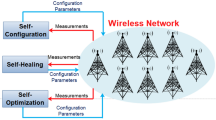
Abstract
Optimization of the performance of the link layer in wireless networks is complex due to multiple parameters involved. Network management in real-time and performance adaptation are extremely challenging. In this paper, we introduce CogMAC, a cognitive link layer approach capable of tuning the network performance in highly dynamic environments. Results obtained using simulations and testbed measurements evince the superiorities of the proposed approach over existing non-adaptive techniques.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ancillotti, E., Bruno, R., & Conti, M. (2008). Experimentation and performance evaluation of rate adaptation algorithms in wireless mesh networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM symposium on performance evaluation of wireless ad hoc, sensor, and ubiquitous networks (pp. 7–14). New York, NY: ACM.
Ayari, M., Movahedi, Z., Pujolle, G., & Kamoun, F. (2009). Adma: Autonomous decentralized management architecture for manets: A simple self-configuring case study. In: Proceedings of the 2009 international conference on wireless communications and mobile computing: Connecting the world wirelessly (pp. 132–137). ACM.
Bononi, L., Conti, M., & Gregori, E. (2004). Runtime optimization of IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs performance. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 15(1), 66–80.
Cali, F., Conti, M., & Gregori, E. (2000). Dynamic tuning of the IEEE 802.11 protocol to achieve a theoretical throughput limit. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (TON), 8(6), 799.
Choi, J., Na, J., Park, K., & Kim, C. (2007) Adaptive optimization of rate adaptation algorithms in multi-rate WLANs. In: Proceeding of IEEE ICNP. Citeseer.
Facchini, C., & Granelli, F. (2009). Towards a model for quantitative reasoning in cognitive nodes. In: GLOBECOM Workshops, IEEE (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Fortuna, C., & Mohorcic, M. (2009). Trends in the development of communication networks: Cognitive networks. Computer Networks, 53(9), 1354–1376.
Goode, B. (2002). Voice over internet protocol (VoIP). Proceedings of the IEEE, 90(9), 1495–1517.
Gunes, M., Hecker, M., & Bouazizi, I. (2003). Influence of adaptive RTS/CTS retransmissions on TCP in wireless and ad-hoc networks. In: Eighth IEEE international symposium on computers and communication (ISCC 2003) (pp. 855–860). IEEE.
IEEE. (1999). Wireless lan medium access control (mac) and physical layer (phy) specifications. IEEE Standard 802.11.
Iperf. Available at http://iperf.sourceforge.net/.
Jain, R. (1991). The art of computer systems performance analysis: Techniques for experimental design, measurement, simulation, and modeling. New York: Wiley.
Love, R. (2010). Linux kernel development (3rd ed.). Boston, MA: Addison-Wesley. ISBN-10: 0672329468, ISBN-13: 9780672329463 .
Mjidi, M., Chakraborty, D., Nakamura, N., Koide, K., Takeda, A., & Shiratori, N. (2008). A new dynamic scheme for efficient RTS threshold handling in wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on advanced information networking and applications (pp. 734–740). IEEE Computer Society.
Ns2 network simulator. Available at http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/.
Sutton, P., Doyle, L., & Nolan, K. (2006). A reconfigurable platform for cognitive networks. In: 1st international conference on cognitive radio oriented wireless networks and communications, 2006 (pp. 1–5). Ieee.
Thomas, R., DaSilva, L., & MacKenzie, A. (2005). Cognitive networks. In: New frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks, DySPAN 2005 (pp. 352–360). IEEE.
Tsertou, A., & Laurenson, D. (2008). Revisiting the hidden terminal problem in a csma/ca wireless network. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7(7), 817–831.
Xia, Q., & Hamdi, M. (2006). Contention window adjustment for IEEE 802.11 WLANs: A control-theoretic approach. In: IEEE international conference on communications, ICC’06, 9.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank FAPESP for the financial support, under grant number 2007/57336-0 and CNPq. Furthermore, the authors would like to acknowledge the funding from National Research Fund, Luxembourg in the framework of ECO-CLOUD project (C12/IS/3977641) and Marie Curie Actions of the European Commission (FP7-COFUND).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira Filho, J.L., Kliazovich, D., Granelli, F. et al. CogMAC: a cognitive link layer for wireless local area networks. Wireless Netw 19, 1337–1347 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-012-0536-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-012-0536-y