Abstract
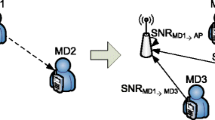
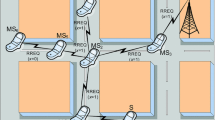
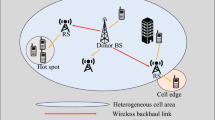
Relaying can improve the coverage and performance of wireless access networks. In presence of a localisation system at the mobile nodes, the use of such location estimates for relay node selection can be advantageous as such information can be collected by access points in linear effort with respect to number of mobile nodes (while the number of links grows quadratically). However, the localisation error and the chosen update rate of location information in conjunction with the mobility model affect the performance of such location-based relay schemes; these parameters also need to be taken into account in the design of optimal policies. This paper develops a Markov model that can capture the joint impact of localisation errors and inaccuracies of location information due to forwarding delays and mobility; the Markov model is used to develop algorithms to determine optimal location-based relay policies that take the aforementioned factors into account. The model is subsequently used to analyse the impact of deployment parameter choices on the performance of location-based relaying in WLAN scenarios with free-space propagation conditions and in an measurement-based indoor office scenario.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiot, N., Laaraiedh, M., & Uguen, B. (2012). Evaluation of a geometric positioning algorithm for hybrid wireless networks. In: 2012 20th international conference on IEEE software, telecommunication and computer networks (SoftCOM).
Amiot, N., Laaraiedh, M., & Uguen, B. (2013). PyLayers: An open source dynamic simulator for indoor propagation and localization. In: IEEE ICC’13—Workshop on advances in network localization and navigation (ANLN).
Amiot, N., Laaraiedh, M., & Uguen, B. (2013). Pylayers: An open source dynamic simulator for indoor propagation and localization. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on, communications workshops (ICC), pp. 84–88. doi:10.1109/ICCW.2013.6649206
Bogsted, M., Olsen, R., & Schwefel, H. (2010). Probabilistic models for access strategies to dynamic information elements. Performance Evaluation, 67(1), 43–60.
Durgin, G., Rappaport, T., & Xu, H. (1998). Measurements and models for radio path loss and penetration loss inand around homes and trees at 5.85 GHz. In: IEEE Transactions on Communications, 46(11).
Gustafsson, F., & Gunnarsson, F. (2005). Mobile positioning using wireless networks: Possibilities and fundamental limitations based on available wireless network measurements. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 22(4), 41–53. doi:10.1109/MSP.2005.1458284.
Jun, J., Peddabachagari, P., & Sichitiu, M. (2003). Theoretical maximum throughput of IEEE 802.11 and its applications. In: Second IEEE international symposium on, network computing and applications, 2003. NCA 2003, pp. 249–256.
Liao, L., Patterson, D. J., Fox, D., & Kautz, H. (2007). Learning and inferring transportation routines. Artificial Intelligence, 171(5), 311–331.
Liu, J. S., & Wong, Y. C. (2004). A relay-based multirate protocol in infrastructure wireless lans. In: Proceedings. 12th IEEE international conference on, networks. (ICON 2004). vol. 1, pp. 201–206. doi:10.1109/ICON.2004.1409124
Liu, P., Tao, Z., Narayanan, S., Korakis, T., & Panwar, S. (2007). CoopMAC: A cooperative MAC for wireless LANs. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communication, 25(2), 340.
Liu, T., Bahl, P., & Chlamtac, I. (1998). Mobility modeling, location tracking, and trajectory prediction in wireless ATM networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communication, 16(6), 922–936.
Mao, G., & Fidan, B. (2009). Localization algorithms and strategies for wireless sensor networks: Monitoring and surveillance techniques for target tracking. Information science reference.
Nasser, Y., Farhat, H., & Helard, J. F. (2009). Positioning information based technique in cooperative mimo-ofdm systems. In: 2009 IEEE 20th international symposium on, personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, pp. 2695–2699.
Nielsen, J. (2011). Location based network optimizations for mobile wireless networks—A study of the impact of mobility and inaccurate information. In: Ph.D. thesis, Aalborg University.
Nielsen, J., Amiot, N., & Madsen, T. (2013). Directional hidden markov model for indoor tracking of mobile users and realistic case study. In: Proceedings of the European wireless, 2013. EW. 19th European wireless conference. VDE Verlag GMBH.
Nielsen, J. J., Madsen, T. K., & Schwefel, H. P. (2010). Location-based mobile relay selection and impact of inaccurate path loss model parameters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE wireless communication and networking conference (WCNC).
Nielsen, J. J., Madsen, T. K., & Schwefel, H. P. (2010). Location-based relay selection and power adaptation enabling simultaneous transmissions. In: Proceedings of the GLOBECOM workshops.
Nielsen, J. J., Olsen, R. L., Madsen, T. K., & Schwefel, H. P. (2012) On the impact of information delay on location-based relaying: A markov modeling approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE wireless communicaion and networking conference (WCNC).
Nielsen, J. J., Olsen, R. L., Madsen, T. K., & Schwefel, H. P. (2013). Optimized policies for improving fairness of location-based relay selection. In: 2013 IEEE 77th vehicular technology conference (VTC Spring).
Nielsen, J. J., Olsen, R. L., Madsen, T. K., Uguen, B., & Schwefel, H. P. (2012). Model-based evaluation of location-based relaying policies in a realistic mobile indoor scenario. In: Proceedings of computer aided modeling and design (CAMAD).
Olsen, R., Figueiras, J., Rasmussen, J., & Schwefel, H. (2010). How precise should localization be? A quantitative analysis of the impact of the delay and mobility on reliability of location information. In: Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM.
Popovski, P., & Yomo, H. (2007). Physical network coding in two-way wireless relay channels. In: IEEE international conference on, communications, 2007. ICC’07, pp. 707–712.
Puterman, M. L. (2009). Markov decision processes: Discrete stochastic dynamic programming (Vol. 414). New York: Wiley.
Sayed, A., Tarighat, A., & Khajehnouri, N. (2005). Network-based wireless location: Challenges faced in developing techniques for accurate wireless location information. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 22(4), 24–40. doi:10.1109/MSP.2005.1458275.
Seyfi, M., Muhaidat, S., & Liang, J. (2011). Performance analysis of relay selection with feedback delay and channel estimation errors. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 18(1), 67–70.
Stephan, J., Lostanlen, Y., Keignart, J., Wang, W., Slock, D., & Kaltenberger, F. (2008). WHERE D4.1—Measurements of location-dependent channel features. In: Tech. rep. http://www.kn-s.dlr.de/where/documents/Deliverable-D4.1. ICT-217033
Suraweera, H., Soysa, M., Tellambura, C., & Garg, H. (2010). Performance analysis of partial relay selection with feedback delay. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 17(6), 531–534.
Yang, H., Petropulu, A. P., Yang, X., & Camp, T. (2008). A novel location relay selection scheme for alliances. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(2), 1272–1284.
Yang, X., Camp, T., Yang, H., & Petropulu, A. P. (2009). Extending network lifetime for alliances. Computer Communications, 32(17), 1837–1851.
Zhao, B., & Valenti, M. (2005). Practical relay networks: A generalization of hybrid-arq. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23(1), 7–18.
Zhu, H., & Cao, G. (2006). rDCF: A relay-enabled medium access control protocol for wireless ad hoc networks. In: IEEE transactions on mobile computing, pp. 1201–1214.
Zorzi, M., & Rao, R. (2004). Geographic random forwarding (GeRaF) for ad hoc and sensor networks: Multihop performance. IEEE Transactions on, Mobile Computing, 2(4), 337–348.
Acknowledgments
This work has been performed in the framework of the ICT project ICT-248894 WHERE2, which is partly funded by the European Union. The Telecommunications Research Center Vienna (FTW) is supported by the Austrian Government and by the City of Vienna within the competence center program COMET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, J.J., Olsen, R.L., Madsen, T.K. et al. Location-quality-aware policy optimisation for relay selection in mobile networks. Wireless Netw 22, 599–618 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0986-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0986-0