Abstract
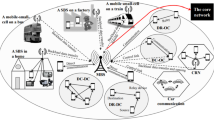
The convergence of real-time multimedia applications, the increasing coverage of heterogeneous wireless networks and the ever-growing popularity of mobile devices are leading to an era of mobile human-centric multimedia services. In this scenario, heterogeneous communications will co-exist and ensure that the end-user is always best connected. The rigorous networking demands of wireless multimedia systems, beyond quality-oriented control strategies, are necessary to guarantee the best user experience over time. Therefore, the Quality of Experience (QoE) support, especially for 2D or 3D videos in multi-operator environments, remains a significant challenge and is crucial for the success of multimedia systems. This paper proposes a QoE Handover Architecture for Converged Heterogeneous Wireless Networks, called QoEHand. QoEHand extends the Media Independent Handover (MIH)/IEEE 802.21 with QoE-awareness, seamless mobility and video adaptation by integrating a set of QoE-based decision-making modules into MIH, namely a video quality estimator, a dynamic class of service mapping and content adaptation schemes. The QoEHand video estimator, mapping and adaptation components operate by coordinating information about video characteristics, available wireless resources in IEEE 802.11e and IEEE 802.16e service classes, and QoE-aware human experience. The video quality estimator works without the need for any decoding, which saves time and minimises processing overheads. Simulations were carried out to show the benefits of QoEHand and its impact on user perception by using objective and subjective QoE metrics.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy, J. J. J., Vaidehi, V., & Sricharan, M. S. (2011). QoS guaranteed integration methodology for a WLAN–WiMAX heterogeneous network. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 37(3), 261–274.
De La Oliva, A., Banchs, A., Soto, I., Melia, T., & Vidal, A. (2008). An overview of IEEE 802.21: media-independent handover services. IEEE Wireless Communications, 15(4), 96–103.
Venkataraman, M., & Chatterjee, M. (2011). Inferring video QoE in real time. IEEE Network, 25(1), 4–13.
Aguiar, E., Riker, A., Mu, M., Zeadally, S., Cerqueira, E., & Abelem, A. (2012). Real-time QoE prediction for multimedia applications in wireless mesh networks. 4th IEEE Future Multimedia Network Workshop/9th IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, CCNC 2012, Las Vegas, USA.
Al-Surmi, I., Othman, M., & Mohd Ali, B. (2012). Mobility management for IP-based next generation mobile networks: review, challenge and perspective. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 35(1), 295–315.
Zhang, J., & Ansari, N. (2011). On assuring end-to-end QoE in next generation networks: challenges and a possible solution. IEEE Communications Magazine, 49(7), 185–191.
Sousa, R., Mota, E. S., Silva, E. N., Paixão, K. S., Faria, B. H. C., & Neto, J. B. P. (2010). GoP size influence in high resolution video streaming over wireless mesh network. IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, 2010, 1–3.
Huszák, Á., & Imre, S. (2010). Analysing GoP structure and packet loss effects on error propagation in mpeg-4 video streams. 4th International Symposium on Communications, Control and Signal Processing (ISCCSP), 1–5.
Matos, F., Matos, A., Simoes, P., & Monteiro, E. (2011). QoS adaptation in inter-domain services. 12th IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management, 257–264.
Aguiar, E. S., Riker, A., Abelem, A., Cerqueira, E, & Mu, M. (2012). Video quality estimator for wireless mesh networks. IEEE/ACM 20th International Workshop on Quality of Service (IEEE/ACM IWQoS 2012), 1–9.
Mu, M., Romaniak, P., Mauthe, A., Leszczuk, M., Janowski, L., & Cerqueira, E. (2012). Framework for the integrated video quality assessment. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 61(3), 787–817.
Keimel, C., Rothbucher, M., Shen, H., & Diepold, K. J. (2011). Video is a cube. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 28(6), 41–49.
Mohamed, S., & Rubino, G. (2002). A study of real-time packet video quality using random neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 12(12), 1071–1083.
Ghareeb, M., & Viho, C. (2010). Hybrid QoE assessment is well-suited for multiple description coding video streaming in overlay networks. 8th Annual Communication Networks and Services Research Conference, 327–333.
Cancela, H., Amoza, F. R., Rodríguez-Bocca, P., Rubino, G., & Sabiguero, A. (2008). A robust P2P streaming architecture and its application to a high quality live-video service. Electronic Notes in Discrete Mathematics, 30, 219–224.
Da Silva, A. P. C., Varela, M., de Souza e Silva, E., Leão, R. M. M., & Rubino, G. (2008). Quality assessment of interactive voice applications. Computer Networks, 52(6), 1179–1192.
Rubino, G., Varela, M., & Bonnin, J.-M. (2006). Controlling multimedia QoS in the future home network using the PSQA metric. The Computer Journal, 49(2), 137.
Piamrat, K., Viho, C. G., Bonnin, J.-M. M., & Ksentini, A. (2009). Quality of experience measurements for video streaming over wireless networks. IEEE Sixth International Conference on New Generations in Information Technology, 1184–1189.
Piamrat, K., Ksentini, A., Viho, C. G., & Bonnin, J.-M. M. (2008). QoE-based network selection for multimedia users in IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. 33rd IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN 2008), 388–394.
Kim, Y., Pack, S., Kang, C. G., & Park, S. (2011). An enhanced information server for seamless vertical handover in IEEE 802.21 MIH networks. Computer Networks, 55(1), 147–158.
Lim, W.-S., Kim, D.-W., Suh, Y.-J., & Won, J.-J. (2009). Implementation and performance study of IEEE 802.21 in integrated IEEE 802.11/802.16e networks. Computer Communications, 32(1), 134–143.
Zhou, L., Chao, H.-C., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2011). Joint forensics-scheduling strategy for delay-sensitive multimedia applications over heterogeneous networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 29(7), 1358–1367.
Lin, C.-P., Chen, H.-L., & Leu, J.-S. (2012). A predictive handover scheme to improve service quality in the IEEE 802.21 network. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 38(3), 681–693.
Brooks, P., & Hestnes, B. (2010). User measures of quality of experience: why being objective and quantitative is important. IEEE Network, 24(2), 8–13.
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., & Williams, R. J. (1986). Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 323, 533–536.
Recommendation ITU-R BT.500-11. Methodology for the subjective assessment of the quality of television pictures. (2012). http://www.dii.unisi.it/~menegaz/DoctoralSchool2004/papers/ITU-R_BT.500-11.pdf. Accessed March 11, 2013.
VTL. (2012). Video trace library. trace.eas.asu.edu. Accessed March 11, 2013.
Zhenxing, C., & Satoshi, G. (2011). Efficient motion vector prediction algorithm using pattern matching. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 22(8), 727–733.
Majdi, E., Abdelkrim, E., Samy, E., Jean-Luc, D., & Rached, T. (2012). A low-pow oriented architecture for H.264 variable block size motion estimation based on a resource sharing scheme. The VLSI Journal, Available online 3 October 2012, ISSN 0167-9260, doi:10.1016/j.vlsi.2012.09.001.
Roma, N., & Sousa, L. (2001). A tutorial overview on the properties of the discrete cosine transform for encoded image and video processing. Signal Processing Journal, 91(11), 2443–2464.
Quadros, C., Melo, A., Douglas, A., Abelém, A., Cerqueira, E., Neto, A., Riker, A., & Curado, M. (2012). QoE-based packet drop control for 3D-video streaming over wireless networks. 7th IFIP/ACM Latin American Networking Conference, 59201366.
Zheng, Y., & Meng, Y. (2011). Modular neural networks for multi-class object recognition. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2927–2932.
Choi, H., & Lee, C. H. (2011). Motion adaptive deinterlacing with modular neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 21(6), 844–849.
So-In, C., Jain, R., & Tamimi, A.-K. (2009). Scheduling in IEEE 802.16e mobile WiMAX networks: key issues and a survey. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 27(2), 156–171.
Lee, J.-F. F., Liao, W., Chen, J.-M., & Lee, H.-H. (2009). A practical QoS solution to voice over IP in IEEE 802.11 WLANs. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(4), 111–117.
Rouil, R., Golmie, N., & Montavont, N. (2010). Media independent handover transport using cross-layer optimized stream control transmission protocol. Computer Communications, 33(9), 1075–1085.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by The National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq). Authors would like to thank PROPESP/FADESP/UFPA. Eduardo Cerqueira receives a CNPq Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosário, D., Cerqueira, E., Neto, A. et al. A QoE handover architecture for converged heterogeneous wireless networks. Wireless Netw 19, 2005–2020 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-013-0584-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-013-0584-y