: Copy-Move Video Forgery Detection Using Histogram of Second Order Gradients. Wireless Pers Commun 122, 1617–1654 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08964-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08964-5