Abstract
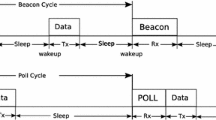
The wireless body area network requires an optimized algorithm and protocols for the error-free communication for sports application. The communication process that takes between the hub and other nodes must be reliable and error-free without any collision. Time division multiple access is a technique in which synchronization between nodes takes place and less reliable when compared to the other multiple access techniques. This paper primarily focuses on the TDMA and Polling TDMA protocols that could be used for the communication between the nodes. Comparison of the performance metrics such as packet delivery ratio, an end to end delay, jitter and throughput gives the network reliability between the TDMA and Polling TDMA. Based on the study, various MAC techniques could be used and the latest, TDMA could be used for error-free communication, and then followed by the Polling TDMA. The Reliability of 90% was achieved using time division multiple access and was increased to 97% using Polling TDMA. This comparison can be used to propose new algorithms to find the kinematic movement of the human and also reduce the energy of the nodes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hagem, R. M., Sabti, H. A., & Thiel, D. V. (2015). Coach-Swimmer communications based on wrist mounted 2.4 GHz accelerometer sensor. Procedia Engineering,112, 512–516.
Sabti, H. A. A., & Thiel, D. V. (2015). Self-calibrating body sensor network based on periodic human movements. IEEE Sensors Journal,15(3), 1552–1558.
Zhao, J., & Govindan, R. (2003). Understanding packet delivery performance in dense wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 1st international conference on embedded networked sensor systems (pp. 1–13). ACM.
Matsuo, R., Nabetani, T., Tanakay, H., Chin, W. H., &Subramani, S. (2015). Performance of simple and Smart PHY/MAC mechanisms for Body Area Networks. In Communications (ICC), 2015 IEEE international conference on (pp. 501–506). IEEE.
Sabti, H. A., & Thiel, D. V. (2014). A study of wireless communication links on a body centric network during running. Procedia Engineering,72, 3–8.
Sabti, H. A., & Thiel, D. V. (2015). High reliability body sensor network using gesture triggered burst transmission. Procedia Engineering,112, 507–511.
Sabti, H. A., & Thiel, D. V. (2014). Node position effect on link reliability for body centric wireless network running applications. IEEE Sensors Journal,14(8), 2687–2691.
Mustafa, M. M., Parthasarathy, V., Kumar, M. R., & Hemalatha, S. An Efficient DTDM H-MAC Protocol with self-calibrating algorithm in BSN for sporting application.
Gopal, R., & Parthasarathy, V. (2016). CAND-IDS: A novel context aware intrusion detection system in cooperative wireless sensor networks by nodal node deployment. Circuits and Systems,7(11), 3504.
Krishnamachari, B., Estrin, D., & Wicker, S. (2002). Modelling data-centric routing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE infocom,2, 39–44.
Hu, S., Yao, Y. D., & Yang, Z. (2014). MAC protocol identification using support vector machines for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Wireless Communications,21(1), 52–60.
Hulyalkar, S. N., Shekhter, E., & Steiner, L., North American Philips Lighting Corp. (2002).Method of timestamp synchronization of a reservation-based TDMA protocol. U.S. Patent 6347084.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mustafa, M., Parthasarathy, V. A design and implementation of polling TDMA with a comparative analysis with time division multiple access for sporting application. Wireless Netw 26, 1897–1904 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1879-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1879-9