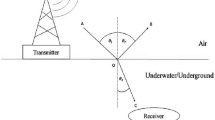
Abstract
Electromagnetic (EM) techniques enable efficient wireless communications in different media with high material absorptions, such as underground soil, water and oil medium. A wide range of novel and important applications in such challenged environments can be realized based on the EM communication mechanism. In this paper, the propagation based on EM waves in the megahertz (MHz) and gigahertz (GHz) band through a different types of oil is analyzed in order to explore its applicability in pipelines and oil sands. The developed model evaluates the total path loss and the transmission characteristics. Moreover, based on the proposed channel model, the resulting bit error rate (BER) is analyzed that an EM wave experiences when propagating through the oil medium. The propagation characteristics are investigated through simulation. The theoretical analysis and the simulation results prove the feasibility of wireless communication in the MHz and GHz band in oil environment and highlight several important aspects in this field.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkas, M. A., & Sokullu, R. (2015). Wireless underground sensor networks: channel modeling and operation analysis in the terahertz band. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation. Article ID 780235.
Akkas, M. A., & Sokullu, R. (2015). Channel modeling and analysis for wireless underground sensor networks in water medium using electromagnetic waves in the 300–700 MHz range. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-015-2697-3.
Akkaş, M. A., Akyildiz, I. F., & Sokullu, R. (2012). Terahertz channel modeling of underground sensor networks in oil reservoirs. IEEE GLOBECOM 2012, Anaheim, California, December 2012.
Vuran, M. C., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2010). Channel modeling and analysis for wireless underground sensor networks. Physical Communication Journal, 3(4), 245–254.
Elson, J., & Estrin, D. (2004). Sensor networks: a bridge to the physical world. In C. S. Raghavendra, K. M. Sivalingam, & T. F. Znati (Eds.), Wireless sensor networks. Boston: Kluwer.
Li, L., Vuran, M. C., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2007). Characteristics of underground channel for wireless underground sensor networks. In Proceedings of Med-Hoc-Net’07, Corfu, Greece, June 2007.
Sobral, T. (2012). Wireless sensor network for oil & gas industry. www.siliconreef.com.br, 2012, November.
Attanasi, E. D., & Meyer, R. F. (2010). Natural bitumen and extra-heavy oil. Survey of energy resources (22 ed., pp. 123–140). World Energy Council. ISBN:0-946121-26-5.
Charpentier, A. D., Bergerson, J. A., & MacLean, H. L. (2009). Understanding the canadian oil sands industry’s greenhouse gas emissions. Environmental research letters, 4(1), 014005.
(2006). Bitumen and heavy crudes: The energy security problem solved? Oil and Energy Trends, 31(6): 3–5. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7992.2006.310603.x.
Jin, Y., & Eydgahi, A. (2008). Monitoring of distributed pipeline systems by wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 IJAC-IJME international conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 2008.
Shinde, S., Patil, S. B., & Patil, A. J. (2012). Development of movable gas tanker leakage detection using wireless sensor network based on embedded system. International Journal of Engineering Research and Application, 2, 1180–1183.
Mohamed, N., Jawhar, I., Al-Jaroodi, J., & Zhang, L. (2011). Sensor network architectures for monitoring underwater pipelines. Sensors, 11(11), 10738–10764. doi:10.3390/s111110738.
Anupama, K. R., Nishad, K., Santosh, K. K., Vyas, D., Sahu, S., & Shah, S. (2014). A wireless sensor network based pipeline monitoring system. International conference on signal processing and integrated networks (SPIN) (pp. 412–419).
Yu, H., & Guo, M. (2012, August). An efficient oil and gas pipeline monitoring systems based on wireless sensor networks. In Information security and intelligence control (ISIC), 2012 International Conference on IEEE, (pp. 178–181).
Dong, X., Vuran, M. C., & Irmak, S. (2013). Autonomous precision agricultrue through integration of wireless underground sensor networks with center pivot irrigation systems. Ad Hoc Networks, 11, 1975–1987.
UgMO (2014). Knows irrigation control systems. http://www.ugmo.com/solutions/sports-turf.
Sokullu R., Akkas M. A., & Demirel F. (2011). Data gathering system for watering and gas pipelines using wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the seventh international conference on networking and services ICNS, Venice, Italy, May 2011, pp. 190–195.
Sun, Z., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2010). On capacity of magnetic induction-based wireless underground sensor networks. IEEE INFOCOM, March 2010, pp. 370–378.
Stüber, G. L. (2011). Principles of mobile communication. Springer Science & Business Media.
Sarri A., Batisti M., & Bientinesi M. (2012). Measurements of complex permittivity of geological materials mixtures at RF frequencies. 6th European conference on antennas and propagation (EUCAP), 26–30 March 2012, Prague, Czech Republic, pp. 2109–2113. doi:10.1109/EuCAP.2012.6205920.
Porch, A., Slocombe, D., Beutler, J., Edwards, P., Aldawsari, A., Xiao, T., et al. (2012). Microwave treatment in oil refining. Applied Petrochemical Research, 2, 37–44.
Elrashidi, A., Elleithy, A. Albogame, M., & Elleithy, K. (2001). Underwater wireless sensor network communication using electromagnetic waves at resonance frequency 2.4 GHz. In CNS ‘12 Proceedings of the 15th communications and networking simulation symposium, March 2012, Article No. 13.
Crossbow Mica2 node. http://www.xbow.com.
Cheng, D. (1989). Field and wave electromagnetics (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Addison Wesley.
Boifot, A. M. (1989). Broadband method for measuring dielectric constant of liquids using an automatic network analyser. IEE Proceedings H-Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation, 136(6), 492–498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akkaş, M.A. Channel Modeling of Wireless Sensor Networks in Oil. Wireless Pers Commun 95, 4337–4355 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4083-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4083-9