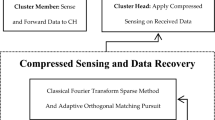
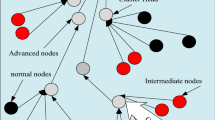
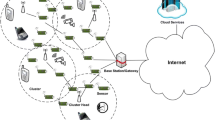
Abstract
The problem of Data acquisition in large distributed Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) scale is a hindrance in the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT). Recently, the combination of compressive sensing (CS) and routing techniques has attracted great interest from researchers. An open question of this approach is how to effectively integrate these technologies for specific tasks. The objective of this paper is two parts. First, we propose an effective deterministic clustering scheme based CS technique (EDCCS) for data collection in IoT based homogeneous and heterogeneous WSN to deal with the data acquisition problem, reduce the consumption of energy and increase the lifetime of network. Second, we propose random matching pursuit (RMP) as an effective CS reconstruction algorithm to improve the recovery process by reducing the error average at the base station (BS). The simulation results show that our proposed novel EDCCS scheme reduces at least 60% of the average power consumption and increases the network lifetime at least 1.3 times of the other schemes in homogeneous network while, it increases the network lifetime and residual energy by 1.9 times and 1.3 times respectively, compared to the other schemes in heterogeneous network. Also, our proposed RMP algorithm reduces the error average of reconstruction at least 35% compared to other reconstruction algorithms.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availibility
The datasets generated during the Simulation and Analysis of our proposed algorithm are randomly generated and also we used Intel Berkeley Research Lab Data Set. Available at: http://db.csail.mit.edu/labdata/labdata.html where, RMP algorithm is used to reconstruct the data that collected by Intel Berkeley Research Lab Data.
References
Oberländer, A. M., Röglinger, M., Rosemann, M., & Kees, A. A. (2017). Conceptualizing business-to-thing interactions-A sociomaterial perspective on the Internet of Things. European Journal of Information Systems, 27, 1–17.
Krishnamurthi, R., Kumar, A., Gopinathan, D., Nayyar, A., & Qureshi, B. (2020). An overview of IoT sensor data processing, fusion, and analysis techniques. Sensors, 20(21), 6076.
Xu, L. (2011). Enterprise systems: State-of-the-art and future trends. IEEE transactions on industrial informatics 7(4), 630640.
Ejaz, A., Yaqoob, I., Gani, A., Imran, M., Guizani, M., Rabbat, M., & Nowak, R. (2016). Internet-of-things-based smart environments: state of the art, taxonomy, and open research challenges. IEEE Wireless Communications, 23, 10–16.
Zheng, J., Simplot-Ryl, D., Bisdikian, C., & Mouftah, H. T. (2011). The internet of things. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(11), 3031.
Palopoli, L., Passerone, R., & Rizano, T. (2011). Scalable of- fline optimization of industrial wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 7(2), 328329.
Balaji, B. S., Raja, P. V., Nayyar, A., Sanjeevikumar, P., & Pandiyan, S. (2020). Enhancement of security and handling the inconspicuousness in IoT using a simple size extensible blockchain. Energies, 13(7), 1795.
Haupt, J., Bajwa, W. U., Rabbat, M., & Nowak, R. (2008). Compressed sensing for networked data: A different approach to decentralized compression. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 92101.
Ulusoy, A., Gurbuz, O., & Onat, A. (2011). Wireless model- based predictive networked control system over cooperative wireless network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 7(1), 4151.
Al-Kashoash, H. A., Kharrufa, H., Al-Nidawi, Y., & Kemp, A. H. (2018). Congestion control in wireless sensor and 6LoWPAN networks: toward the Internet of Things. Wireless Networks, 25, 1–30.
Rahmani, A. M., Gia, T. N., Negash, B., Anzanpour, A., Azimi, I., Jiang, M., & Liljeberg, P. (2018). Exploiting smart e-Health gateways at the edge of healthcare Internet-of-Things: A fog computing approach. Future Generation Computer Systems, 78, 641–658.
Dhumane, A. V., & Prasad, R. S. (2019). Multi-objective fractional gravitational search algorithm for energy efficient routing in IoT. Wireless Networks, 25(1), 399–413.
Palopoli, L., Passerone, R., & Rizano, T. (2011). Scalable offline optimization of industrial wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 7(2), 328329.
Li, S., Xu, L., & Wang, X. (2013). Compressed sensing signal and data acquisition in wireless sensor networks and Internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(4), 2177–2186.
Kavitha, M., & Geetha, B. G. (2017). An efficient city energy management system with secure routing communication using WSN. Cluster Computing, 22, 1–12.
Candes, E., & Wakin, M. (2008). An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 21–30.
Baraniuk, R. (2007). Compressive sensing [Lecture Notes]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 24(4), 118–121.
Haupt, J., Bajwa, W., Rabbat, M., & Nowak, R. (2008). Compressed sensing for networked data. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 92–101.
Luo, J., Xiang, L., Rosenberg, C. (2010). Does compressed sensing improve the throughput of wireless sensor networks?. In 2010 IEEE International Conference on Communications (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Xiang, L., Luo, J., & Vasilakos, A. (2011). Compressed data aggregation for energy efficient wireless sensor networks. In 2011 8th annual IEEE communications society conference on sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks (pp. 46-54). IEEE.
Tsai, T., Lan, W., Liu, C., & Sun, M. (2013). Distributed compressive data aggregation in large-scale wireless sensor networks. Journal of Advances in Computer Networks, 1, 294.
Zhang, C., Zhang, X., Li, O., Yang, Y., & Liu, G. (2017). Dynamic clustering and compressive data gathering algorithm for energy-efficient wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 13(10), 1550147717738905.
Osamy, W., Khedr, A. M., Aziza, A., & El-Sawya, A. (2018). Cluster-tree routing schemefor data gathering in periodic monitoring applications. IEEE Access, 6, 77372–77387.
Aziz, A., Singh, K., Osamy, W., & Khedr, A. M. (2019). Effective algorithm for optimizing compressive sensing in IoT and periodic monitoring applications. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 126(15), 12–28.
Omar, D., & Khedr, A. M. (2019). Prolonging stability period of wireless sensor networks using compressive sensing. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS), 11, 6.
Omar, D. M., & Khedr, A. M. (2018). ERPLBC: energy efficient routing protocol for load balanced clustering in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc & Sensor Wireless Networks, 42, 145–169.
Omar, D. M., Khedr, A. M., & Agrawal, D. P. (2017). Optimized clustering protocol for balancing energy in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS), 9(3), 367–375.
Khedr, A. M., & Omar, D. M. (2015). SEP-CS: effective routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc & Sensor Wireless Networks, 26, 211–232.
Donoho, D. (2006). Compressed sensing. IEEE Transmitted In- form Theory, 52(4), 1289–1306.
Ali, S., & Refaay, S. (2011). Chain-chain based routing protocol. International Journal of Computer Science Issues, 8, 694–0814.
Xie, R., & Jia, X. (2014). Transmission-efficient clustering method for wireless sensor networks using compressive sensing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 25(3), 806815.
Singh, S., Chand, S., Kumar, R., Malik, A., & Kumar, B. (2016). NEECP: Novel energy-efficient clustering protocol for prolonging lifetime of WSNs. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 6(5), 151–157.
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., Balakrishnan, H.(2000) Energy efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks, In: Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference, pp. 3005–3014
Aziz, A., Salim, A., Osamy, W. (2013). Adaptive and efficient compressive sensing based technique for routing in wire- less sensor networks, In Proceedings, INTHITEN (IoT and its Enablers) Conference, pp. 3-4,
Aderohunmu F.A., Deng J.D., Purvis M.K., (2011). A deterministic energy-efficient clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks, In: Proceedings of Seventh IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing, pp. 341–346.
Salim, A., & Osamy, W. (2015). Distributed multi chain compressive sensing based routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 21, 1379–1390.
Smaragdakis, G., Matta, I., & Bestavros, A. (2004). SEP: A stable election protocol for clustered heterogeneous wireless sensor networks, In Proceeding of the International Workshop on SANPA,
Al-Zubaidi, A. S., Ariffin, A. A., & Al-Qadhi, A. K. (2018). Enhancing the stability of the improved-LEACH routing protocol for WSNs. Journal of ICT Research & Applications, 12(1), 1–13.
Smaragdakis, G., Matta, I., & Bestavros, A. (2004) SEP: A Stable ElectionProtocol for clustered heterogeneous wireless sensor networks, In Proceeding of the International Workshop on SANPA,
Mittal, N., Singh, U., & Sohi, B. Singh. (2017). A stable energy efficientclustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 23, 809–1821.
Kumar, S., Kant, S., & Kumar, A. (2015). Enhanced threshold sensitive stable election protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor network. Wireless Pers Communication, 85, 2643–2656.
Luo, C., Wu, F., Sun, J., et al. (2013). An efficient compressive data gathering routing scheme for large-scale wireless sensor networks. Computer Electronical Engineering, 39(6), 19351946.
Haupt, J., Bajwa, W., & Rabbat, M. (2008). Compressed sensing for networked data. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 92–101.
Chong, L., Feng, W., Jun, S., & Chang, C.(2009) Compressive data gathering for large-scale wireless sensor networks, In Proceedings of the 15th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, MobiCom ’09, pp. 145-156, New York, NY, USA, ACM.
Duarte, M., Sarvotham, S., Wakin, M., Baron, D., & Baraniuk, R. (2005). jointsparsity models for distributed compressed sensing., Online Proceedings of the Workshop on Signal Processing with Adaptative Sparse Structured Representations (SPARS),
Jin, W., ShaoJie, T., Baocai, Y., & Yang, X. (2013). Data gathering in wireless sensor networks through intelligent compressive sensing. Digital Signal Processing, 23, 1539–1548.
Luo, C., Wu, F., Sun, J., et al. (2010). Efficient measurement generation and pervasive sparsity for compressive data gathering. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 9(12), 37283738.
Nguyen, M. T., Teague, K. A., & Rahnavard, N. (2016). CCS: energy-efficient data collection in clustered wireless sensor networks utilizing block-wise compressive sensing. Computer Networks, 106, 171185.
Nguyen MT (2013) Minimizing energy consumption in random walk routing for Wireless Sensor Networks utilizing compressed sensing, In Proceedings of the 2013 8th international conference on system of systems engineering, Maui, HI, 26, pp. 297301. New York: IEEE, June 2013.
Khedr, A. M. (2015). Effective data acquisition protocol for multi-hop heterogeneous wireless sensor networks using compressive sensing. Algorithms, 8(4), 910–928.
Yin, X., Neamtiu, I., Patil, S., & Andrews, S. T. (2020). Implementation-induced Inconsistency and Nondeterminism in Deterministic Clustering Algorithms. In 2020 IEEE 13th international conference on software testing, validation and verification (ICST) (pp. 231–242). IEEE.
Wang, Q., Lin, D., Yang, P., & Zhang, Z. (2019). An energy-efficient compressive sensing-based clustering routing protocol for WSNs. IEEE Sensors Journal, 19(10), 3950–3960.
Osamy, W., Aziz, A., & Khedr, A. M. (2021). Deterministic clustering based compressive sensing scheme for fog-supported heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Peer Journal Computer Science, 7, e463.
Tsiropoulou, E. E., Mitsis, G., & Papavassiliou, S. (2018). Interest-aware energy collection & resource management in machine to machine communications. Ad Hoc Networks, 68, 48–57.
Aziz, A., Osamy, W., Khedr, A. M., & Salim, A. (2021). Chain-routing scheme with compressive sensing-based data acquisition for Internet of Things-based wireless sensor networks. IET Networks, 10(2), 43–58.
Venkataramani, R., Bresler, Y. (1998). Sub-nyquist sampling of multiband signals: perfect reconstruction and bounds on aliasing error, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), pp. 12-15, Feb.
Aziz, A., Osamy, W., Khedr, A. M., & Salim, A. (2020). Iterative selection and correction based adaptive greedy algorithm for compressive sensing reconstruction. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences.
Triantafyllou, A., Sarigiannidis, P., & Lagkas, T. D. (2018). Network protocols, schemes, and mechanisms for internet of things (iot): Features, open challenges, and trends. Wireless communications and mobile computing, 2018.
Tropp, J., & Gilber, A. (2007). Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Transactions on information theory, 53(14), 4655–4666.
Dai, Wei, & MilenkovicOlgica. (2009). Dai, W., & Milenkovic, O. (2009). Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE transactions on Information Theory, 55(5), 2230–2249.
needell, D., & tropp, J. a. (2009). COSAMP: iterative signal re- covery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Applied and computational harmonic analysis, 26(3), 301–321.
Burak, N., & Erdogan, H. (2013). Compressed sensing signal recovery via forward-backward pursuit. Digital Signal Processing, 23, 1539–1548.
Aziz, A., Salim, A., & Osamy, W. (2014). Sparse signals reconstruction via adaptive iterative greedy algorithm. International Journal of Computer Applications, 90(17), 5–11.
Heinzelman, WB. (2000). Application-specific protocol architectures for wireless networks. Diss. Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aziz, A., Osamy, W., Alfawaz, O. et al. EDCCS: effective deterministic clustering scheme based compressive sensing to enhance IoT based WSNs. Wireless Netw 28, 2375–2391 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02973-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02973-3