Abstract
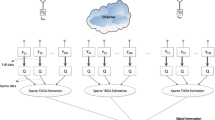
The performance of the existing direction of arrival (DOA) estimation algorithms for source localization in the wireless sensor networks (WSN) degrades when the sources are correlated. The degradation is due to the rank deficiency of the source covariance matrix which is reflected in the high cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) for correlated sources. Unlike subspace based techniques, maximum likelihood (ML) based technique does not require any preprocessing technique for DOA estimation of correlated signals. Hence ML technique can be directly applied for WSN with arbitrary array geometry. The DOA estimation accuracy for correlated signals is improved by employing distributed ML approach in this paper. The subarray formed at a particular node which is experiencing highest CRLB can improve its estimation accuracy by receiving better DOA estimates from its neighbors. The corresponding distributed CRLB is derived and found a substantial improvement in the distributed scenario. The distributed CRLB lies between that of local CRLB for the subarray formed at the node and global CRLB for the array formed by all sensors in the WSN. Diffusion quantum particle swarm optimization is used to optimize ML estimator for fully correlated signals as it has only a single parameter for tuning. Simulation results show that the estimation accuracy improves at a node even for correlated signals yielding highest CRLB using distributed approach. The root mean square error at a specific node using distributed algorithm approaches to the derived distributed CRLB.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rawat, P., Singh, K. D., Chaouchi, H., & Bonnin, J. M. (2014). Wireless sensor networks: A survey on recent developments and potential synergies. The Journal of Supercomputing, 68(1), 1–48.
Akyildiz, I. F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). A survey on sensor networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(8), 102–114.
Yetgin, H., Cheung, K. T. K., El-Hajjar, M., & Hanzo, L. H. (2017). A survey of network lifetime maximization techniques in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 19(2), 828–854.
Zeng, Y., Zhang, R., & Lim, T. J. (2016). Wireless communications with unmanned aerial vehicles: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 54(5), 36–42.
Guvenc, I., Koohifar, F., Singh, S., Sichitiu, M. L., & Matolak, D. (2018). Detection, tracking, and interdiction for amateur drones. IEEE Communications Magazine, 56(4), 75–81.
Krim, H., & Viberg, M. (1996). Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 13(4), 67–94.
Wei, X., Wang, T., Tang, C., & Fan, J. (2018). Collaborative mobile jammer tracking in multi-hop wireless Network. Future Generation Computer Systems, 78(3), 1027–1039.
Mpitziopoulos, A., Gavalas, D., Konstantopoulos, C., & Pantziou, G. (2009). A survey on jamming attacks and countermeasures in WSNs. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 11(4), 42–56.
Yau, S. F., & Bresler, Y. (1992). Worst case Cramer–Rao bounds for parametric estimation of superimposed signals with applications. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 40(12), 2973–2986.
Rabbat, M., & Nowak, R. (2004). Distributed optimization in sensor networks. In Third International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, 2004. IPSN 2004 (pp. 20–27). Berkeley: CA, USA.
Panigrahi, T., Panda, G., & Mulgrew, B. (2012). Distributed bearing estimation technique using diffusion particle swarm optimisation algorithm. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 2(4), 385–393.
Sharma, A., & Mathur, S. (2018). Comparative analysis of ML-PSO DOA estimation with conventional techniques in varied multipath channel environment. Wireless Personal Communications, 100, 803–817.
Shan, T. J., Wax, M., & Kailath, T. (1985). On spatial smoothing for direction-of-arrival estimation of coherent signals. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 33(4), 806–811.
Vanderveen, M. C., Papadias, C. B., & Paulraj, A. (1997). Joint angle and delay estimation (JADE) for multipath signals arriving at an antenna array. IEEE Communications Letters, 1(1), 12–14.
Han, F. M., & Zhang, X. D. (2005). An ESPRIT—like algorithm for coherent DOA estimation. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 4, 443–446.
Gan, L., & Luo, X. (2013). Direction-of-arrival estimation for uncorrelated and coherent signals in the presence of multipath propagation. IET Microwaves, Antennas Propagation, 7(9), 746–753.
Chen, H., Hou, C. P., Wang, Q., Huang, L., & Yan, W. Q. (2014). Cumulants-based toeplitz matrices reconstruction method for 2-D coherent DOA estimation. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(8), 2824–2832.
Si, W., Zhao, P., Qu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2016). Real-valued DOA estimation for a mixture of uncorrelated and coherent sources via unitary transformation. Digital Signal Processing, 58, 102–114.
Liu, Q., So, H. C., & Gu, Y. (2017). Off-grid DOA estimation with nonconvex regularization via joint sparse representation. Signal Processing, 140(C), 171–176.
Abolfath-Beygi, M., & Olfat, A. (2014). Subspace smoothing for direction of arrival estimation in DS-CDMA systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 74(2), 211–228.
Ariananda, D. D., & Leus, G. (2013). Direction of arrival estimation for more correlated sources than active sensors. Signal Processing, 93(12), 3435–3448.
Izedi, F., Karimi, M., & Derakhtian, M. (2017). Joint DOA estimation and source number detection for arrays with arbitrary geometry. Signal Processing, 140(C), 149–160.
Meng, C. L., Chen, S. W., & Chang, A. C. (2015). Direction-of-arrival estimation based on particle swarm optimization searching approaches for CDMA signals. Wireless Personal Communications, 81(1), 343–357.
Panigrahi, T., Roula, S., & Gantayat, H. (2016). Application of comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization algorithm for maximum likelihood DOA estimation in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Swarm Intelligence, 2, 2–4.
Sun, J., Xu, W., & Feng, B. (2004). A global search strategy of quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. IEEE Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems, 1, 111–116.
Trees, H. L. V. (2002). Detection, estimation, and modulation theory. Part IV. Optimum array processing. Hoboken: Wiley-Interscience.
Marano, S., Matta, V., & Willett, P. (2008). Distributed estimation in large wireless sensor networks via a locally optimum approach. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(2), 748–756.
Panigrahi, T., Panda, G., & Majhi, B. (2013). Maximum likelihood source localisation in wireless sensor network using particle swarm optimisation. International Journal of Signal and Imaging Systems Engineering, 6(2), 83–90.
Xiao, L., Boyd, S., & Lall, S. (2005). A scheme for robust distributed sensor fusion based on average consensus. Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, 2005, 63–70.
Kay, S. M. (1993). Fundamentals of statistical processing, volume I: Estimation theory. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Sun, J., Xu, W., & Fang, W. (2006). Quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm with controlled diversity. In V. N. Alexandrov, G. D. van Albada, P. M. A. Sloot, & J. Dongarra (Eds.), Computational science ICCS 2006 (ICCS 2006). Lecture notes in computer science, 3993. Berlin: Springer.
Sayed, A. H. (2014). Adaptation, learning, and optimization over networks. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 7(4–5), 683–686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, M.S., Panigrahi, T. Distributed Maximum Likelihood DOA Estimation Algorithm for Correlated Signals in Wireless Sensor Network. Wireless Pers Commun 105, 1527–1544 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06158-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06158-8