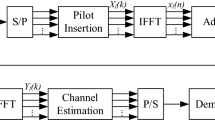
Abstract
In the cooperative cognitive radio networks (CRN), often secondary user (SU) relays the information of primary user (PU) as a rewarding relay to improve diversity gain of PU without being a legitimate user. So the SU needs to detect the signal, blindly estimate the parameters introduced in channel and reconstruct the signal before relaying it to the primary receiver. In this paper, a joint scheme for signal detection and non-data-aided (blind) parameter estimation of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) based CRN has been discussed. Based upon binary hypothesis testing problem, the SU formulates a minimum cost signal detection scheme for the presence of OFDM based PU signal in CRN. The probability of detection, probability of false alarm and receiver operating characteristics have been presented to illustrate the performance of signal detection scheme in the CRN. Further, the effective throughput analysis of the secondary system has been demonstrated in the context when the primary system is detected as idle. Blind synchronous parameters of OFDM signal such as carrier frequency offset and symbol timing offset has been presented over the wireless fading channel in the CRN. Existing theoretical studies on blind parameter estimation algorithms for signals have been carried out but most of them have not been implemented in order to validate their feasibility. Here, a software-defined radio testbed has been implemented using national instruments hardware in a multipath indoor environment and experimental results have been provided using real measurement system. The preliminary measurement and simulation results demonstrate that the proposed blind estimator is capable of estimating the concerned parameters and constellation symbols over an indoor propagation environment.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axell, E., Leus, G., Larsson, E. G., & Poor, H. V. (2012). Spectrum sensing for cognitive radio: State-of-the-art and recent advances. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 29(3), 101–116.
Ghosh, C., Roy, S., & Cavalcanti, D. (2011). Coexistence challenges for heterogeneous cognitive wireless networks in TV white spaces. IEEE Wireless Communications, 18(4), 22–31.
Zhang, Q., Jia, J., & Zhang, J. (2009). Cooperative relay to improve diversity in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(2), 111–117.
Zhao, N., & Sun, H. (2011). Robust power control for cognitive radio in spectrum underlay networks. KSII Transactions on Internet & Information Systems, 5(7), 1214–1229.
Cadambe, V. R., & Jafar, S. A. (2008). Interference alignment and degrees of freedom of the \(K\)-user interference channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(8), 3425–3441.
Zhao, N., Yu, F. R., Sun, H., Nallanathan, A., & Yin, H. (2013). A novel interference alignment scheme based on sequential antenna switching in wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(10), 5008–5021.
Zhao, N., Yu, F. R., Sun, H., Yin, H., Nallanathan, A., & Wang, G. (2015). Interference alignment with delayed channel state information and dynamic AR-model channel prediction in wireless networks. Wireless Networks, 21(4), 1227–1242.
Zhao, N., Yu, F. R., Sun, H., & Li, M. (2016). Adaptive power allocation schemes for spectrum sharing in interference-alignment-based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(5), 3700–3714.
El Ayach, O., Peters, S. W., & Heath, R. W. (2013). The practical challenges of interference alignment. IEEE Wireless Communications, 20(1), 35–42.
Zhao, N., Yu, F. R., & Leung, V. C. M. (2015). Opportunistic communications in interference alignment networks with wireless power transfer. IEEE Wireless Communications, 22(1), 88–95.
Li, X., Zhao, N., Sun, Y., & Yu, F. R. (2016). Interference alignment based on antenna selection with imperfect channel state information in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(7), 5497–5511.
Gao, F., Zhang, R., Liang, Y. C., & Wang, X. (2010). Design of learning-based MIMO cognitive radio systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(4), 1707–1720.
Xie, H., Wang, B., Gao, F., & Jin, S. (2016). A full-space spectrum-sharing strategy for massive MIMO cognitive radio systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34(10), 2537–2549.
van Nee, R., & Prasad, R. (2000). OFDM for wireless multimedia communications. Boston: Artech House.
Sidhu, G. A. S., Gao, F., Wang, W., & Chen, W. (2013). Resource allocation in relay-aided OFDM cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(8), 3700–3710.
Ali, A., & Hamouda, W. (2015). Spectrum monitoring using energy ratio algorithm for OFDM-based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(4), 2257–2268.
Jntti, J., Chaudhari, S., & Koivunen, V. (2015). Detection and classification of OFDM waveforms using cepstral analysis. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 63(16), 4284–4299.
Dikmese, S., Ilyas, Z., Sofotasios, P., Renfors, M., & Valkama, M. (2016). Novel frequency domain cyclic prefix autocorrelation based compressive spectrum sensing for cognitive radio. In 2016 IEEE 83rd vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–6). VTC Spring.
Shi, Z., McLernon, D., Ghogho, M., & Wu, Z. (2014). Improved spectrum sensing for OFDM cognitive radio in the presence of timing offset. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2014(1), 224. doi:10.1186/1687-1499-2014-224.
Lei, Z., & Chin, F. (2008). OFDM signal sensing for cognitive radios. In 2008 IEEE 19th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 1–5).
Chaudhari, S., Koivunen, V., & Poor, H. V. (2009). Autocorrelation-based decentralized sequential detection of OFDM signals in cognitive radios. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 57(7), 2690–2700.
Lei, Z., & Chin, F. P. S. (2010). Sensing OFDM systems under frequency-selective fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(4), 1960–1968.
Speth, M., Fechtel, S., Fock, G., & Meyr, H. (2001). Optimum receiver design for OFDM-based broadband transmission. II. A case study. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 49(4), 571–578.
Mostofi, Y., & Cox, D. (2006). Mathematical analysis of the impact of timing synchronization errors on the performance of an OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 54(2), 226–230.
Filippi, A., & Serbetli, S. (2009). OFDM symbol synchronization using frequency domain pilots in time domain. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(6), 3240–3248.
Hsieh, H.-T., & Wu, W.-R. (2009). Maximum likelihood timing and carrier frequency offset estimation for OFDM systems with periodic preambles. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(8), 4224–4237.
van de Beek, J.-J., Sandell, M., & Borjesson, P. (1997). ML estimation of time and frequency offset in OFDM systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 45(7), 1800–1805.
Fusco, T., & Tanda, M. (2009). Blind synchronization for OFDM systems in multipath channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(3), 1340–1348.
Chen, B., & Wang, H. (2004). Blind estimation of OFDM carrier frequency offset via oversampling. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(7), 2047–2057.
Younis, S., Al-Dweik, A., Hazmi, A., Tsimenidis, C. C., & Sharif, B. S. (2010). Symbol timing offset estimation scheme for OFDM systems based on power difference measurements. In 21st Annual IEEE international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 927–932).
Jeon, H.-G., Kim, K.-S., & Serpedin, E. (2011). An efficient blind deterministic frequency offset estimator for OFDM systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 59(4), 1133–1141.
Pan, Y. C., Phoong, S. M., & Lin, Y. P. (2014). An improved ESPRIT-based blind CFO estimation algorithm in OFDM systems. In 2014 48th Asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers (pp. 258–262).
Liu, J. G., Wang, X., & Chouinard, J. Y. (2012). Iterative blind OFDM parameter estimation and synchronization for cognitive radio systems. In 2012 IEEE 75th vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–5). VTC Spring.
Shaat, M., & Bader, F. (2012). Asymptotically optimal resource allocation in OFDM-based cognitive networks with multiple relays. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(3), 892–897.
Majhi, S., & Ho, T. S. (2015). Blind symbol-rate estimation and test bed implementation of linearly modulated signals. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(3), 954–963.
Kumar, M., & Majhi, S. (2015). Blind synchronization of OFDM system and CRLB derivation of CFO over fading channels. In 2015 10th International conference on information, communications and signal processing (ICICS) (pp. 1–6).
Majhi, S., Kumar, M., & Xiang, W. (2017). Implementation and measurement of blind wireless receiver for single carrier systems. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 66(8), 1965–1975.
Majhi, S., Gupta, R., Xiang, W., & Glisic, S. (2017). Hierarchical hypothesis and feature based blind modulation classification for linearly modulated signals. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 99, 1–1.
Majhi, S., Gupta, R., & Xiang, W. (2017). Novel blind modulation classification of circular and linearly modulated signals using cyclic cumulant. In 28th Annual IEEE international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (pp. 1–6).
Van Trees, H. L. (2002). Detection, estimation, and modulation theory. Part IV: Optimum array processing. New York: Wiley. http://opac.inria.fr/record=b1105852.
Hyder, C. S., Al Islam, A. B. M. A., Xiao, L., & Torng, E. (2016). Interference aware reliable cooperative cognitive networks for real-time applications. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2(1), 53–67.
Kay, S. (1998). Fundamentlas of statistical signal processing, volume 2: Detection theory. Englewood: Prentice-Hall.
Goldsmith, A., Jafar, S. A., Maric, I., & Srinivasa, S. (2009). Breaking spectrum gridlock with cognitive radios: An information theoretic perspective. Proceedings of the IEEE, 97(5), 894–914.
Chang, C.-S. (1994). Stability, queue length, and delay of deterministic and stochastic queueing networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 39(5), 913–931.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Majhi, S. Joint signal detection and synchronization for OFDM based cognitive radio networks and its implementation. Wireless Netw 25, 699–712 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-017-1586-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-017-1586-y