Abstract
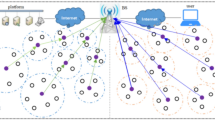
Wireless sensor network (WSN) is a communication network with several sensor nodes connected without any wired connection. Sensor nodes in the WSN are battery operated; therefore, recharging or replacement of the sensor node is a crucial task. Efficient energy consumption of sensor nodes is one of the significant challenges in WSN. In cluster based WSN, sensor nodes are grouped to form clusters. Gateway collects data from sensor nodes, aggregates data and transmits to the base station directly or through other gateways using the routing path. This causes heavy traffic load at the sink and forms an energy hole around the sink. In this paper, an energy efficient routing structure using the multi-layer network model is proposed to avoid the energy hole around the sink. The routing structure considers the one-to-one connection for all gateways to balance the overall load on the network. In the designed network model, the number of gateways increases in each layer towards the sink to minimize the traffic load around the sink. The extensive simulations on four different scenarios are performed in terms of network parameters such as the first gateway dies, first sensor node dies, half of the sensor nodes alive over the number of rounds, energy consumption rate and residual energy of sensor nodes and gateways. The experimental results are significant and proven the competency of the proposed algorithm.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raghavendra, C. S., Sivalingam, K. M., & Znati, T. (2006). Wireless sensor networks. London: Springer.
Akyildiz, I. F., Weilian, S., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 38(4), 393–422.
Bari, A., Wazed, S., Jaekel, A., & Bandyopadhyay, S. (2009). A genetic algorithm based approach for energy efficient routing in two-tiered sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 7(4), 665–676.
Kuila, P., & Jana, P.K. (2011). Improved load balanced clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. In International conference on advanced computing, networking and security (pp. 399–404).
Edla, D. R., Kongara, M. C., & Cheruku, R. (2018). SCE-PSO based clustering approach for load balancing of gateways in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks (pp. 1–15).
Edla, D. R., Kongara, M. C., & Cheruku, R. (2018). A PSO based routing with novel fitness function for improving lifetime of WSNs. Wireless Personal Communications (pp. 1–17).
Lipare, A., & Edla, D. R. (2018). Novel fitness function for SCE algorithm based energy efficiency in WSN. In 9th IEEE International conference on computing, communication and networking technologies (ICCCNT) (pp. 1–7).
Handy, M. J., Haase, M., Timmermann, D. (2002). Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy with deterministic cluster-head selection. In 4th international workshop on mobile and wireless communications network, Stockholm, Sweden, Sweden (pp. 368–372). IEEE.
Zhang, J., & Yang, T. (2013). Clustering model based on node local density load balancing of wireless sensor networks. In Forth international conference on emerging intelligent data and web technologies (pp. 273–276).
Gattani, V. S., & Haider Jafri, S. M. (2016). Data collection using score based load balancing algorithm in wireless sensor networks. In IEEE international conference on computing technologies and intelligent data engineering (ICCTIDE) (pp. 1–3).
Chatterjee, P., Ghosh, S. C., & Das, N. (2017). Load balanced coverage with graded node deployment in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Multi-Scale Computing Systems, 3(2), 100–112.
Kuila, P., Gupta, S. K., & Jana, P. K. (2013). A novel evolutionary approach for load balanced clustering problem for wireless sensor networks. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 12, 48–56.
Edla, D. R., Lipare, A., & Cheruku, R. (2018). Shuffled complex evolution approach for load balancing of gateways in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 98(4), 3455–3476.
Edla, D. R., Lipare, A., Cheruku, R., & Kuppili, V. (2017). An efficient load balancing of gateways using improved shuffled frog leaping algorithm and novel fitness function for WSNs. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(20), 6724–6733.
Kuila, P., & Jana, P. K. (2014). Energy efficient clustering and routing algorithms for wireless sensor networks: Particle swarm optimization approach. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 33, 127–140.
Al-Aboody, N. A., Al-Raweshidy, H. S. (2016). Grey wolf optimization-based energy-efficient routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. In 4th international symposium on computational and business intelligence (ISCBI), Olten (pp. 101–107).
Mirjalili, S., Mirjalili, S. M., & Lewis, A. (2014). Grey wolf optimizer. Advances in Engineering Software, 69, 46–61.
Chanak, P., Banerjee, I., & Rahaman, H. (2015). Load management scheme for energy holes reduction in wireless sensor networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 48, 343–357.
Salehi Panahi, M., & Abbaszadeh, M. (2018). Proposing a method to solve energy hole problem in wireless sensor networks. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 57(3), 1585–1590.
Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). Application specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–670.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lipare, A., Edla, D.R. & Dharavath, R. Energy Efficient Routing Structure to Avoid Energy Hole Problem in Multi-Layer Network Model. Wireless Pers Commun 112, 2575–2596 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07165-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07165-w