Abstract
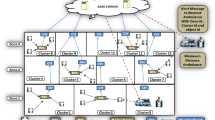
Wireless sensor networks are network of the large number of sensors having lesser batteries. Such networks and clustering of the nodes for energy efficiency go hand in hand. Clustering protocols like low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy, stable election protocol, improved low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy etc. allow the nodes to grouped together, form clusters and transmit their information to the base station via their leader, i.e. cluster head. Selection of cluster head follows various approaches and vary from protocol to protocol. While some of the approaches use single hop communication of the cluster head with the base station, others opt for multi-hop communication. This paper describes energy effective procedure for heterogeneous network consisting of super, advance and normal nodes. The protocol operates according to the type of the nodes. For the high energy super nodes, the protocol follows centralized procedure and for other nodes it follows decentralized approach. The selection of cluster head among the super nodes is optimized by the use of cost function depending upon distance of the nodes from the centroid of their residual energies and their signal to interference plus noise ratio. The nodes other than super nodes achieve lesser energy consumption by using the mobile agents to transfer their data to the base station. The proposed protocol has shown improvements in terms of throughput and number of dead nodes as equated to other state-of-the-art protocols.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raghavendra, C. S., Sivalingam, K. M., & Znati, T. (Eds.). (2006). Wireless sensor networks. Berlin: Springer.
Akyildiz, I. F., Melodia, T., & Chowdhury, K. R. (2007). A survey on wireless multimedia sensor networks. Computer Networks, 51(4), 921–960.
Feng, J., Koushanfar, F., &Potkonjak, M. (2002). System-architectures for sensor networks issues, alternatives, and directions. In Proceedings. 2002 IEEE international conference on computer design: VLSI in computers and processors, 2002 (pp. 226–231). IEEE.
Yang, S.-H. (2014). Wireless sensor networks principles, design and applications. London: Springer.
Megerian, S., & Potkonjak, M. (2003). Wireless sensor networks. Wiley Encyclopedia of Telecommunications. Wiley: New York
Krishnamachari, L., Estrin, D., & Wicker, S. (2002). The impact of data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings. 22nd international conference on distributed computing systems workshops, 2002 (pp. 575–578). IEEE.
Mainwaring, A., Culler, D., Polastre, J., Szewczyk, R., & Anderson, J. (2002, September). Wireless sensor networks for habitat monitoring. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM international workshop on Wireless sensor networks and applications (pp. 88–97). ACM.
Lewis, F. L. (2004). Wireless sensor networks. Smart Environments: Technologies, Protocols, and Applications, 11, 46.
Li, J., Zhang, J., Xiande, L., & Scheme, A. W. D. H. L. (2005). Wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 international conference on scalable computing and communications (pp. 269–272).
Pottie, G. J., & Kaiser, W. J. (2000). Wireless integrated network sensors. Communications of the ACM, 43(5), 51–58.
Akyildiz, I. F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., & Cayirci, E. (2002). A survey on sensor networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(8), 102–114.
Manjeshwar, A., & Agrawal, D. P. (2001, April). TEEN: A routing protocol for enhanced efficiency in wireless sensor networks. In null (p. 30189a). IEEE.
Chang, J. H., & Tassiulas, L. (2004). Maximum lifetime routing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 12(4), 609–619.
Ye, W., Heidemann, J., &Estrin, D. (2002). An energy-efficient MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. In INFOCOM 2002. Twenty-first annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies. Proceedings. IEEE (Vol. 3, pp. 1567–1576). IEEE.
Li, S., Da Xu, L., & Wang, X. (2013). Compressed sensing signal and data acquisition in wireless sensor networks and internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(4), 2177–2186.
Turkanović, M., Brumen, B., & Hölbl, M. (2014). A novel user authentication and key agreement scheme for heterogeneous ad hoc wireless sensor networks, based on the Internet of Things notion. Ad Hoc Networks, 20, 96–112.
Mainetti, L., Patrono, L., & Vilei, A. (2011, September). Evolution of wireless sensor networks towards the internet of things: A survey. In 2011 19th international conference on software, telecommunications and computer networks (SoftCOM) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Christin, D., Reinhardt, A., Mogre, P. S., & Steinmetz, R. (2009). Wireless sensor networks and the internet of things: Selected challenges. In Proceedings of the 8th GI/ITG KuVSFachgesprächDrahtlosesensornetze (pp. 31–34).
Zhang, D. G., Zhu, Y. N., Zhao, C. P., & Dai, W. B. (2012). A new constructing approach for a weighted topology of wireless sensor networks based on local-world theory for the Internet of Things (IoT). Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 64(5), 1044–1055.
Sadek, R. A. (2018). Hybrid energy aware clustered protocol for IoT heterogeneous network. Future Computing and Informatics Journal, 3, 166–177.
Aoun, B., & Boutaba, R. (2006). Clustering in WSN with latency and energy consumption constraints. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 14(3), 415–439.
Younis, O., Krunz, M., & Ramasubramanian, S. (2006). Node clustering in wireless sensor networks: Recent developments and deployment challenges. IEEE Network, 20(3), 20–25.
Wu, W., Xiong, N., & Wu, C. (2017). Improved clustering algorithm based on energy consumption in wireless sensor networks. IET Networks, 6(3), 47–53.
Nayak, P., & Devulapalli, A. (2016). A fuzzy logic-based clustering algorithm for WSN to extend the network lifetime. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(1), 137–144.
Kuila, P., & Jana, P. K. (2014). Energy efficient clustering and routing algorithms for wireless sensor networks: Particle swarm optimization approach. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 33, 127–140.
Yuan, X., Elhoseny, M., El-Minir, H. K., & Riad, A. M. (2017). A genetic algorithm-based, dynamic clustering method towards improved WSN longevity. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 25(1), 21–46.
Rao, P. S., Jana, P. K., & Banka, H. (2017). A particle swarm optimization based energy efficient cluster head selection algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 23(7), 2005–2020.
Javaid, N., Rasheed, M. B., Imran, M., Guizani, M., Khan, Z. A., Alghamdi, T. A., et al. (2015). An energy-efficient distributed clustering algorithm for heterogeneous WSNs. EURASIP Journal on Wireless communications and Networking, 2015(1), 151.
Al-Fuqaha, A., Guizani, M., Mohammadi, M., Aledhari, M., & Ayyash, M. (2015). Internet of things: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(4), 2347–2376.
Li, X., Niu, J., Kumari, S., Wu, F., Sangaiah, A. K., & Choo, K. K. R. (2018). A three-factor anonymous authentication scheme for wireless sensor networks in internet of things environments. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 103, 194–204.
Qadori, H. Q., Zukarnain, Z. A., Hanapi, Z. M., & Subramaniam, S. (2018). FuMAM: Fuzzy-based mobile agent migration approach for data gathering in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 6, 15643–15652.
Trivedi, K., & Srivastava, A. K. (2014, December). An energy efficient framework for detection and monitoring of forest fire using mobile agent in wireless sensor networks. In 2014 IEEE international conference on computational intelligence and computing research (ICCIC) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Wang, X., Chen, M., Kwon, T., & Chao, H. C. (2011). Multiple mobile agents’ itinerary planning in wireless sensor networks: Survey and evaluation. IET Communications, 5(12), 1769–1776.
Ardakani, S. P., Padget, J., & De Vos, M. (2017). A mobile agent routing protocol for data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 24(1), 27–41.
Vimal, V., & Nigam, M. J. (2017). Ensuring uniform energy consumption in non-deterministic wireless sensor network to protract networks lifetime. International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering, 11(9), 1006–1008.
Vimal, V., & Nigam, M. J. (2018). Estimation of optimum rendezvous point for mobile sink (ORP-MS) in WSN. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 7(3), 1322–1328.
Raghuvanshi, A. S., Tiwari, S., & Tripathi, R. (2011). Optimal number of clusters in wireless sensor networks: An FCM approach. International Journal of Sensor Networks. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCT.2010.5640391.
Chen, T.-Y., Wei, H.-W., Lee, C.-R., Huang, F.-N., Hsu, T.-S., & Shih, W.-K. (2013). Energy efficient geographic routing algorithms in wireless sensor network. Journal of Interconnection Networks, 14(01), 1350001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, H., Bala, M. & Bamber, S.S. Augmenting network lifetime for heterogenous WSN assisted IoT using mobile agent. Wireless Netw 26, 5965–5979 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02422-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02422-z