Abstract
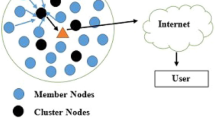
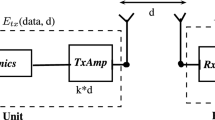
Efficient cluster formation is an important aspect of wireless sensor networks. But to transfer the data from the cluster heads to the static sink may lead to an energy hole problem where the cluster heads near the sink deplete their energy faster than those away from the sink. Using a mobile sink helps in alleviating this hot-spot problem. This work thus proposes a differential evolution and mobile sink based energy-efficient clustering protocol. In this work, differential evolution has been used to determine the cluster heads and the position of the mobile sink which gathers data from the cluster heads. Moreover, instead of performing clustering in every round, this paper follows an on-demand based clustering. The proposed work has been compared with relevant existing works using MATLAB. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can significantly increase the network lifetime and provides good delivery ratio.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Zahhad, M., Ahmed, S. M., Sabor, N., & Sasaki, S. (2015). Mobile sink-based adaptive immune energy-efficient clustering protocol for improving the lifetime and stability period of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(8), 4576–4586.
Ahmad, A., Javaid, N., Khan, Z. A., Qasim, U., & Alghamdi, T. A. (2014). \((\text{ ACH })^{2}\) : Routing scheme to maximize lifetime and throughput of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(10), 3516–3532.
Almi’ani, K., Viglas, A., & Libman, L. (2010, October). Energy-efficient data gathering with tour length-constrained mobile elements in wireless sensor networks. In 2010 IEEE 35th conference on local computer networks (LCN) (pp. 582–589).
Cai, Z., Gong, W., Ling, C. X., & Zhang, H. (2011). A clustering-based differential evolution for global optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 11(1), 1363–1379.
Ghosh, N., Sett, R., & Banerjee, I. (Sept 2016). Efficient polling point determination and physical model based throughput maximisation in wireless sensor network. In 2016 24th international conference on software, telecommunications and computer networks (SoftCOM) (pp. 1–5).
Ghosh, N., & Banerjee, I. (2015). An energy-efficient path determination strategy for mobile data collectors in wireless sensor network. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 48, 417–435.
Ghosh, N., Sett, R., & Banerjee, I. (2017). An efficient trajectory based routing scheme for delay-sensitive data in wireless sensor network. Computers & Electrical Engineering., 64, 288–304.
Gu, Y., Ren, F., Ji, Y., & Li, J. (2016). The evolution of sink mobility management in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 18(1), 507–524.
Halder, U., Das, S., & Maity, D. (2013). A cluster-based differential evolution algorithm with external archive for optimization in dynamic environments. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 43(3), 881–897.
Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–670.
Izadi, D., Abawajy, J., & Ghanavati, S. (2015). An alternative clustering scheme in WSN. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(7), 4148–4155.
Khan, A. W., Abdullah, A. H., Razzaque, M. A., & Bangash, J. I. (2015). Vgdra: A virtual grid-based dynamic routes adjustment scheme for mobile sink-based wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(1), 526–534.
Kim, J., In, J., Hur, K., Kim, J., & Eom, D. (2010). An intelligent agent-based routing structure for mobile sinks in WSNs. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 56(4), 2310–2316.
Kwedlo, W. (2011). A clustering method combining differential evolution with the k-means algorithm. Pattern Recognition Letters, 32(12), 1613–1621.
Lee, E., Park, S., Yu, F., Choi, Y., Jin, M. S., & Kim, S. H. (2008, March). A predictable mobility-based data dissemination protocol for wireless sensor networks. In 22nd international conference on advanced information networking and applications (AINA 2008) (pp. 741–747).
Lee, J. S., & Cheng, W. L. (2012). Fuzzy-logic-based clustering approach for wireless sensor networks using energy predication. IEEE Sensors Journal, 12(9), 2891–2897.
Lee, E., Park, S., Seungmin, O., & Kim, S.-H. (2014). Rendezvous-based data dissemination for supporting mobile sinks in multi-hop clustered wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 20(8), 2319–2336.
Liang, W., Luo, J., & Xu, X. (Dec 2010). Prolonging network lifetime via a controlled mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. In 2010 IEEE global telecommunications conference GLOBECOM 2010 (pp. 1–6).
Lindsey, S., Raghavendra, C., & Sivalingam, K. M. (2002). Data gathering algorithms in sensor networks using energy metrics. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 13(9), 924–935.
Liu, J.-L., & Ravishankar, C. V. (2011). LEACH-GA: Genetic algorithm-based energy-efficient adaptive clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing, 1(1), 79–85.
Liu, X., Zhao, H., Yang, X., & Li, X. (2013). Sinktrail: A proactive data reporting protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 62(1), 151–162.
Moh’d Alia, O. (2017). Dynamic relocation of mobile base station in wireless sensor networks using a cluster-based harmony search algorithm. Information Sciences, 385–386, 76–95.
Nayak, P., & Devulapalli, A. (2016). A fuzzy logic-based clustering algorithm for wsn to extend the network lifetime. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(1), 137–144.
Qasem, A. A., Fawzy, A. E., Shokair, M., Saad, W., El-Halafawy, S., & Elkorany, A. (2017). Energy efficient intra cluster transmission in grid clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications., 97, 915–932.
Salarian, H., Chin, K. W., & Naghdy, F. (2014). An energy-efficient mobile-sink path selection strategy for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(5), 2407–2419.
Shah, R. C., Roy, S., Jain, S., & Brunette, W. (May 2003). Data mules: Modeling a three-tier architecture for sparse sensor networks. In 2003 IEEE international workshop on sensor network protocols and applications, 2003. Proceedings of the first IEEE (pp. 30–41).
Shi, Y., & Hou, Y. T. (2008, April). Theoretical results on base station movement problem for sensor network. In IEEE INFOCOM 2008—The 27th conference on computer communications.
Somasundara, A. A., Ramamoorthy, A., & Srivastava, M. B. (2007). Mobile element scheduling with dynamic deadlines. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 6(4), 395–410.
Thakkar, A., & Kotecha, K. (2014). Cluster head election for energy and delay constraint applications of wireless sensor network. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(8), 2658–2664.
Tvrdík, J., & Křivý, I. (2015). Hybrid differential evolution algorithm for optimal clustering. Applied Soft Computing, 35, 502–512.
Vijayvargiya, K. G., & Shrivastava, V. (2012). An amend implementation on leach protocol based on energy hierarchy. International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, 2(4), 427–431.
Wang, C. F., Shih, J. D., Pan, B. H., & Wu, T. Y. (2014). A network lifetime enhancement method for sink relocation and its analysis in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(6), 1932–1943.
Wang, J., Cao, Y., Li, B., Kim, H. J., & Lee, S. (2016). Particle swarm optimization based clustering algorithm with mobile sink for WSNs. Future Generation Computer Systems, 76, 452–457.
Zhao, M., & Yang, Y. (2012). Bounded relay hop mobile data gathering in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 61(2), 265–277.
Zhu, C., Wu, S., Han, G., Shu, L., & Wu, H. (2015). A tree-cluster-based data-gathering algorithm for industrial WSNs with a mobile sink. IEEE Access, 3, 381–396.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, N., Prasad, T. & Banerjee, I. Differential Evolution and Mobile Sink Based On-Demand Clustering Protocol for Wireless Sensor Network. Wireless Pers Commun 109, 1875–1895 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06657-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06657-8