Abstract
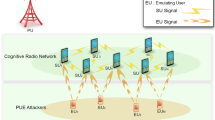
One of the most challenging issues in Cognitive Radio Networks (CRN) is to detect Primary User Emulation Attack (PUEA). In the absence of Primary Users (PU), the attackers mimic PUs’ signal characteristics to fool legitimate Secondary Users (SU) that evacuate the channel for them, in order to use the channel selfishly. Many works have been done to detect PUEA; among them, localization and encryption and so on are the examples. Recently, game theory has been used to detect PUEA. In this paper, a method based on game theory is proposed, that without using any complex calculation and second methods (RSS, GPS and so on), PUEA can be detected. This method is especially proposed for MANET and can be used in any circumstance of CRNs (ad-hoc, centralized, distributed…). It is reliable, with minimum miss detection and no false alarm of PU. Simulation results show that the proposed method has good operations even in dense networks and ultra-dense networks.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Primary users.
Secondary users.
PUEA.
Received signal strength.
Time difference of arrival.
Frequency difference of arrival.
References
Ruiliang, C., & Jung-Min, P. (2006). Ensuring trustworthy spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. In 1st IEEE workshop on networking technologies for software defined radio networks, 2006. SDR ‘06 (pp. 110–119).
Fragkiadakis, A. G., Tragos, E. Z., & Askoxylakis, I. G. (2013). A survey on security threats and detection techniques in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 15, 428–445.
Ruiliang, C., Jung-Min, P., & Reed, J. H. (2008). Defense against primary user emulation attacks in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 26, 25–37.
ChunSheng, X., & Song, M. (2014). Detection of PUE attacks in cognitive radio networks based on signal activity pattern. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 13, 1022–1034.
Jin, Z., Anand, S., & Subbalakshmi, K. P. (2009). Mitigating primary user emulation attacks in dynamic spectrum access networks using hypothesis testing. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 13, 74–85.
Zhou, Y., Niyato, D., Husheng, L., Ju Bin, S., & Zhu, H. (2012). Defeating primary user emulation attacks using belief propagation in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 30, 1850–1860.
Celebi, H., & Arslan, H. (2007). Utilization of location information in cognitive wireless networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 14, 6–13.
Niculescu, D. (2004). Positioning in ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Network, 18, 24–29.
León, O., Hernández-Serrano, J., & Soriano, M. (2012). Cooperative detection of primary user emulation attacks in CRNs. Computer Networks, 56, 3374–3384.
Blesa, J., Romero, E., Rozas, A., & Araujo, A. (2013). PUE attack detection in CWSNs using anomaly detecttion techniques. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2013, 1–13.
Lianfen, H., Liang, X., Han, Y., Wumei, W., & Yan, Y. (2010). Anti-PUE attack based on joint position verification in cognitive radio networks. In 2010 International conference on communications and mobile computing (CMC) (pp. 169–173).
Caidan, Z., Wumei, W., Lianfen, H., & Yan, Y. (2009). Anti-PUE attack base on the transmitter fingerprint identification in cognitive radio. In 5th International conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, 2009. WiCom ‘09. (pp. 1–5).
Salam, D., Taggu, A., & Marchang, N. (2016). An effective emitter-source localisation-based PUEA detection mechanism in cognitive radio networks. In 2016 International conference on advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI) (pp. 2557–2561).
Borle, K. M., Biao, C., & Wenliang, D. (2013). A physical layer authentication scheme for countering primary user emulation attack. In 2013 IEEE international conference onacoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2935–2939).
Alahmadi, A., Abdelhakim, M., Jian, R., & Tongtong, L. (2014). Defense against primary user emulation attacks in cognitive radio networks using advanced encryption standard. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 9, 772–781.
Chandrashekar, S., & Lazos, L. (2010). A primary user authentication system for mobile cognitive radio networks. In 2010 3rd international symposium on applied sciences in biomedical and communication technologies (ISABEL) (pp. 1–5).
Ureten, O., & Serinken, N. (2007). Wireless security through RF fingerprinting. Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 32, 27–33.
Harini, S. V. V., & Aruna, T. (2016). A mitigation strategy for primary user emulation attacks in cognitive radio networks. In 2016 10th international conference on intelligent systems and control (ISCO) (pp. 1–5).
Nguyen-Thanh, N., Ciblat, P., Pham, A. T., & Nguyen, V. T. (2014). Attack and surveillance strategies for selfish primary user emulator in cognitive radio network. In 2014 IEEE global conference on signal and information processing (GlobalSIP) (pp. 1199–1203).
Ta, D. -T., Nhan, N.-T., Ciblat, P., & Van-Tam, N. (2015). Extra-sensing game for malicious primary user emulator attack in cognitive radio network. In 2015 European conference on networks and communications (EuCNC) (pp. 306–310).
Nhan Nguyen, T., Ciblat, P., Pham, A. T., & Van-Tam, N. (2015). Surveillance strategies against primary user emulation attack in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14, 4981–4993.
Tan, Y., Sengupta, S., & Subbalakshmi, K. P. (2012). Primary user emulation attack in dynamic spectrum access networks: a game-theoretic approach. IET Communications, 6, 964–973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaziri Yazdi, S.A., Ghazvini, M. Countermeasure with Primary User Emulation Attack in Cognitive Radio Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 108, 2261–2277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06521-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06521-9