Abstract
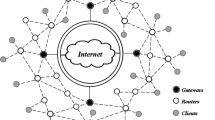
Wireless mesh networks (WMNs) consist of static nodes that usually have one or more radios or media. Optimal channel assignment (CA) for nodes is a challenging problem in WMNs. CA aims to minimize interference in the overall network and thus increase the total capacity of the network. This paper proposes a new method for solving the CA problem that comparatively performs more efficient than existing methods. The link layer in the TCP/IP model is a descriptive realm of networking protocols that operates on the local network link in routers discovery and neighboring hosts. TCP/IP employs the link-layer protocol (LLP) that is included among the hybrid states in CA methods, and learning automata are used to complete the algorithm with an intelligent method for suitable CA. We call this algorithm LLLA, which are short for LLP and learning automata. Our simulation results show that LLLA performs more efficient than ad hoc on-demand distance vector (AODV) types with respect to parameters such as packet drop, end-to-end delay, average goodput, jitter in special applications, and energy usage.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cordeschi, N., Shojafar, M., & Baccarelli, E. (2013). Energy-saving self-configuring networked data centers. Computer Networks, 57(17), 3479–3491.
Xu, S., & Saadawi, T. (2001). Does the IEEE 802.11MAC protocol work well in multi hop wireless adhoc networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 39, 130–137.
Ahmadi, A., Shojafar, M., Hajeforosh, S. F., Dehghan, M., & Singhal, M. (2014). An efficient routing algorithm to preserve k-coverage in wireless sensor networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, 68(2), 599–623. doi:10.1007/s11227-013-1054-0.
Wanli, D., Kun, B., & Lei, Z. (2008). Distributed channel assignment algorithm for multi-channel wireless mesh networks. International Colloquium on Computing, Communication, Control, and Management (CCCM), 2, 444–448.
Sridhar, S., Guo, J., & Jha, S. (2009). Channel assignment in multi-radio wireless mesh networks: A graph-theoretic approach. In First international conference on communication systems and networks (COMSNETS), Bangalore, India.
Kyasanur, P., & Vaidya, N. (2005). Routing and interface assignment in multi-channel multi-interface wireless networks. In Proceedings IEEE conference on wireless communications and networks conference (pp. 2051–56).
Gao, L., & Wang, X. (2008). A game approach for multi-channel allocation in multi-hop wireless networks. In Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc (pp. 303–312). doi:10.1145/1374618.1374659.
Pal, A., & Nasipuri, A. (2011). JRCA: A joint routing and channel assignment scheme for wireless mesh networks. In IEEE IPCCC (pp. 1–8). doi:10.1109/PCCC.2011.6108059.
Shojafar, M., Pooranian, Z., Shojafar, M., & Abraham, A. (2014). LLLA: New efficient channel assignment method in wireless mesh networks. In A. Abraham, P. Krömer and V. Sná\(\check{\rm s}\)el (Ed.), Innovations in bio-inspired computing and applications (Vol. 237, pp. 143–152). Berlin: Springer.
Kyasanur, P., & Vaidya, N. (2006). Routing and link-layer protocols for multi-channel multi-interface ad hoc wireless networks. Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 10(1), 31–43.
Pirzada, A. A., Portmann, M., & Indulska, J. (2006). Evaluation of multi-radio extensions to AODV for wireless mesh networks. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM international workshop on mobility management and wireless access (pp. 45–51). doi:10.1145/1164783.1164791.
Pirzada, A. A., Wishart, R., & Portmann, M. (2007). Multi-linked AODV routing protocol for wireless mesh networks. In IEEE global telecommunications conference (pp. 4925–4930). doi:10.1109/GLOCOM.2007.934.
Boppana, R., & Halldorsson, M. M. (1992). Approximating maximum independent sets by excluding subgraphs. BIT Magazine, 32(2), 180–196. ISSN:0006-3835. doi:10.1007/BF01994876.
Bui, T. N., & Eppley, P. H. (1995). A hybrid genetic algorithm for the maximum clique problem. In Proceedings of 6th international conference on genetic algorithms (pp. 478–484).
Narendra, K. S., & Thathachar, M. A. L. (1989). Learning automata: An introduction. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Poznyak, A. S., & Najim, K. (1997). Learning automata and stochastic optimization. Berlin: Springer. ISBN:3-540-76154-3.
Sayyad, A., Shojafar, M., Delkhah, Z., & Ahamadi, A. (2011). Region directed diffusion in sensor network using learning automata: RDDLA. Journal of Advances in Computer Research, 2(1), 71–83.
Das, A. K., Alazemi, H. M. K., Vijayakumar, R., & Roy, S. (2005). Optimization models for fixed channel assignment in wireless mesh networks with multiple radios. In SECON (pp. 463–474).
Subramaniam, A. P., Gupta, H., & Das, S. R. (2008). Minimum-interference channel assignment in multi-radio wireless mesh networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7(12), 1459–1473.
Raniwala, A., Gopalan, K., & Chiueh, T. (2004). Centralized channel assignment and routing algorithms for multi-channel wireless mesh networks. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 8(2), 50–65.
Alicherry, M., Bhatia, R., & Li, L. (2006). Joint channel assignment and routing for throughput optimization in multiradio wireless mesh networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 24(11), 1960–1971.
Tang, J., Xue, G., & Zhang, W., (2005). Interference-aware topology control and qos routing in multi-channel wireless mesh networks. In MobiHoc (pp. 68–77). doi:10.1145/1062689.1062700.
Ding, Y., Huang, Y., Zeng, G., & Xiao, L. (2008). Channel assignment with partially overlapping channels in wireless mesh networks. In WICON (pp. 1–9).
Yang, J., Jiang, Q., Manivannan, D., & Singhal, M. (2005). A fault-tolerant distributed channel allocation scheme for cellular networks. IEEE Transaction on Computers, 54(5), 616–629.
Cao, G., & Singhal, M. (2000). Distributed fault-tolerant channel allocation for cellular networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 18(9), 1326–1337.
Ding, Y., & Xiao, L. (2011). Channel allocation in multi-channel wireless mesh networks. Computer Communications, 34(7), 803–815.
Pediaditaki, S., Arrieta, Ph., & Marina, M. K. (2009). A learning-based approach for distributed multi-radio channel allocation in wireless mesh networks. In ICNP (pp. 31–41). doi:10.1109/ICNP.2009.5339701.
Ko, B., Misra, V., Padhye, J., & Rubenstein, D. (2007). Distributed channel assignment in multi-radio 802.11 mesh networks. In Proceedings of IEEE WCNC (pp. 3978–3983). doi:10.1109/WCNC.2007.727.
Raniwala, A., & Chiueh, T. (2005). Architecture and algorithms for an ieee 802.11-based multi-channel wireless mesh network. In IEEE INFOCOM (Vol. 3, pp. 2223–2234). doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2005.1498497.
Aryafar, E., Gurewitz, O., & Knightly, E. W. (2008). Distance-1 constrained channel assignment in single radio wireless mesh networks. In IEEE INFOCOM. doi:10.1109/INFOCOM.2008.127.
Ramachandran, K. N., Belding, E. M., Almeroth K. C., & Buddhikot, M. M. (2006). Interference-aware channel assignment in multi-radio wireless mesh networks. In IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1–12). doi:10.1109/INFOCOM.2006.177.
Wu, S.-L., Lin, C.-Y. Tseng, Y.-C., & Sheu, J.-P. (2000). A new multi-channel mac protocol with on-demand channel assignment for multi-hop mobile ad hoc networks. In I-SPAN (pp. 232–237). doi:10.1109/ISPAN.2000.900290.
So, J., & Vaidya, N., (2004). Multi-channel mac for ad hoc networks: Handling multichannel hidden terminals using a single transceiver. In MobiHoc (pp. 222–233). doi:10.1145/989459.989487.
Bahl, P., Chandra, R., & Dunagan, J. (2004). Ssch: Slotted seeded channel hopping for capacity improvement ieee 802.11 ad-hoc wireless networks. In MobiCom (pp. 216–230). doi:10.1145/1023720.1023742.
Dhananjay, A., Zhang, H., Li, J., & Subramanian, L. (2009). Practical distributed channel assignment and routing in dual-radio mesh networks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 39(4), 99–110.
Ding, Y., Pongaliur, K., & Xiao, L. (2009). Hybrid multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks. In Workshop IWQoS (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/IWQoS.2009.5201403.
Jahanshahi, M., Dehghan, M., & Meybodi, M. R. (2011). A mathematical formulation for joint channel assignment and multicast routing in multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 34(6), 1869–1882.
Chianga, C., Chenb, H., Liaoc, W., & Shiha, K. (2014). A decentralized minislot scheduling protocol (DMSP) in TDMA-based wireless mesh networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 206–215. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2013.02.017.
Chen, T., Bansal, A., & Zhong, S. (2011). A reputation system for wireless mesh networks using network coding. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 34(2), 535–541. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2010.12.016.
Prakash, R., Shivaratri, N., & Singhal, M. (1999). Distributed dynamic fault-tolerant channel allocation for mobile computing. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 48(6), 1874–1888.
Thathachar, M. A. L., & Sastry, P. S. (2002). Varieties of learning automata: An overview. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 32(6), 711–722.
Omranpour, H., Ebadzadeh, M. M., Barzegar, S., & Shojafar, M. (2008). Distributed coloring of the graph edges. In IEEE CIS (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/UKRICIS.2008.4798944.
Tanenbaum, A. S. (2002). Computer networks (4th ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Fehnker, A., Glabbeek, R. V., Hofner, P., Mciver, A., Portmann, M., & Tan, W. L. (2013). A process algebra for wireless mesh networks used for modelling, verifying and analysing AODV. Technical report 5513, NICTA.
Shamshirband, Sh., Amini, A., Anuar N. B., Kiah, M. L. M., Wah, T. Y., Furnell, S. (2014). D-FICCA: A density-based fuzzy imperialist competitive clustering algorithm for intrusion detection in wireless sensor networks. Measurement, 55, 212–226.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shojafar, M., Abolfazli, S., Mostafaei, H. et al. Improving Channel Assignment in Multi-radio Wireless Mesh Networks with Learning Automata. Wireless Pers Commun 82, 61–80 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2194-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2194-0