Abstract
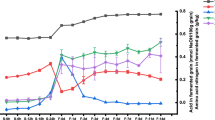
Daqu is of great significance to the brewing process of Baijiu, and there are variations in the light-flavor Baijiu Daqu in different regions. However, few studies have been conducted on light-flavor Daqu from the north and south regions of China. In this study, the physicochemical indices, volatile flavor components, and microbial community structure of two types of Daqu from the north and south regions of China were comparatively analyzed. The study findings reveal that Daqu originating from the southern region of China (HB) exhibits superior moisture content, acidity, starch content, and saccharification power. In contrast, Daqu from the northern region of China (SX) displays higher fermentation, esterification, and liquefaction power. The analysis of the microbial community structure revealed that HB was dominated by Bacillus, Kroppenstedtia, Saccharomycopsis, and Thermoascus, while SX was dominated by Bacillus, Prevotella, and Saccharomycopsis. The analysis detected a total of 47 volatile components in both HB Daqu and SX Daqu. The volatile components of pyrazine were significantly more abundant in HB Daqu than in SX Daqu, while alcohol compounds were more prominent in SX Daqu than in HB Daqu. In addition, the RDA analysis established a correlation between dominant microorganisms and volatile components. Cyanobacteria, Fusobacteriota, Ascomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mucormyce exhibited positive correlations with a significant proportion of the key volatile compounds. This study establishes a scientific foundation for improving the quality of light-flavor Daqu liquor in different regions of China.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [Shangling Fang], upon reasonable request.
References
Chen Y, Li K, Liu T, Li R, Fu G, Wan Y, Zheng F (2021) Analysis of difference in microbial community and physicochemical indices between surface and central parts of Chinese special-flavor baijiu daqu. Front Microbiol 11:592421. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.592421
Chi Z, Chi Z, Liu G, Wang F, Ju L, Zhang T (2009) Saccharomycopsis fibuligera and its applications in biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 27(4):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.03.003
Deng L, Mao X, Liu D, Ning XQ, Shen Y, Chen B, Nie HF, Huang D, Luo HB (2020) Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties and microbial composition in high-temperature daqu with different colors. Front Microbiol 11:588117. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.588117
Du H, Wang X, Zhang Y, Xu Y (2019) Exploring the impacts of raw materials and environments on the microbiota in Chinese daqu starter. Int J Food Microbiol 297:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.02.020
Fan G, Sun B, Fu Z, Xia Y, Huang M, Xu C, Li X (2018) Analysis of physicochemical indices, volatile flavor components, and microbial community of a light-flavor daqu. J Am Soc Brew Chem 76(3):209–218. https://doi.org/10.1002/jib.583
Fan G, Du Y, Fu Z, Chen M, Wang Z, Liu P, Li X (2020) Characterisation of physicochemical properties, flavour components and microbial community in Chinese guojing roasted sesame-like flavour daqu. J Inst Brew 126(1):105–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610470.2018.1424402
Fu G, Deng M, Chen Y, Chen Y, Wu S, Lin P, Huang B, Liu C, Wan Y (2021) Analysis of microbial community, physiochemical indices, and volatile compounds of Chinese Te -flavor baijiu daqu produced in different seasons. J Sci Food Agric 101(15):6525–6532. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11324
Gan SH, Yang F, Sahu SK, Luo RY, Liao SL, Wang HY, Jin T, Wang L, Zhang PF, Liu X, Xu J, Xu J, Wang YY, Liu H (2019) Deciphering the composition and functional profile of the microbial communities in Chinese moutai liquor starters. Front Microbiol 10:1540. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01540
Gao Z, Wu Z, Zhang W (2020) Effect of pit mud on bacterial community and aroma components in yellow water and their changes during the fermentation of Chinese strong-flavor liquor. Foods 9(3):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030372
He X, Yangming H, Górska-Horczyczak E, Wierzbicka A, Jeleń HH (2021) Rapid analysis of baijiu volatile compounds fingerprint for their aroma and regional origin authenticity assessment. Food Chem 337:128002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128002
Huang B, Lei Y, Tang Y, Zhang J, Qin L, Liu J (2011) Comparison of HS-SPME with hydrodistillation and SFE for the analysis of the volatile compounds of zisu and baisu, two varietal species of perilla frutescens of Chinese origin. Food Chem 125(1):268–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.08.043
Jia W, Fan Z, Du A, Shi L, Ren J (2022) Characterisation of key odorants causing honey aroma in Feng-flavour baijiu during the 17-year ageing process by multivariate analysis combined with foodomics. Food Chem 374:131764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131764
Le VD, Zheng XW, Chen JY, Han BZ (2012) Characterization of volatile compounds in Fen-Daqu a traditional Chinese liquor fermentation starter: characterization of volatile compounds in Fen-Daqu. J Inst Brew 118(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1002/jib.8
Li Z, Bai Z, Wang D, Zhang W, Zhang M, Lin F, Gao L, Hui B, Zhang H (2014) Cultivable bacterial diversity and amylase production in three typical Daqus of Chinese spirits. Int J Food Sci Technol 49(3):776–786. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12365
Li A, Jia J, Fan Y, Chen H, Wang S, Shen C, Dai H, Zhou C, Fu H, She Y (2021) Furfural and organic acid targeted carbon dot sensor array for the accurate identification of Chinese baijiu. J Food Sci 86(7):2924–2938. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15766
Liu H, Sun B (2018) Effect of fermentation processing on the flavor of baijiu. J Agric Food Chem 66(22):5425–5432. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00692
Liu Y, Li X, Li H, Zhang H, Shen X, Zhang L, Han S, Pan C (2022a) Taorong-type Baijiu starter: analysis of fungal community and metabolic characteristics of middle-temperature daqu and high-temperature daqu. PLoS ONE 17(10):e0274881. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0274881
Liu Y, Wan B, Yang F, Zhang X, Li J, Du G, Wang L, Chen J (2022b) Metabolomics-driven elucidation of interactions between saccharomyces cerevisiae and lactobacillus panis from Chinese baijiu fermentation microbiome. Fermentation-Basel 8(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8010033
Ma S, Shang Z, Chen J, Shen Y, Li Z, Huang D, Luo H (2022) Differences in structure, volatile metabolites, and functions of microbial communities in Nongxiangxing Daqu from different production areas. LWT - Food Science and Technology 166:113784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113784
Mao J, Liu X, Gao T, Gu S, Wu Y, Zhao L, Ma J, Li X, Zhang J (2022) Unraveling the correlations between bacterial diversity, physicochemical properties and bacterial community succession during the fermentation of traditional Chinese strong-flavor Daqu. LWT - Food Science and Technology 154:112764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112764
Nie Z, Zheng Y, Du H, Xie S, Wang M (2015) Dynamics and diversity of microbial community succession in traditional fermentation of Shanxi aged vinegar. Food Microbiol 47:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2014.11.006
Shi F, Zhou X, Zhou Q, Tan Z, Yao M, Wei B, Ji S (2018) Membrane lipid metabolism changes and aroma ester loss in low-temperature stored nanguo pears. Food Chem 245:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.091
Song X, Jing S, Zhu L, Ma C, Song T, Wu J, Zhao Q, Zheng F, Zhao M, Chen F (2020) Untargeted and targeted metabolomics strategy for the classification of strong aroma-type baijiu (liquor) according to geographical origin using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Chem 314:126098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.126098
Wang JW, Han PJ, Han DY, Zhou S, Li K, He PY, Zhen P, Yu HX, Liang ZR, Wang XW, Bai FY (2021) Genetic diversity and population structure of the amylolytic yeast Saccharomycopsis fibuligera associated with Baijiu fermentation in China. J Microbiol 59(8):753–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-1115-7
Wang Z, Wang S, Liao P, Chen L, Sun J, Sun B, Zhao D, Wang B, Li H (2022) HS-SPME combined with GC-MS/O to analyze the flavor of strong aroma baijiu daqu. Foods 11(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010116
Wei Y, Zou W, Shen C, Yang J (2020) Basic flavor types and component characteristics of Chinese traditional liquors: a review. J Food Sci 85(12):4096–4107. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15536
Wu Q, Chen L, Xu Y (2013) Yeast community associated with the solid state fermentation of traditional Chinese maotai-flavor liquor. Int J Food Microbiol 166(2):323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.07.003
Xia Y, Luo H, Wu Z, Zhang W (2023) Microbial diversity in jiuqu and its fermentation features: saccharification, alcohol fermentation and flavors generation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107(1):25–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12291-5
Xiao C, Yang Y, Lu ZM, Chai LJ, Zhang XJ, Wang ST, Shen CH, Shi JS, Xu ZH (2021) Daqu microbiota exhibits species-specific and periodic succession features in Chinese baijiu fermentation process. Food Microbiol 98:103766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2021.103766
Yan Y, Wei S, Qian W, Xin H, Jingya G (2016) Comparison of aroma compounds in traditional fermented and inoculated douchies. Chin Traditional Fermented Soybean Food 37(20):86–94. https://doi.org/10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201620015
Yan Y, Chen S, He Y, Nie Y, Xu Y (2020) Quantitation of pyrazines in baijiu and during production process by a rapid and sensitive direct injection UPLC-MS/MS approach. LWT - Food Science and Technology 128:109371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109371
Yang L, Fan W, Xu Y (2021) GC & times; GC-TOF/MS and UPLC-Q-TOF/MS based untargeted metabolomics coupled with physicochemical properties to reveal the characteristics of different type daqus for making soy sauce aroma and flavor type baijiu. LWT-Food Science and Technology 146(1):111416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111416
Zhang Q, Yuan Y, Luo W, Zeng L, Wu Z, Zhang W (2017b) Characterization of prokaryotic community diversity in new and aged pit muds from Chinese luzhou-flavor liquor distillery. Food Sci Technol Res 23(2):213–220. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.23.213
Zhang Q, Huo N, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang R, Hou H (2017a) Aroma-enhancing role of pichia manshurica isolated from daqu in the brewing of Shanxi aged vinegar. Int J Food Prop 20(9):2169–2179. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2017.1297823
Zhang H, Wang L, Tan Y, Wang H, Yang F, Chen L, Hao F, Lv X, Du H, Xu Y (2021) Effect of pichia on shaping the fermentation microbial community of sauce-flavor baijiu. Int J Food Microbiol 336:108898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108898
Zheng XW, Yan Z, Nout MJR, Smid EJ, Zwietering MH, Boekhout T, Han JS, Han BZ (2014) Microbiota dynamics related to environmental conditions during the fermentative production of fen-daqu, a Chinese industrial fermentation starter. Int J Food Microbiol 183:5762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.05.008
Zheng J, He Z, Yang K, Liu Z, Zhao D, Qian MC (2022) Volatile analysis of wuliangye baijiu by lichrolut ENSPE fractionation coupled with comprehensive GC×GC-TOFMS. Molecules 27(4):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041318
Zhou R, Chen X, Xia Y, Chen M, Zhang Y, Li Q, Zhen D, Fang S (2021) Research on the application of liquid-liquid extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (LLE-GC-MS) and headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) in distinguishing the baiyunbian aged liquors. Int J Food Eng 17(2):83–96. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijfe-2019-0382
Zhu BF, Xu Y (2010) A feeding strategy for tetramethylpyrazine production by bacillus subtilis based on the stimulating effect of ammonium phosphate. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33(8):953–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-010-0419-5
Zuo Q, Huang Y, MinGuo (2020) Evaluation of bacterial diversity during fermentation process: a comparison between handmade and machine-made high-temperature daqu of maotai-flavor liquor. Ann Microbiol 70(1):57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13213-020-01598-1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by"13th Five-Year Plan” National Key R&D Program Key Special Project (2016YFD0400500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FYM, SLF, and QY conceived and designed the research. FYM performed the experiments and all authors analyzed data. QY, and FYM wrote the article with input from the other authors. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that they have no financial or personal relationships that may have influenced the research findings presented in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Q., Mou, F., Xiao, J. et al. Correlational analysis of physicochemical indexes, microbial communities, and volatile components in light-flavor Daqu from north and south regions of China. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 54 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03865-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03865-0