Abstract
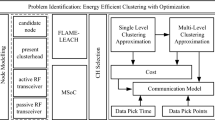
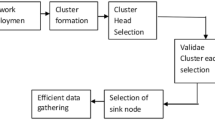
The paper presents a technique called as Mobility-Enabled Multi Level Optimization (MeMLO) that addressing the existing problem of clustering in wireless sensor net-work (WSN). The technique enables selection of aggregator node based on multiple optimization attribute which gives better decision capability to the clustering mechanism by choosing the best aggregator node. The outcome of the study shows MeMLO is highly capable of minimizing the halt time of mobile node that significantly lowers the transmit power of aggregator node. The simulation outcome shows negligible computational complexity, faster response time, and highly energy efficient for large scale WSN for longer simulation rounds as compared to conventional LEACH algorithm.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Selvi, G. V., & Manoharan, R. (2013). A survey of energy efficient unequal clustering algorithms for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2, 1–4.
Kumar, V., Bansal, M., & Rai, M. K. (2015). Literature survey on energy efficient clustering and routing in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Computer Application, 5(3), 1–5.
Anwar, A., & Sridharan, D. (2015). A survey on routing protocols for wireless sensor networks in various environments. International Journal of Computer Applications, 112(5), 13–29.
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocols for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaaian international conference on systems science (HICSS).
Lindsey, S., & Raghavendra, C. (2002). PEGASIS: Power- efficient gathering in sensor information systems. In IEEE aerospace conference proceedings, pp. 1125–1130.
Manjeshwar, A., & Agarwal, D. P. (2001). TEEN: A routing protocol for enhanced efficiency in wireless sensor networks. In 1st international workshop on parallel and distributed computing issues in wireless networks and mobile computing.
Manjeshwar, A., & Agarwal, D. P. (2002). APTEEN: A hybrid protocol for efficient routing and comprehensive information retrieval in wireless sensor networks. In Parallel and distributed processing symposium., proceedings international, IPDPS 2002, pp. 195–202.
Younis, O., & Fahmy, S. (2004). Distributed clustering in ad hoc sensor networks: A hybrid, energy-efficient approach. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, Hong Kong, an extended version appeared in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (Vol. 3, Issue 4).
Rajalakshmi, M. C. (2014). Review of typical power conservation techniques in wireless sensor network. International Journal of Computer Applications, 88(10), 7–13.
Adnan, M. A., Razzaque, M. A., Abedin, M. A., Reza, S. M. S., & Hussein, M. R. (2016). A novel Cuckoo search based clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. In H. Sulaiman, M. Othman, M. Othman, Y. Rahim & N. Pee (Eds.), Advanced computer and communication engineering technology. Lecture notes in electrical engineering (Vol. 362). Cham: Springer.
Seelam, K., Sailaja, M., & Madhu, T. (2015). An improved BAT-optimized cluster-based routing for wireless sensor networks. In D. Mandal, R. Kar, S. Das & B. Panigrahi (Eds.), Intelligent computing and applications. Advances in intelligent systems and computing (Vol. 343). New Delhi: Springer.
Pei, E., Han, H., Sun, Z., Shen, B., & Zhang, T. (2015). LEAUCH: Low-energy adaptive uneven clustering hierarchy for cognitive radio sensor network. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2015(1), 122.
Udompongsuk, K., So-In, C., Phaudphut, C., Rujirakul, K., Soomlek, C., & Waikham, B. (2014). MAP: An optimized energy-efficient cluster header selection technique for wireless sensor networks. In H. Jeong, M. S. Obaidat, N. Yen & J. Park (Eds.), Advances in computer science and its applications. Lecture notes in electrical engineering (Vol. 279). Berlin: Springer.
Patil, P. R., & Kulkarni, U. P. (2014). Energy-efficient cluster-based aggregation protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. In D. Mohapatra & S. Patnaik (Eds.), Intelligent computing, networking, and informatics. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing (Vol. 243). New Delhi: Springer.
Gautam, N., Sofat, S., & Vig, R. (2014). An ant voronoi based clustering approach for wireless sensor networks. In M. Sherif, A. Mellouk, J. Li & P. Bellavista (Eds.), Ad Hoc Networks. ADHOCNETS 2013. Lecture notes of the institute for computer sciences, social informatics and telecommunications engineering (Vol. 129). Cham: Springer
Meenakshi, D., & Kumar, S. (2012). Energy efficient hierarchical clustering routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. N. Meghanathan, N. Chaki & D. Nagamalai (Eds.), Advances in computer science and information technology. networks and communications. CCSIT 2012. Lecture notes of the institute for computer sciences, social informatics and telecommunications engineering (Vol. 84). Berlin: Springer.
Neamatollahi, P., Taheri, H., & Naghibzadeh, M. (2011). DESC: Distributed energy efficient scheme to cluster wireless sensor networks. International Federation for Information Processing, 17, 234–246.
Wei, D., Jin, Y., Vural, S., Moessner, K., & Tafazolli, R. (2011). An energy-efficient clustering solution for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(11), 3973–3983.
Yu, J., Qi, Y., & Wang, G. (2011). An energy-driven unequal clustering protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Journal of Control Theory and Applications, 9(1), 133–139.
Zhu, X., Shen, L., & Yum, T. S. P. (2009). Hausdorff clustering and minimum energy routing for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(2), 990–997.
Rajalakshmi, M. C., & Gnana Prakash, A. P. (2014). Energy optimization for large scale wireless sensor network using real-time dynamics. International Journal of Computer Applications, 108(7), 40–46.
Rajalakshmi, M. C., & Gnana Prakash, A. P. (2015). MLO: Multi-level optimization to enhance the network lifetime in large scale WSN. In N. Shetty, N. Prasad, N. Nalini (Eds.), Emerging research in computing, information, communication and applications. New Delhi: Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajalakshmi, M.C., Gnana Prakash, A.P. MeMLO: Mobility-Enabled Multi-level Optimization Sensor Network. Wireless Pers Commun 97, 5675–5689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4802-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4802-2