Abstract
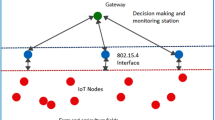
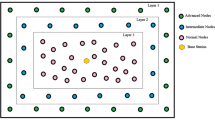
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a subclass of the Industry 4.0 standard. The functionality of IoT depends on the Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) design. The IoT-empowered WSNs received the researcher's attention for the Smart Farming (SF) applications. SF nowadays is required to enhance farm productivity while minimizing the cost and resources. The agriculture sensors devices disposed over the farm collect the on-field farm data and transfer it wirelessly to the base station for decision-making and agriculture monitoring. As the nodes are resource restrained, the process of periodic farm data gathering and multi-hop delivery needs to be effective in terms of Quality of Service (QoS) and energy-efficiency of information transmission by reflecting the long-distance transmission difficulties of SF applications. To enhance the network lifetime substantially of densely deployed WSN for periodically monitoring of farm conditions, we propose a novel Nature-Inspired algorithm-based Cross-layer Clustering (NICC) protocol. We design NICC to find a reasonably better solution for clustering and routing in SF applications. NICC explores the idea of a nature-inspired optimization algorithm called Bacterial Foraging Optimization (BFO) with optimal fitness function, which models the trade-off among the energy efficiency and optimal data transmission. We design a BFO algorithm to select the optimal sensor node for clustering and routing problems based on cross-layer parameters-based fitness value computation. The cross-layer parameter includes the sensor parameters from layers like network layer, physical layer, and Medium Access Control (MAC). The numerical results show the superiority of the NICC protocol for various WSN-assisted SF scenarios against state-of-art clustering techniques.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhagwat, P., Raman, B., & Sanghi, D. (2004). Turning 802.11 inside-out. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 34(1), 33–38. https://doi.org/10.1145/972374.972381/
Chebrolu, K., & Raman, B. (2007). FRACTEL: A fresh perspective on (rural) mesh networks (Vol. 8). https://doi.org/10.1145/1326571.1326583.
Hussain, M. I., Ahmed, Z. I., Sarma, N., & Saikia, D. K. (2016). An efficient TDMA MAC protocol for multi-hop WiFi-based long distance networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(4), 1971–1994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-3165-9
Tordera, E. M., Masip-Bruin, X., Garca-Almiñana, J., et al. (2016). What is a fog node a tutorial on current concepts towards a common definition. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.09193.
Armbrust, M., Stoica, I., Zaharia, M., Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A. D., Katz, R., Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D., & Rabkin, A. (2010). A view of cloud computing. Communications of the ACM, 53(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.1145/1721654.1721672
Mohd Kassim, M. R., Mat, I., & Harun, A. N. (2014). Wireless sensor network in precision agriculture application. In 2014 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS). https://doi.org/10.1109/cits.2014.6878963.
Zhu, Y., Song, J., & Dong, F. (2011). Applications of wireless sensor network in the agriculture environment monitoring. Procedia Engineering, 16, 608–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.08.1131
Ojha, T., Misra, S., & Raghuwanshi, N. S. (2015). Wireless sensor networks for agriculture: The state-of-the-art in practice and future challenges. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 118, 66–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.08.011
Mahajan, H. B., & Badarla, A. (2018). Application of Internet of Things for smart precision farming: Solutions and challenges. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 2018, 37–45.
Mahajan, H. B., & Badarla, A. (2019). Experimental analysis of recent clustering algorithms for wireless sensor network: Application of IoT based smart precision farming. Journal of Advanced Research in Dynamical & Control Systems. https://doi.org/10.5373/JARDCS/V11I9/20193162
Mahajan, H. B., & Badarla, A. (2020). Detecting HTTP vulnerabilities in IoT-based precision farming connected with cloud environment using artificial intelligence. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 29(3), 214–226.
Kuila, P., & Jana, P. K. (2014). Energy efficient clustering and routing algorithms for wireless sensor networks: Particle swarm optimization approach. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 33, 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2014.04.009
Kim, Y.-M., Lee, E.-J., Park, H.-S., Choi, J.-K., & Park, H.-S. (2012). Ant colony based self-adaptive energy saving routing for energy efficient Internet. Computer Networks, 56(10), 2343–2354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2012.03.024
Bari, A., Wazed, S., Jaekel, A., & Bandyopadhyay, S. (2009). A genetic algorithm based approach for energy efficient routing in two-tiered sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 7(4), 665–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2008.04.003
Muruganathan, S. D., Ma, D. C. F., Bhasin, R. I., & Fapojuwo, A. O. (2005). A centralized energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 43(3), S8-13. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcom.2005.1404592
Ammari, H. M., & Das, S. K. (2008). A trade-off between energy and delay in data dissemination for wireless sensor networks using transmission range slicing. Computer Communications, 31(9), 1687–1704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2007.11.006
Calhoun, B. H., Daly, D. C., Verma, N., Finchelstein, D. F., Wentzloff, D. D., Wang, A., Cho, S. H., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2005). Design considerations for ultra-low energy wireless microsensor nodes. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 54(6), 727–740. https://doi.org/10.1109/tc.2005.98
Potdar, V., Sharif, A., & Chang, E. (2009). Wireless Sensor Networks: A survey. In 2009 International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops. https://doi.org/10.1109/waina.2009.192.
Kim, D., Song, S., & Choi, B.-Y. (2013). Energy-efficient adaptive geosource multicast routing for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Sensors, 2013, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/142078
Kaur, M., & Sohi, B. S. (2018). Comparative analysis of bio ınspired optimization techniques in wireless sensor networks with GAPSO approach. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2018/v11i4/114658
Patnaik, S. S., & Panda, A. K. (2012). Particle swarm optimization and bacterial foraging optimization techniques for optimal current harmonic mitigation by employing active power filter. Applied Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing, 2012, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/897127
Khedo, K. K., Hosseny, M. R., & Toonah, M. Z. (2014). PotatoSense: A wireless sensor network system for precision agriculture. In 2014 IST-Africa Conference Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1109/istafrica.2014.6880613.
Nikolidakis, S. A., Kandris, D., Vergados, D. D., & Douligeris, C. (2015). Energy efficient automated control of irrigation in agriculture by using wireless sensor networks. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 113, 154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.02.004
Maurya, S., & Jain, V. (2017). Energy-efficient network protocol for precision agriculture: Using threshold sensitive sensors for optimal performance. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 6, 42–51. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCE.2017.2684960
Hamouda, Y., & Msallam, M. (2018). Variable sampling interval for energy-efficient heterogeneous precision agriculture using wireless sensor networks. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2018.04.010
Parganiha, P., & Anil Kumar, K. (2018). An energy-efficient clustering with hybrid coverage mechanism (EEC—HC) in Wireless Sensor Network for precision agriculture. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 11, 97–103. https://doi.org/10.25103/jestr.113.13
Fathallah, K., Abid, M. A., & Hadj-Alouane, N. B. (2018). PA-RPL: A partition aware IoT routing protocol for precision agriculture. In 2018 14th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC). https://doi.org/10.1109/iwcmc.2018.8450396.
Agrawal, H., Dhall, R., Iyer, K. S. S., & Chetlapalli, V. (2019). An improved energy efficient system for IoT enabled precision agriculture. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01359-2
Xu, X., Hu, H., Wu, Y., Ying, W., & Zhou, Y. (2014). Improved differential evolution algorithm for wireless sensor network coverage optimization. Sensors and Transducers, 168, 179–184.
Sumithra, S., & Victoire, T. A. A. (2015). Differential evolution algorithm with diversified vicinity operator for optimal routing and clustering of energy efficient wireless sensor networks. The Scientific World Journal, 2015, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/729634
Neamatollahi, P., Naghibzadeh, M., & Abrishami, S. (2017). Fuzzy-based clustering-task scheduling for lifetime enhancement in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(20), 6837–6844. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2017.2749250
Zhang, W., Li, L., Han, G., & Zhang, L. (2017). E2HRC: An energy-efficient heterogeneous ring clustering routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 5, 1702–1713. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2017.2666818
Behera, T. M., Samal, U. C., & Mohapatra, S. K. (2018). Energy-efficient modified LEACH protocol for IoT application. IET Wireless Sensor Systems. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-wss.2017.0099
Kaur, S., & Mahajan, R. (2018). Energy efficient clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. Modern Physics Letters B, 32(32), 1850400. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0217984918504006
Kaur, T., & Kumar, D. (2018). Particle swarm optimization-based unequal and fault tolerant clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 18(11), 4614–4622. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2018.2828099
Anthony Jesudurai, S., & Senthilkumar, A. (2018). An improved energy efficient cluster head selection protocol using the double cluster heads and data fusion methods for IoT applications. Cognitive Systems Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.10.021
Wang, Z., Qin, X., & Liu, B. (2018). An energy-efficient clustering routing algorithm for WSN-assisted IoT. In 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC). https://doi.org/10.1109/wcnc.2018.8377171.
Preeth, S. K. S. L., Dhanalakshmi, R., Kumar, R., & Shakeel, P. M. (2018). An adaptive fuzzy rule based energy efficient clustering and immune-inspired routing protocol for WSN-assisted IoT system. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1154-z
Aftab, F., Khan, A., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Hybrid self-organized clustering scheme for drone based cognitive Internet of Things. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2913912
Faizan Ullah, M., Imtiaz, J., & Maqbool, K. (2019). Enhanced three layer hybrid clustering mechanism for energy efficient routing in IoT. Sensors, 19(4), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040829
Saranraj, G., Selvamani, K., & Kanagachidambaresan, G. (2019). Optimal energy-efficient cluster head selection (OEECHS) for Wireless Sensor Network. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-019-00390-3
Micheletti, M., Mostarda, L., & Navarra, A. (2019). CER-CH: Combining election and routing amongst cluster heads in heterogeneous WSNs. IEEE Access, 7, 125481–125493. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2938619
Chalapathi, G. S. S., Chamola, V., Gurunarayanan, S., & Sikdar, B. (2019). E-SATS: An efficient and simple time synchronization protocol for cluster-based wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2019.2922366
Behera, T. M., et al. (2020). I-SEP: An improved routing protocol for heterogeneous WSN for IoT-based environmental monitoring. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(1), 710–717. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2940988
Bremermann, H. J., & Anderson, R. W. (1990). An alternative to back-propagation: A simple rule of synaptic modification for neural net training and memory. Technical Report PAM-483, Center for Pure and Applied Mathematics, University of California.
Passino, K. M. (2002). Biomimicry of bacterial foraging for distributed optimization and control. IEEE Control Systems, 22(3), 52–67. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcs.2002.1004010
Mishra, S. (2005). A hybrid least square-fuzzy bacterial foraging strategy for harmonic estimation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 9(1), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1109/tevc.2004.840144
Kim, D. H., & Cho, J. H. (2005). Adaptive tuning of PID controller for multivariable system using bacterial foraging based optimization. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/11495772_36
Tripathy, M., Mishra, S., Lai, L. L., & Zhang, Q. P. (2006). Transmission loss reduction based on FACTS and bacteria foraging algorithm. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/11844297_23
Lalwani, P., & Das, S. (2016). Bacterial Foraging Optimization Algorithm for CH selection and routing in wireless sensor networks (95–100). https://doi.org/10.1109/RAIT.2016.7507882.
Mahajan, H. B., Badarla, A., & Junnarkar, A. A. (2021). CL-IoT: Cross-layer Internet of Things protocol for intelligent manufacturing of smart farming. Journal of Ambient Intelligence Humanized Computing, 12, 7777–7791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02502-0
Alhayani, B., Abbas, S. T., Mohammed, H. J., & Mahajan, H. B. (2021). Intelligent secured two-way image transmission using corvus corone module over WSN. Wireless Personal Communications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08484-2
Funding
No Funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declares that they has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahajan, H.B., Badarla, A. Cross-Layer Protocol for WSN-Assisted IoT Smart Farming Applications Using Nature Inspired Algorithm. Wireless Pers Commun 121, 3125–3149 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08866-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08866-6