Abstract
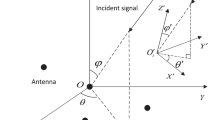
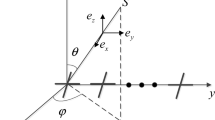
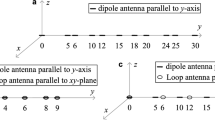
The problem of multiple incident signals’ direction of arrival (DOA) and polarization estimation with linear spatially separated polarization sensitive array (SS-PSA) is investigated in sparse Bayesian learning (SBL) framework. SS-PSA is widely studied due to its low mutual coupling compared with the spatially collocated polarization sensitive array. On the one hand, the sparse representation of data model of proposed array can be expressed skillfully as a block-sparse representation. On the other hand, block sparse Bayesian learning (BSBL) algorithm has excellent performance in recovering the block-sparse signals. Therefore, in this paper, BSBL algorithm is extended to SS-PSA for DOA and polarization estimation. Firstly, a sparse representation model without parameters coupling is established, where the sparse coefficient vector is a block-sparse signal. Secondly, the expectation–maximization method in BSBL framework, i.e., BSBL-EM algorithm, is proposed to recover the block-sparse signal. Lastly, angles estimation can be obtained from the recovered sparse signal according to the intra-block correlation. Simulation results demonstrate that the BSBL-EM algorithm used in DOA and polarization estimation with SS-PSA exhibits better performance compared with Block Orthogonal Matching Pursuit algorithm and Group Basis Pursuit.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, J., & Compton, R. T. (1991). Angle and polarization estimation using ESPRIT with a polarization sensitive array. Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,39(9), 1376–1383.
Li, J., & Compton, R. T. (1992). Two-dimensional angle and polarization estimation using the ESPRIT algorithm. Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,40(5), 550–555.
Zoltowski, M. D., & Wong, K. T. (2000). ESPRIT-based 2-D direction finding with a sparse uniform array of electromagnetic vector sensors. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,48(8), 2195–2204.
Bihan, N. L., Miron, S., & Albera, L. (2007). MUSIC algorithm for vector-sensors array using biquaternions. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,55(9), 4523–4533.
Chevalier, P., Ferréol, A., Albera, L., et al. (2007). Higher order direction finding from arrays with diversely polarized antennas: The PD-2q-MUSIC algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,55(11), 5337–5350.
Xu, Y., & Liu, Z. (2007). Polarimetric angular smoothing algorithm for an electromagnetic vector-sensor array. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation,1(3), 230–240.
Gong, X. F., Liu, Z. W., & Xu, Y. G. (2011). Coherent source localization: Bicomplex polarimetric smoothing with electromagnetic vector-sensors. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems,47(3), 2268–2285.
He, J., Jiang, S., Wang, J., et al. (2010). Polarization difference smoothing for direction finding of coherent signals. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems,46(1), 469–480.
Donoho, D. (2006). Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,52(4), 1289–1306.
Tian, Y., Sun, X., & Zhao, S. (2015). Sparse-reconstruction-based direction of arrival, polarization and power estimation using a cross-dipole array. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation,9(6), 727–731.
Zheng, G., & Zhang, D. (2017). BOMP-based angle estimation with polarimetric MIMO radar with spatially spread crossed-dipole. IET Signal Processing,12(1), 113–118.
Roemer, F., Ibrahim, M., & Alieiev, R. et al.: (2014). Polarimetric compressive sensing based DOA estimation. In International Itg workshop on smart antennas (pp. 1–8).
Eldar, Y. C., Kuppinger, P., & Bolcskei, H. (2010). Block-sparse signals: Uncertainty relations and efficient recovery. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,58(6), 3042–3054.
Baraniuk, R. G., Cevher, V., Duarte, M. F., et al. (2010). Model-based compressive sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,56(4), 1982–2001.
Yuan, M., & Lin, Y. (2006). Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society,68, 49–67.
Berg, E. V. D., & Friedlander, M. (2008). Probing the Pareto frontier for basis pursuit solutions. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing,31(2), 890–912.
Eldar, Y. C., & Mishali, M. (2009). Robust recovery of signals from a structured union of subspaces. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,55(11), 5302–5316.
Zhang, Z., & Rao, B. D. (2013). Extension of SBL algorithms for the recovery of block sparse signals with intra-block correlation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,61(8), 2009–2015.
Zhang, Z., & Rao, B. D. (2011). Sparse signal recovery with temporally correlated source vectors using sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing,5(5), 912–926.
Malioutov, D., Cetin, M., & Willsky, A. S. (2005). A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,53(8), 3010–3022.
Panahi, A., & Viberg, M. (2011). On the resolution of the LASSO-based DOA estimation method. In International ITG workshop on smart antennas (WSA) (pp. 1–5).
Zheng, J., Kaveh, M., & Tsuji, H. (2009). Sparse spectral fitting for direction of arrival and power estimation. In IEEE/SP 15th workshop on statistical signal processing, (SSP ‘09) (pp. 429–432).
Zhang, Z., & Rao, B. D. (2012). Recovery of block sparse signals using the framework of block sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,22(10), 3345–3348.
Zheng, G., Wu, B., Ma, Y., et al. (2014). Direction of arrival estimation with a sparse uniform array of orthogonally oriented and spatially separated dipole-triads. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation,8(8), 885–894.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61501504.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Bai, W., Zheng, G. et al. BSBL-Based DOA and Polarization Estimation with Linear Spatially Separated Polarization Sensitive Array. Wireless Pers Commun 109, 2051–2065 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06667-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06667-6